What Is an Anti-Static Agent?
An anti-static agent is a substance used to prevent the generation of static electricity on the surfaces of insulators like plastics and synthetic fibers. Static electricity can attract dust and pollen, leading to stains, discomfort, or even malfunctions in home appliances and electronic equipment. Anti-static agents are applied to avoid these issues.
In addition, electrostatic attraction and repulsion between charged objects often cause problems in manufacturing processes. An Anti-Static agent is used to avoid such problems caused by static electricity.
There are two main types of anti-static agents: coated antistatic agents applied to molded plastic products or films, and kneaded antistatic agents mixed into the product material.
Uses of Anti-Static Agents
Anti-static agents are used in various industries, including electrical products, automotive, paper, textiles, printing, resins, films, plastics, and electronics. They serve dual purposes: improving product performance and enhancing productivity during manufacturing.
1. Uses of Anti-Static Agents to Improve the Performance of Products
- Prevention of dust adhesion and static electricity on furniture and clothing
- Preventing dust from adhering to home appliances and electronic devices, and preventing damage and malfunctions caused by static electricity
- Preventing static electricity from adhering to plastic parts of cars, interior linings, engine covers, and intake parts inside air intake boxes.
- Prevention of static electricity on electronic equipment carrying cases and cushioning materials
- Prevention of adhesion of films, etc.
- Prevention of powder adhesion to bags containing powder
2. Uses of Anti-Static Agents for Productivity Improvement
In some cases, anti-static agents are removed in the post-process to improve productivity, while in other cases, anti-static agents are left in place to improve product performance.
- Anti-static in spinning, drawing, and spinning processes in textile manufacturing
- Preventing films from sticking to each other in the film manufacturing process
Principle of Anti-Static Agents
Anti-static agents are applied to plastics (surface treatment) or incorporated into plastics to improve the ion conductivity of the plastic surface or the plastic itself. This is because improving ion conductivity makes plastic surfaces less likely to become charged.
Although there are ways to improve the electronic conductivity of objects to prevent plastics from becoming charged, most Anti-Static agents improve ionic conductivity.
Improving electronic conductivity is also an extremely effective means of antistatic. However, it requires the application of metal plating to the surface of the plastic or the addition of conductive fillers with high electronic conductivity, such as carbon black or metal powder.
However, most of these treatments are limited to applications where black or metal coloration is acceptable since carbon or metal coloration will be applied to the plastic surface.
Mechanism of Action of Anti-Static Agents
Anti-static agents make plastic surfaces less likely to be charged with static electricity by making the plastic surfaces more susceptible to static electricity by the presence of anti-static agents. There are two types of application methods: application type and knead-in type.
Anti-static agents of low molecular weight type such as antistatic agents are mainly used, while anti-static agents of a high-molecular-weight type such as polymers with ion conductive moieties in their molecules are used in the kneaded-in type.
1. Coating-Type Anti-Static Agent
Anti-static agents are applied to the surface of molded plastic products and release static electricity by adsorbing moisture into the air. However, since it is only applied to the surface, it is removed by wiping with water when cleaning, etc., and has low durability.
2. Baked-in Low-Molecular-Weight Anti-Static Agent
Anti-static agents are designed to ooze onto the surface of plastics when kneaded into them. After the plastic is molded, a film of anti-static agents is formed on the surface, and moisture is adsorbed to this area to release static electricity. Therefore, the amount of antistatic agent kneaded into the plastic is as low as 0.2~2% to be effective.
As with the coating type, the anti-static agents are easily removed by wiping with water. However, as long as the anti-static agents remain inside the plastic, they will reappear from the inside, thereby restoring the anti-static properties.
3. Kneaded Polymeric Anti-Static Agents
Unlike the low-molecular-weight type, the molecular size of the kneaded-in polymer anti-static agents is large, so there is no oozing effect. Therefore, it is necessary to have the required amount present on the surface immediately after molding.
Although it is necessary to knead in a considerable amount of 5~20%, it is firmly incorporated into the plastic, and the attractive point is that it will not be wiped off with a simple water wipe. Therefore, it has the longest-lasting effect.
