What Is a Cell Culture Vessel?
 A cell culture vessel is a vessel used for culturing cells in the life science and drug discovery research and development fields.
A cell culture vessel is a vessel used for culturing cells in the life science and drug discovery research and development fields.
There are several types of culture vessels, such as petri dishes and flasks. The culture surface is uniform and even, providing a clear field of view and making them ideal for observing cultures.
Traditionally, glass culture vessels were the norm, but nowadays disposable cell culture vessels are usually made of polyethylene or other resin materials due to their transparency and ease of processing. Since the surface of the resin remains hydrophobic and has a poor affinity with cells, the surface is made hydrophilic to improve cell adhesion.
In addition, various innovations have been made to meet the needs of each application, such as sterilization and a film structure for the bub that the culture material comes in contact with so that the entire top plate can be removed.
Uses of Cell Culture Vessels
The main purpose of cell culture vessels is to culture adherent cells and floating cells. They are used in various bio-processes in the life science and pharmaceutical fields at all stages, from research and other development stages to manufacturing release.
Cultured cells have many uses and are used by cell biologists and other researchers, including biomaterials scientists and clinicians, as well as regulatory authorities.
Important cell cultures include cell culture in vaccine research and production, among others. The ability to grow large numbers of viruses in cultured cells has led to the use of cell culture technology for the mass production of vaccines against a variety of diseases.
Other applications include protein expression in mammalian cells and culturing cancer cells for cancer research and testing new therapeutic candidates.
Principles of Cell Culture Vessels
Cell culture vessels must meet the following requirements while in use:
- The culture surface is in a suitable condition for culture and can be processed
- They are free of toxicity, etc.
- Can be sterilized and remain sterile
- Clear vision and does not interfere with microscopic observation
To meet these requirements, appropriate materials are selected for cell culture vessels. The culture surface is not only processed to be uniform and smooth, but also treated with hydrophilic treatment and sterilization.
Types of Cell Culture Vessels

Figure 1. Culture vessel used in adherence culture
Types of cell culture vessels include petri dishes, well plates, and flasks.
The size, shape, coating, and whether the vessel has a lid or not all add up to a very wide variety of products, so it is important to select the appropriate type of cell culture vessel according to the target organisms and application.
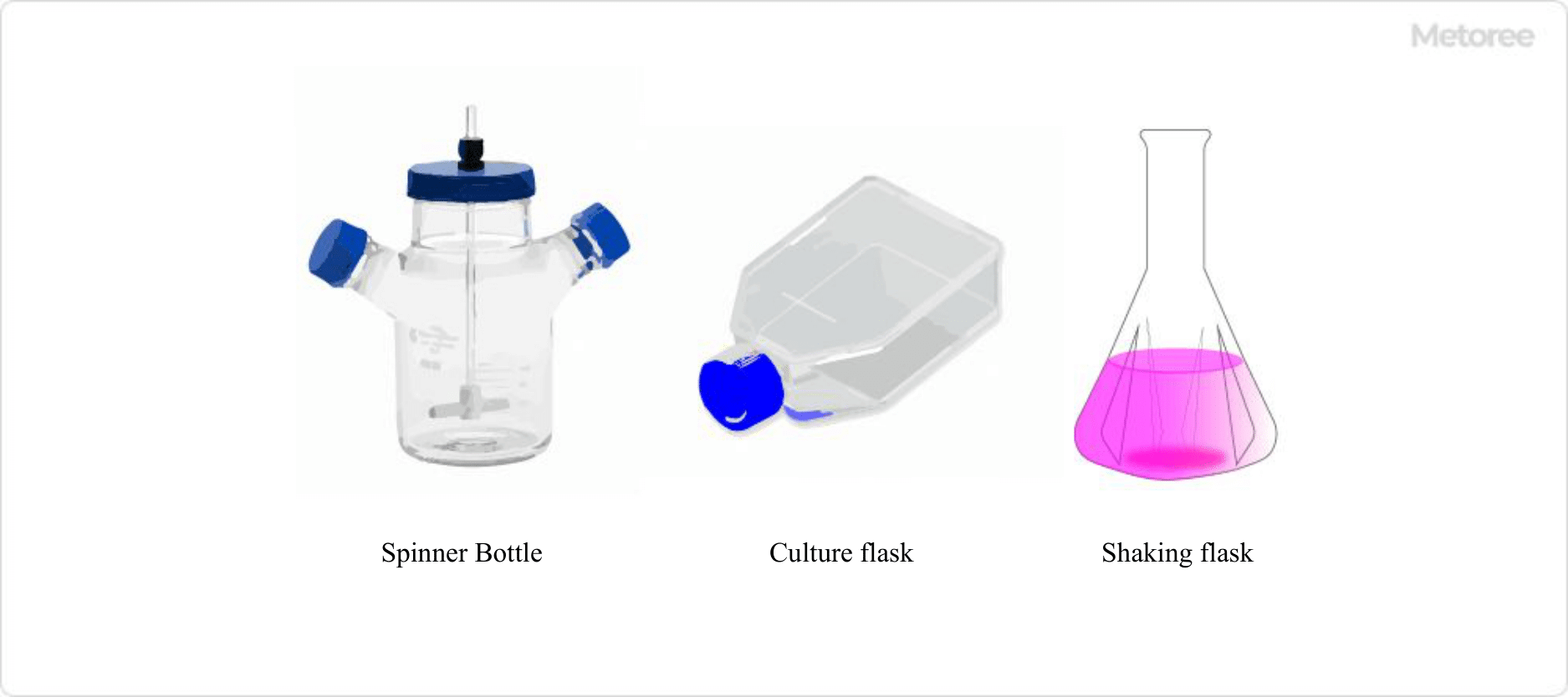

Figure 2. Culture vessel used for floating culture
