What Is Acetyl Chloride?
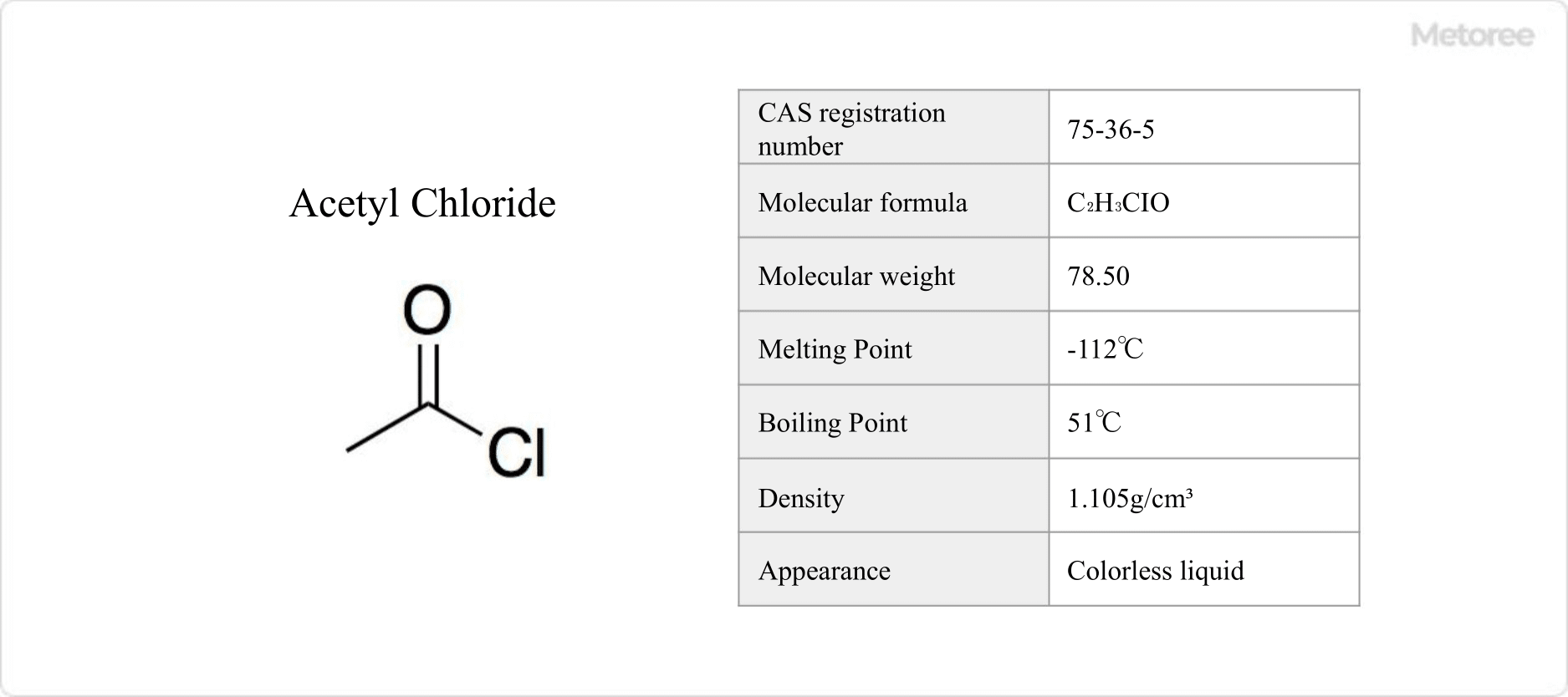
Figure 1. Basic Information on Acetyl Chloride
Acetyl chloride, derived from acetic acid, is known chemically as ethanoyl chloride. It produces white smoke in moist air due to its reaction with water, resulting in acetic acid and hydrogen chloride. This reactivity means it is seldom found naturally.
Available commercially, acetyl chloride can be synthesized through reactions involving acetic acid with thionyl chloride or phosphorus trichloride.
Uses of Acetyl Chloride
Acetyl chloride is pivotal in organic synthesis, particularly for introducing the acetyl group (CH3CO-) into organic compounds. Its application in the Friedel-Crafts reaction, alongside a Lewis acid catalyst like AlCl3, aids in synthesizing aromatic ketones. It is also used to produce acetophenone and ethyl acetate via acetylation of benzene and ethanol, respectively.