Types of Anti-Static Agents
As for the types of anti-static agents, as mentioned above, each type has different features and optimum applications, so appropriate selection must be made depending on the situation.
 A file set is a collection of files in various shapes and sizes, designed for shaping and smoothing materials. The most common file sets include 5-file, 8-file, and 12-file sets. The 5-file set, which includes typical shapes like cylindrical, flat, and triangular, suffices for most purposes. The 12-file set, with more variety, is often used by professionals in intricate work, such as jewelry engravers.
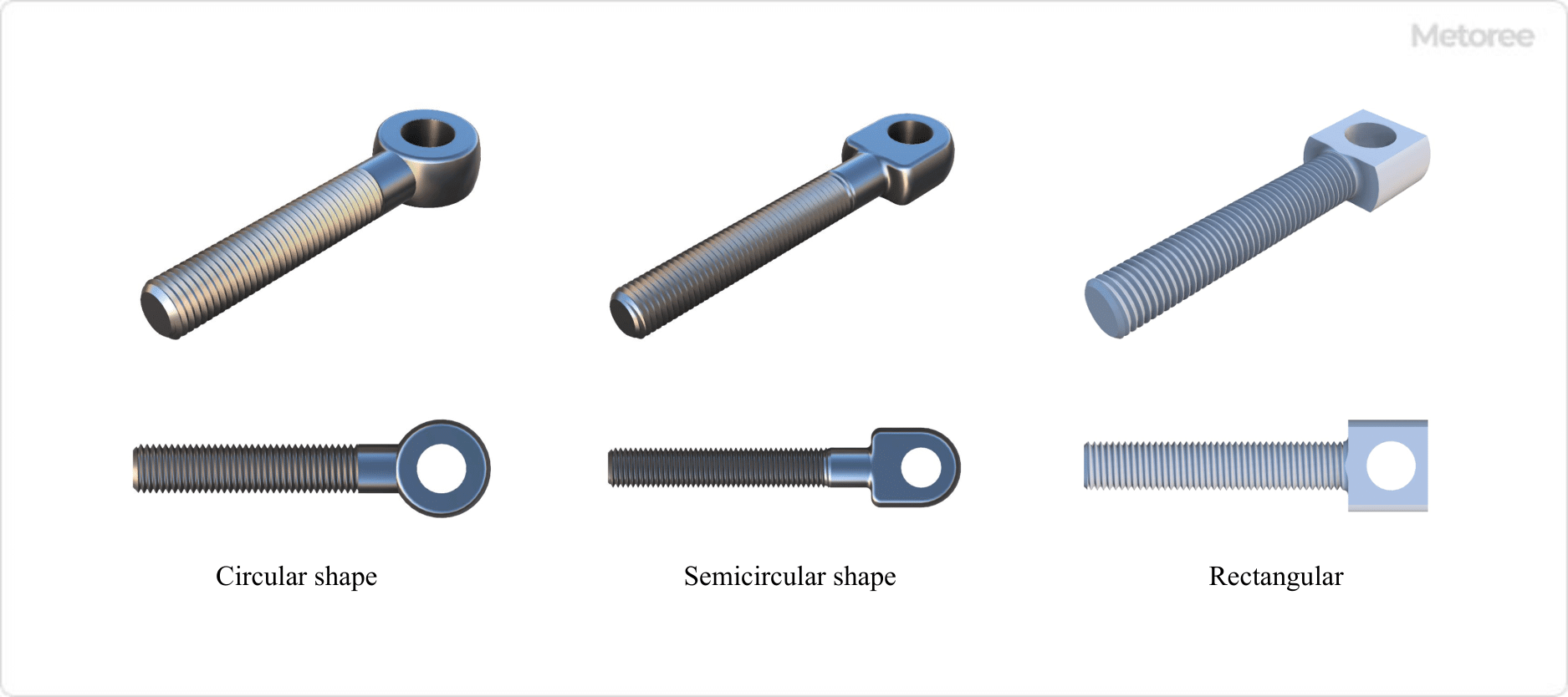
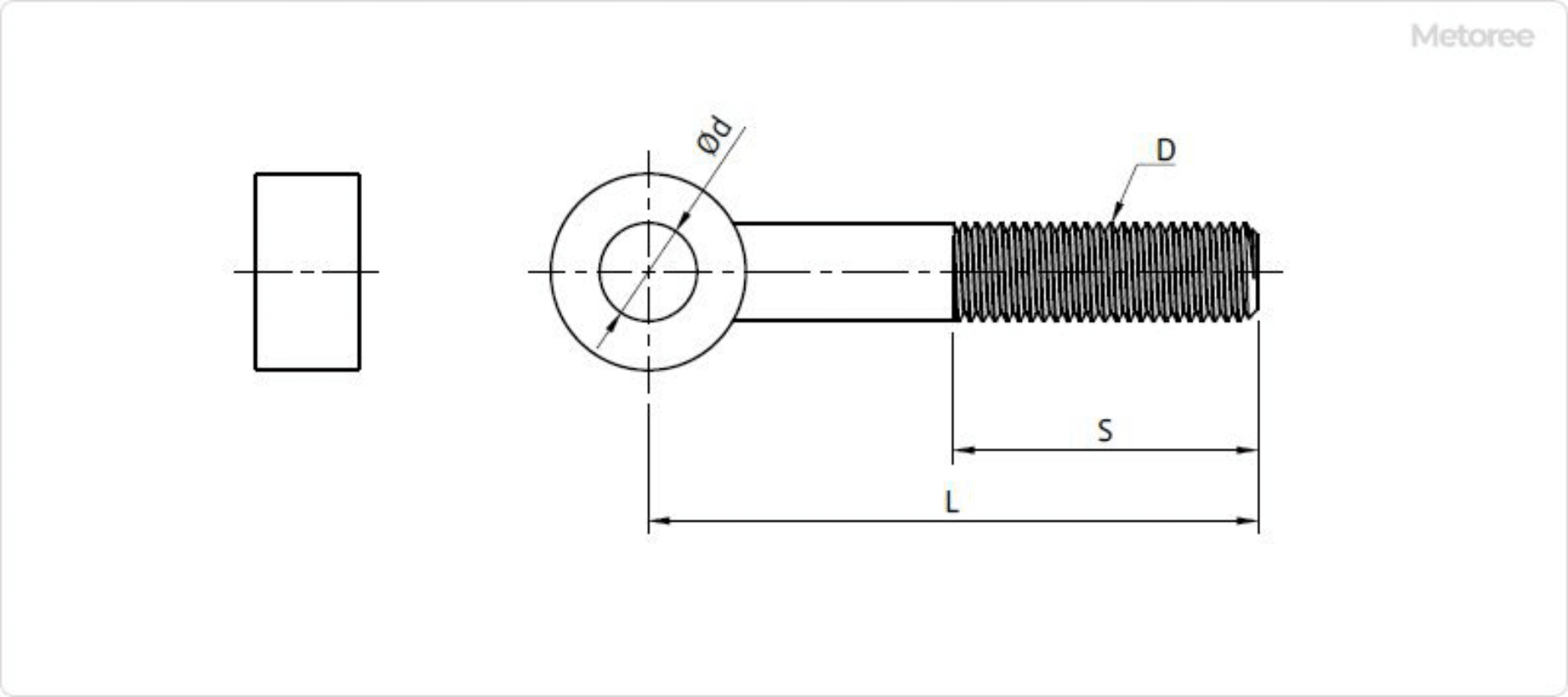
A file set is a collection of files in various shapes and sizes, designed for shaping and smoothing materials. The most common file sets include 5-file, 8-file, and 12-file sets. The 5-file set, which includes typical shapes like cylindrical, flat, and triangular, suffices for most purposes. The 12-file set, with more variety, is often used by professionals in intricate work, such as jewelry engravers. An eye bolt, also known as a rod-end bolt, is a bolt with a circular or rectangular head that features a hole in the center. Synonyms for eye bolt include “swing bolt,” although “rod-end bolt” is the more commonly used term. Eye bolts, including
An eye bolt, also known as a rod-end bolt, is a bolt with a circular or rectangular head that features a hole in the center. Synonyms for eye bolt include “swing bolt,” although “rod-end bolt” is the more commonly used term. Eye bolts, including