Petri dishes (petri dishes), culture flasks, and multi-well plates are used to culture adhesion cultures, while culture flasks, spinner flasks, and shaking flasks are used to culture suspension cells. In both cases, it is important to use coated or non-adhesive culture vessels for adhesion culture or for suspension culture.
1. Petri Dish-Type Cell Culture Vessel
Petri dish-type cell culture vessels are available in diameters of 35 mm, 60 mm, 80 mm, and 90 mm. Most are between 12 and 20 mm in height. Each product has its own unique design for maneuverability, such as non-slip outer rim, and is stackable for storage and culture.
2. Multi-Well Plate-Type Cell Culture Vessel
A multi-well plate is a cell culture vessel with multiple depressions, called wells, in a single vessel. Unlike petri dishes, multiple culture conditions can be studied in a single cell culture vessel. 6, 12, 24, 48, and 96-well plates are available, and the size of each well usually decreases as the number of wells increases.
3. Flask-Type Cell Culture Vessel
Flask-type cell culture vessels are characterized by their screw caps, which can be easily closed for a closed system culture. Depending on the type of cells, the flask can withstand transportation for about one day by filling the flask with a culture medium and sealing it tightly.
In addition, for efficient mass culture, multilayer type flasks are also used, in which multiple flasks are layered on top of each other. Multi-layered flasks are heavy, and during culture, one must repeatedly inject and discharge culture medium into and out of each layer while supporting the cell culture vessel with one hand. This makes the operating procedure complicated, and the size and weight of the container make it difficult to handle.
Recently, however, a system has been developed to mechanize the culture process using multilayer type flasks and to automatically control a series of operations from culture to observation using a computer. In addition, cell culture vessels for floating cells include spinner flasks with stirring rods and shaking flasks that prevent droplets from rising during shaking.
4. Cell Culture Vessel With Cell Culture Insert
Some cell culture vessels use cell culture inserts. A cell culture insert is a device that divides a cell culture vessel into upper and lower sections to enable cell culture.
The dividing surface has a structure with a porous membrane filter made of various materials. This means that cells can be exposed to different conditions from both the medium and the gas phase simultaneously.
Adherent cells can be cultured on either the top or bottom of the membrane filter. In addition, cultures of floating cells can be incorporated. More complex cultures, such as co-cultures with multiple cells, can also be accommodated. In addition, gas-liquid interface cultures can be easily performed by adding medium only to the outside of the insert.
This type of culture method is utilized for culturing cells of organs in contact with the outside air, such as the respiratory system, skin, and cornea. In conventional monolayer cell experiments, it is difficult to evaluate lipid-soluble components or powders exposed as they are. However, models using inserts allow evaluation of such substances.
