What Is Phenylethylamine?
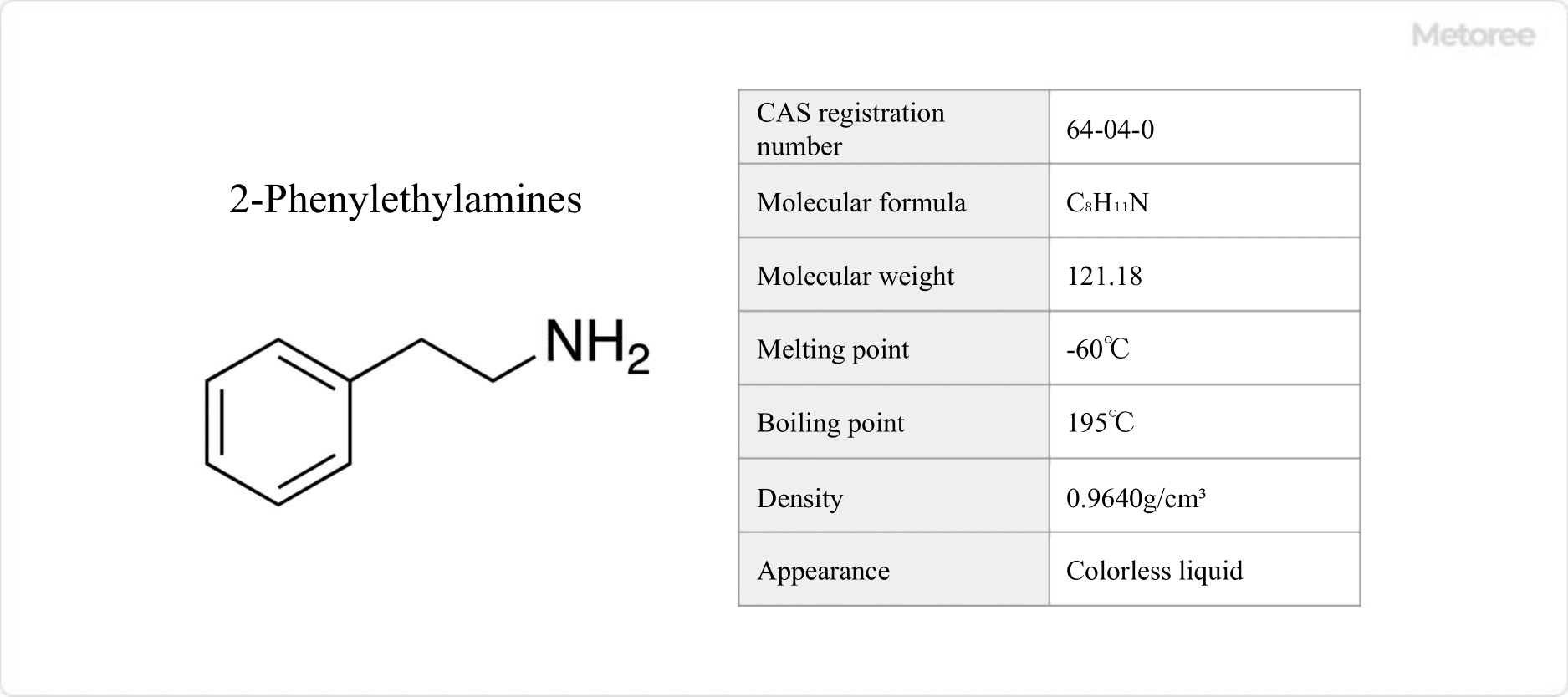
Figure 1. Basic Information on 2-Phenylethylamine
Phenylethylamine is an organic compound with the chemical formula C8H11N, comprising both 2-phenylethylamine and 1-phenylethylamine. The former is also known as phenethylamine.
2-Phenylethylamine, an alkaloid, is a natural organic compound containing nitrogen atoms. It is found in mammals’ bodies and micro-fermented foods like chocolate, where it acts as a neurotransmitter.
Uses of Phenylethylamine
2-Phenylethylamine and its derivatives exhibit antidepressant properties and can be utilized as antidepressants. This compound stimulates dopamine and adrenaline release, hormones associated with enjoyment and anticipation. It is particularly noted for its role in love-related hormone secretion, earning the nickname “love hormone.”
Properties of Phenylethylamine
2-Phenylethylamine has a melting point of -60 °C and boils at 195 °C. It is a colorless liquid at room temperature and pressure. In nature, it is synthesized from the amino acid phenylalanine through enzymatic decarboxylation. When exposed to air, it forms carbonates with CO2.
In the brain, 2-phenylethylamine serves as a neurotransmitter but is rapidly degraded, classifying it as a “trace amine.”
