What Is a Molded Transformer?
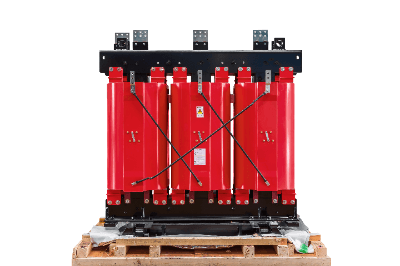 A molded transformer is a transformer in which the winding section is impregnated and molded with epoxy or other resin.
A molded transformer is a transformer in which the winding section is impregnated and molded with epoxy or other resin.
It is also called a dry-type transformer. When a transformer changes voltage, the iron core and windings heat up due to power loss in the transformer, so it is necessary to dissipate the heat. While oil is used to dissipate heat in general transformers, molded transformers do not use oil, making them superior in terms of safety against ignition and other hazards.
Because of their low risk of ignition in the event of an accident and their lightweight and small size, they are suitable for indoor use and are installed in buildings around us.
Uses of Molded Transformers
Molded transformers are used in a variety of locations, mainly for the transforming uses of electricity in indoor facilities of buildings and other structures, due to their high level of safety. One example is subway premises. Subways can consume large amounts of electricity and require transformers.
However, the use of oil-filled transformers is very dangerous in case of an accident. Thus, the use of molded transformers is appropriate in situations where a fire would be very dangerous. They are also used in condominiums and department stores. In addition to safety, the small size and light weight of these transformers make them suitable for use in indoor facilities.
Principle of Molded Transformers
Molded transformers cool the heat generated by ordinary transformers as they change voltage by propagating it into the air through a resin mold, such as epoxy resin, that covers the transformer coils. A typical transformer is constructed using an iron core and windings, which are two coiled windings of conductors wound around an iron core.
When a current is applied to one side of these winding coils, a voltage is generated on the other side by the principle of electromagnetic induction. A transformer is a device that adjusts the voltage generated by adjusting the number of windings.
When changing the voltage, the iron core and windings generate heat due to power loss. In an oil-filled transformer, the heat is removed by the surrounding oil and dissipated outside by water or wind. Molded transformers, on the other hand, are also called dry-type transformers, and their greatest feature is that they do not use oil.
Other Information on Molded Transformers
1. Advantages of Molded Transformers
By not using oil, molded transformers have the following advantages and disadvantages over oil-filled transformers:
Extremely Safe
In the event of an emergency, there is no risk of ignition due to ignition of oil, so it can be used indoors or in enclosed spaces. On the other hand, in the case of oil-filled transformers, there are cases in which a fire extinguishing system is required for large-capacity installation.
Lightweight and Compact
The absence of oil allows for a lightweight and compact structure. They can be installed in high-rise areas of buildings. Also, unlike oil-filled transformers, there is no need to consider maintenance and disposal methods for the oil inside.
2. Disadvantages of Molded Transformers
High Cost
Compared to oil-filled transformers, the cost tends to be higher due to the difference in internal structure. Therefore, when introducing a transformer, oil-filled transformers are often considered first, and if they are not suitable, molded transformers are often selected.
Loud Driving Noise and Vibration
Oil-filled transformers absorb vibration and noise from the surrounding oil, but molded transformers do not, so they are noisier in comparison.