What Is an Automatic Blood Pressure Meter?
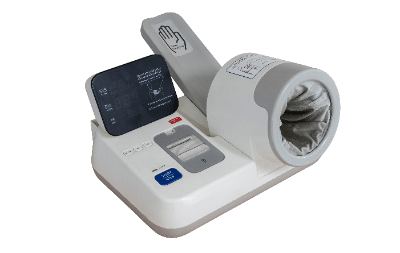 There are various types of blood pressure meters, but an automatic blood pressure meter is designed to be even easier to operate than conventional products and allow anyone to take measurements.
There are various types of blood pressure meters, but an automatic blood pressure meter is designed to be even easier to operate than conventional products and allow anyone to take measurements.
The most common type of sphygmomanometer is one in which a band-like object called a cuff is wrapped around the upper arm of the person being measured. This type cannot measure blood pressure correctly if the cuff is the wrong size or if it is placed in the wrong place.
On the other hand, with the automatic blood pressure meter, you can take a measurement simply by putting your arm through the measuring section. There is no need to wrap the cuff around your arm by yourself, and the optimal pressure is applied simply by pressing a switch for easy measurement. The position and posture of the arm are important for correct blood pressure measurement. Some products are equipped with a function that determines the correct posture based on the angle of the measuring section through the arm and informs the person taking the measurement, making it easier to take correct blood pressure measurements.
Applications of Automatic Blood Pressure Meters
Blood pressure measurement is an important indicator of daily physical condition and is also used to assess the risk of various diseases such as stroke, heart disease, and kidney disease. All hypertensive patients with a blood pressure of 140/190 mmHg or higher, those with an elevated blood pressure of 130-139/80-89 mmHg, and those with a blood pressure of 120/80 mmHg or higher, whose cardiovascular risk increases with rising blood pressure, are considered eligible for blood pressure control. In order to detect abnormalities early, it is important to measure blood pressure regularly and to know one’s own average blood pressure. The automatic blood pressure meter is becoming popular not only in hospitals but also for home use because it is simpler to operate and allows for easy and continuous blood pressure monitoring.
Principle of Automatic Blood Pressure Meter
The Korotkoff method and the oscillometric method are two well-known principles of blood pressure measurement, but the oscillometric method is generally used in the automatic blood pressure meter.
In the oscillometric method, the arterial pulsation caused by the contraction of the heart is measured as the pressure inside the cuff. When the upper arm is placed in the measurement section, the cuff is pressurized and blood flow is stopped. On the other hand, the arterial pulsation is still present even after the blood flow has stopped, and the cuff’s inner pressure oscillates accordingly. Next, as the cuff pressure is gradually decreased, the oscillation of the cuff pressure gradually increases and reaches its peak. As the cuff pressure is further reduced, the cuff pressure oscillation rapidly decreases. The blood pressure value is calculated from the relationship between the cuff inner pressure and the increase/decrease of the cuff inner pressure oscillation in this series of processes.
Generally, the cuff pressure at the time of the rapid increase in oscillation is the maximum blood pressure, and the cuff pressure at the time of the rapid decrease is the minimum blood pressure. In the case of the Korotkoff method, it is necessary to detect the blood vessel sound (Korotkoff sound) when the cuff is depressurized, but the oscillometric method does not require such detection and is said to be a measurement method that is less susceptible to external noise.