Other Information on Cell Culture Vessels
Adherent and Floating Cultures
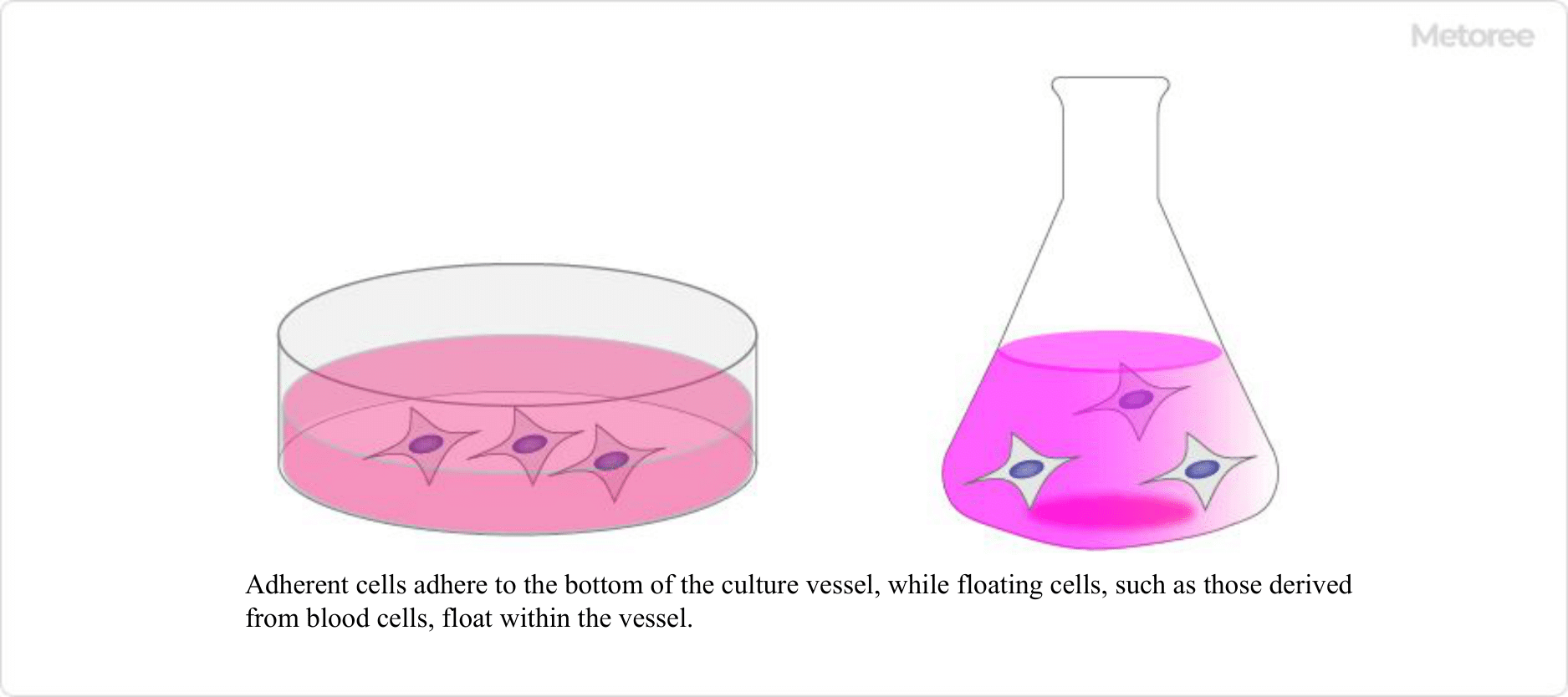
Figure 3. Adherent and floating cells
Cells can be divided into two types: adherent cells, which grow while adhering to a cell culture vessel, and floating cells, which grow while suspended in the culture medium.
The majority of cells derived from spinal cord animals are adherent cells that grow while adhering to tissues, with the exception of some floating cells, such as blood cell-derived cells. Based on the characteristics of the cells, the main types of culture methods are as follows:
1. Static Culture (Monolayer Culture)
This is the usual method of culturing adherent cells in a monolayer by attaching them to a cell culture vessel. Normal cells basically grow in a monolayer. Petri dishes (petri dishes), culture flasks, and multi-well plates are appropriate cell culture vessels.
2. Flotation Culture
Floating culture is a culture method in which floating cells, such as blood cell-derived cells, are grown while suspended in the culture medium. A specialized cell culture vessel coated to prevent cell adhesion is appropriate. Shaking flasks or spinner flasks are used when culturing large quantities of cells.
3. Rotational Culture (Roller Culture)
This is an adhesion culture method in which cells are cultured by gently rotating a roller bottle, which is a specialized cell culture vessel for rotational culture, and then adhering the cells to the inner wall of the bottle.
4. Whirling Culture (Shaking Culture)
This is one of the floating culture methods, in which cells are cultured in a shaking flask while shaking it with a shaker. It is suitable for floating cells such as bacteria, plant cells, and lymphocyte-derived cells.