Properties of Acetyl Chloride
As a colorless, flammable liquid at room temperature, acetyl chloride has a pungent odor and can irritate the eyes and skin. It exhibits a density of 1.105 g/cm3, with melting and boiling points of -112°C and 51°C, respectively. Its solubility extends to benzene, chloroform, ether, and petroleum ether. The compound’s molecular formula is C2H3ClO, with a molecular weight of 78.50.
Other Information on Acetyl Chloride
1. Synthesis of Acetyl Chloride
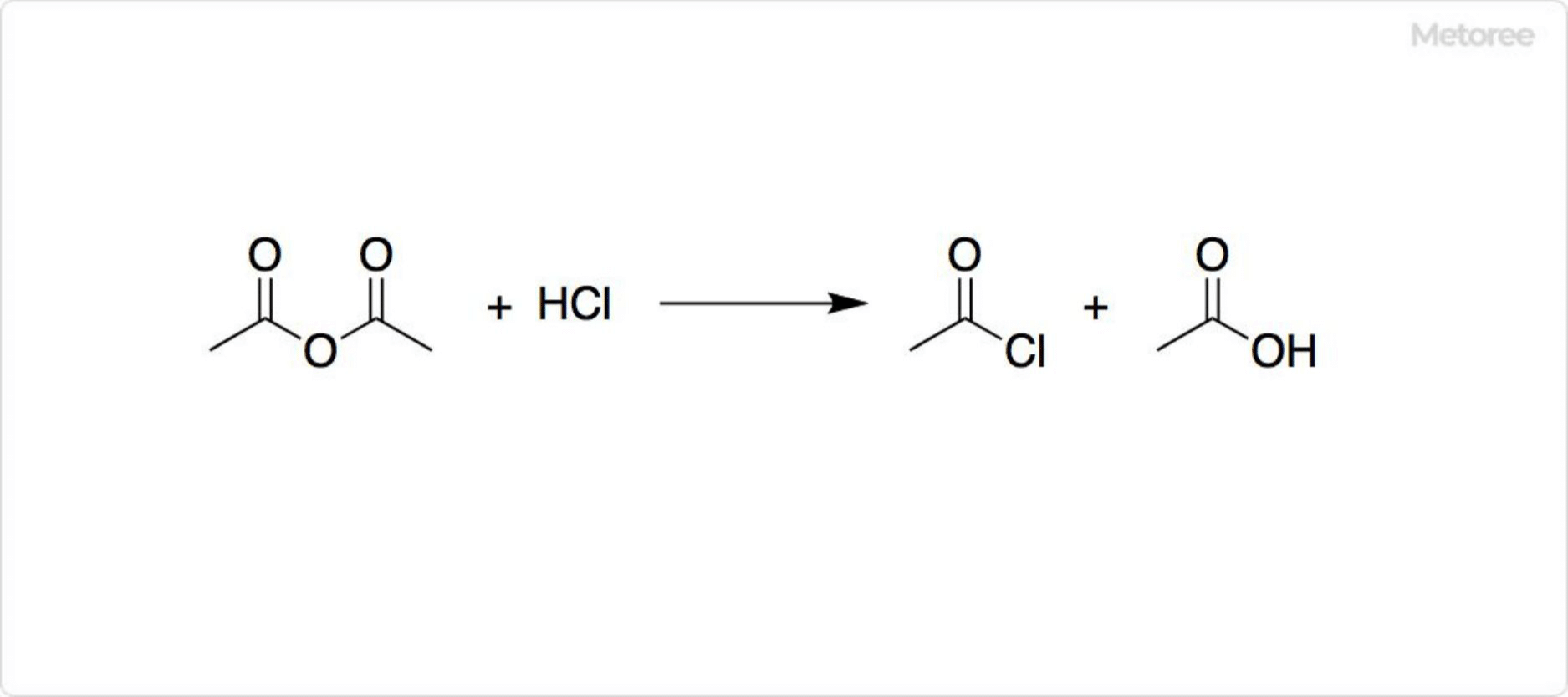
Figure 2. Synthesis of Acetyl Chloride
Industrially, acetyl chloride is produced from acetic anhydride and hydrogen chloride, yielding acetyl chloride and acetic acid. Lab-scale synthesis may involve potassium acetate reacting with phosphoryl chloride. Discovered by Charles Gerhardt in 1852, it can also be synthesized using phosphorus trichloride, pentachloride, sulfuryl chloride, phosgene, and thionyl chloride. These methods may introduce impurities that affect reactions. Clean synthesis options include the carbonylation of methyl chloride or the reaction of acetic acid with acetonitrile and hydrogen chloride.