Structure of Phenylethylamine
Classified as a primary amine, 2-Phenylethylamine has a molecular weight of 121.183 g/mol and a density of 0.9640 g/cm³. Its backbone structure is a component of complex compounds, including the morphinan ring in morphine and the ergoline ring in LSD.
Other Information on Phenylethylamine
1. Derivatives of 2-Phenylethylamine
Figure 2. 2-Phenylethylamine Derivatives
Hundreds of 2-phenylethylamine derivatives exist, with chemical modifications to the phenyl, amino, and side chains. These include neurotransmitters like tyramine and tyrosine, which is also a DNA component. Amphetamine, methamphetamine, catecholamines (e.g., dopamine, levodopa, adrenaline, noradrenaline), and aromatic amino acids (tyrosine, phenylalanine) are examples of such derivatives.
2. Characteristics of 1-Phenylethylamine
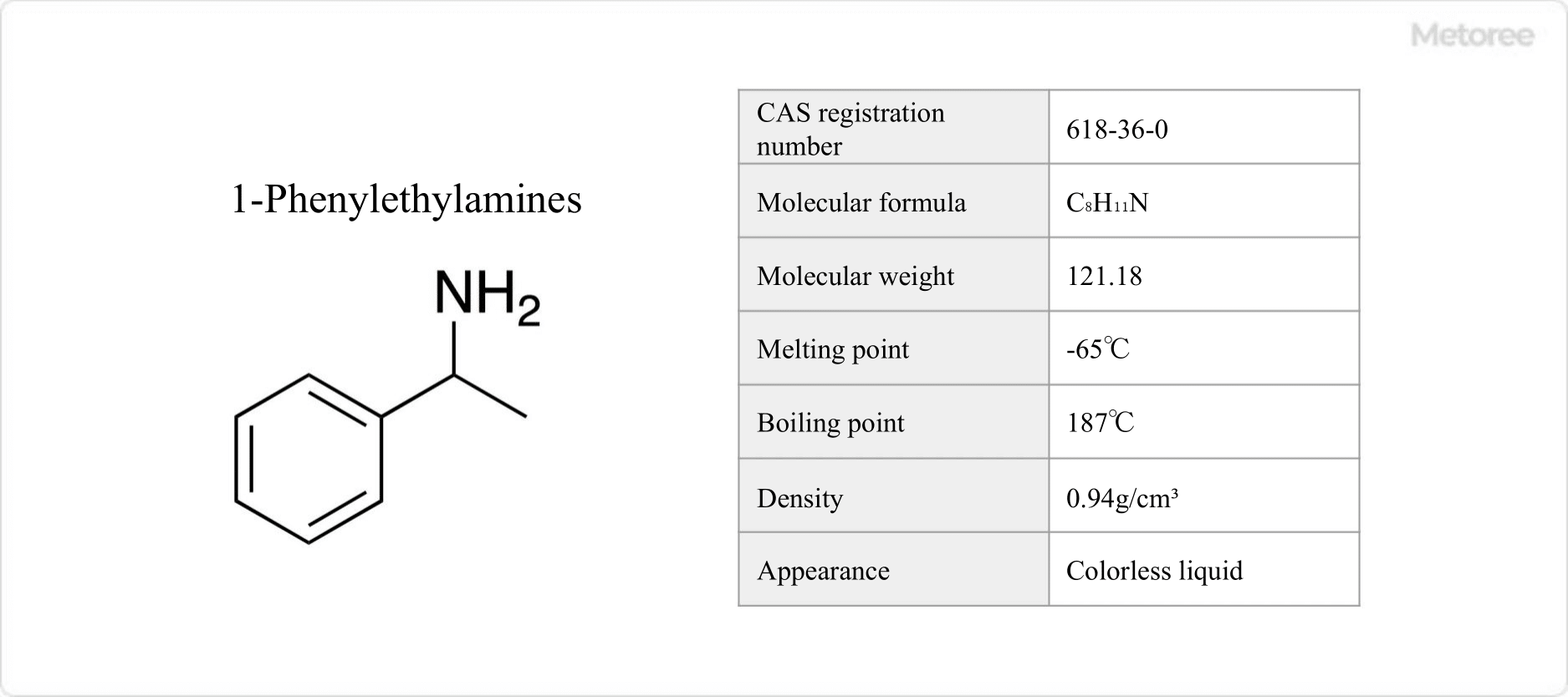
Figure 3. 1-Phenylethylamine Basic Information
1-Phenylethylamine, structurally related to 2-phenylethylamine, is a colorless liquid with a melting point of -65 °C and a boiling point of 187 °C. It has a density of 0.94 g/mL and is used in optical resolution due to its mirror-image isomerism. It forms basic compounds like ammonium salts and imines.
1-Phenylethylamine can be synthesized from acetophenone through reductive amination or the Leuckart reaction with ammonium formate. The l-malic acid method can separate its isomers, crystallizing the right-handed structure and leaving the left-handed one in solution.