What Is Benzyl Chloride?
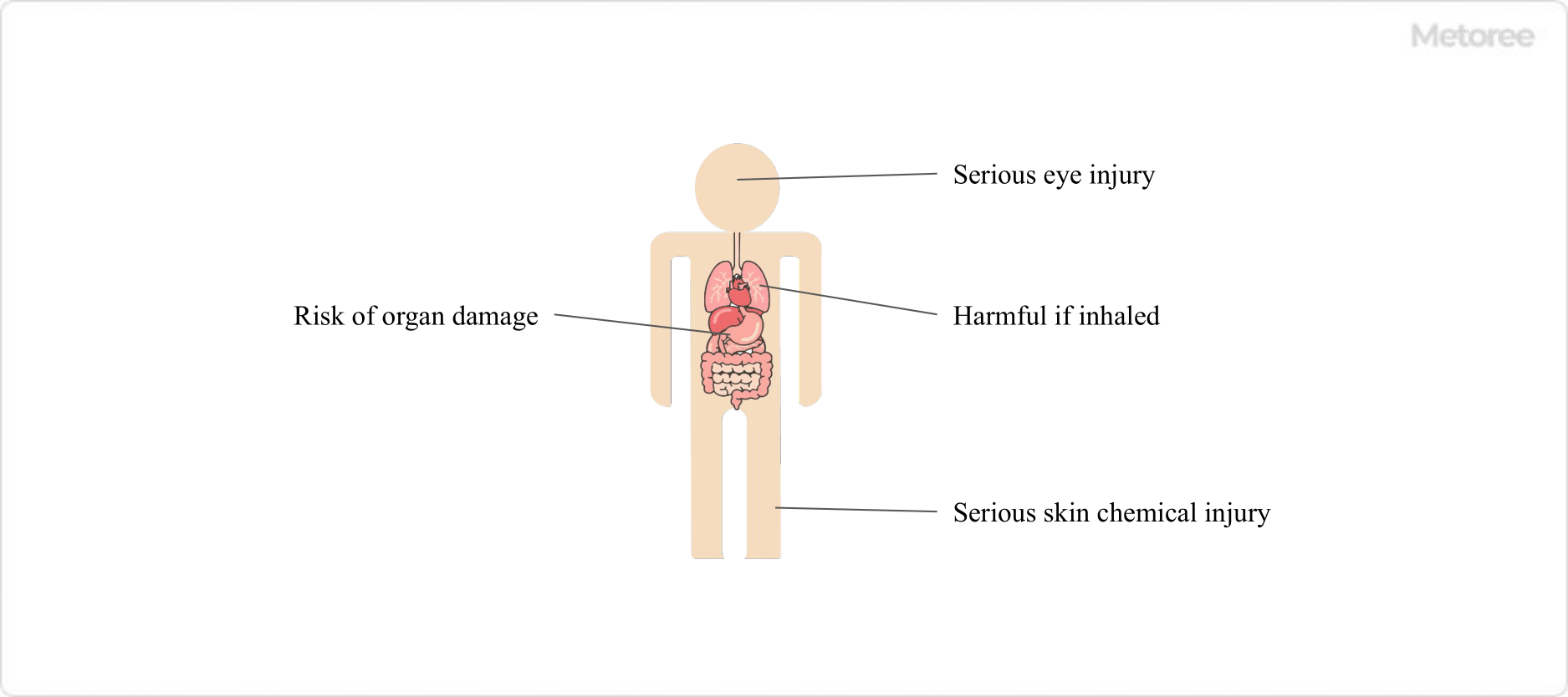
Benzyl chloride, also known as chloromethylbenzene or α-chlorotoluene, is an aromatic organic compound with the formula C6H5CH2Cl. Recognized for its pungent odor and irritant properties, it’s classified as highly toxic and was listed as a nonmedicinal toxicant in Japan in 2016.
Uses of Benzyl Chloride
Historically used as tear gas, benzyl chloride now serves primarily in organic synthesis as a benzylating agent. It’s instrumental in the production of pharmaceuticals, fragrances, and dyes, acting as an intermediate and protecting agent for hydroxy groups in alcohols and phenols.
Properties of Benzyl Chloride
This colorless liquid is characterized by a strong odor and significant irritancy towards eyes, skin, and mucous membranes. It has a melting point of -39°C, boils at 179°C, and is incompatible with water while being soluble in organic solvents like chloroform and ether.
Structure of Benzyl Chloride
With a molecular structure derived from toluene by substituting a chlorine atom for one hydrogen in the methyl group, benzyl chloride has a molecular weight of 126.59 and a density of 1.100 g/cm3.
Other Information on Benzyl Chloride
1. Synthesis of Benzyl Chloride
Initially produced from benzyl alcohol and hydrochloric acid, industrial synthesis now primarily involves the gas-phase photochemical reaction of toluene with chlorine, generating around 100,000 tons annually. Alternative methods include Blanc chloromethylation from benzene, utilizing zinc chloride as a catalyst.
2. Reactions Involving Benzyl Chloride
Benzyl chloride undergoes various reactions, including oxidation to benzoic acid with KMnO4, conversion to benzyl esters, cyanides, quaternary ammonium salts, and ethers through interactions with sodium cyanide, tertiary amines, and sodium hydroxide, respectively. It’s particularly useful for introducing benzyl-protecting groups in organic synthesis.
3. Related Compounds
Reacting readily with magnesium, benzyl chloride forms Grignard reagents, offering a preferable route over benzyl bromide for certain reactions due to its suitability in avoiding unwanted side reactions like the Wurtz-Fittig reaction.