2. Reactions Involving Acetyl Chloride
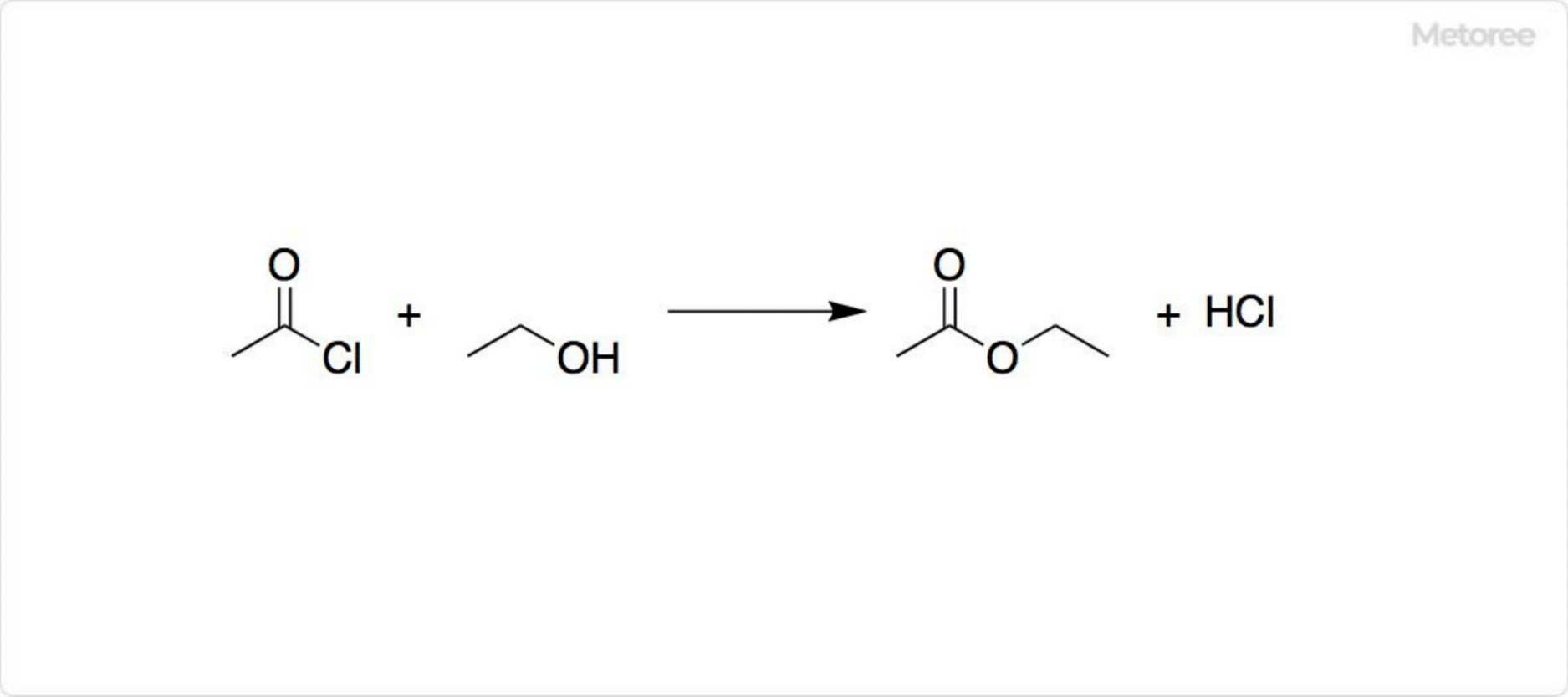
Figure 3. Reactions Involving Acetyl Chloride
Acetyl chloride is used in acetylation reactions to produce esters from alcohols and amides from amines. Reaction with carboxylic acids forms acid anhydrides.
3. Acetylation Reaction With Acetyl Chloride Using a Base
The Schotten-Baumann reaction, which uses bases like triethylamine or sodium hydroxide to neutralize hydrogen chloride, synthesizes esters and amides from alcohols or amines with carboxylic acid chlorides. Depending on the reactivity, sodium bicarbonate or sodium carbonate may be used. Pyridine and 4-dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP) facilitate acetylation of alcohols and amines, acting as catalysts in producing acetylpyridinium salts.