What Is a Globe Valve?
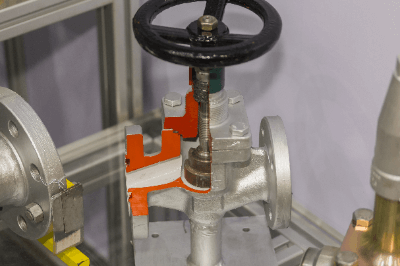 A globe valve is a valve used in process piping.
A globe valve is a valve used in process piping.
Globe valves are used to fully open and close the flow path and to adjust the flow rate and pressure. Originally, process piping refers to piping used to transport process fluids such as chemical products. Because special care is required in some cases, it is distinguished from piping used to convey working fluids such as fluid machinery.
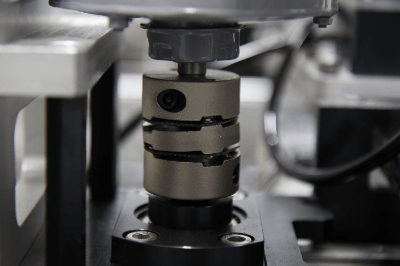
A globe valve is characterized by a rounded valve box (body) section and a curved internal flow path. Since the valve box is ball-shaped, it is also called a ball valve or globe valve.
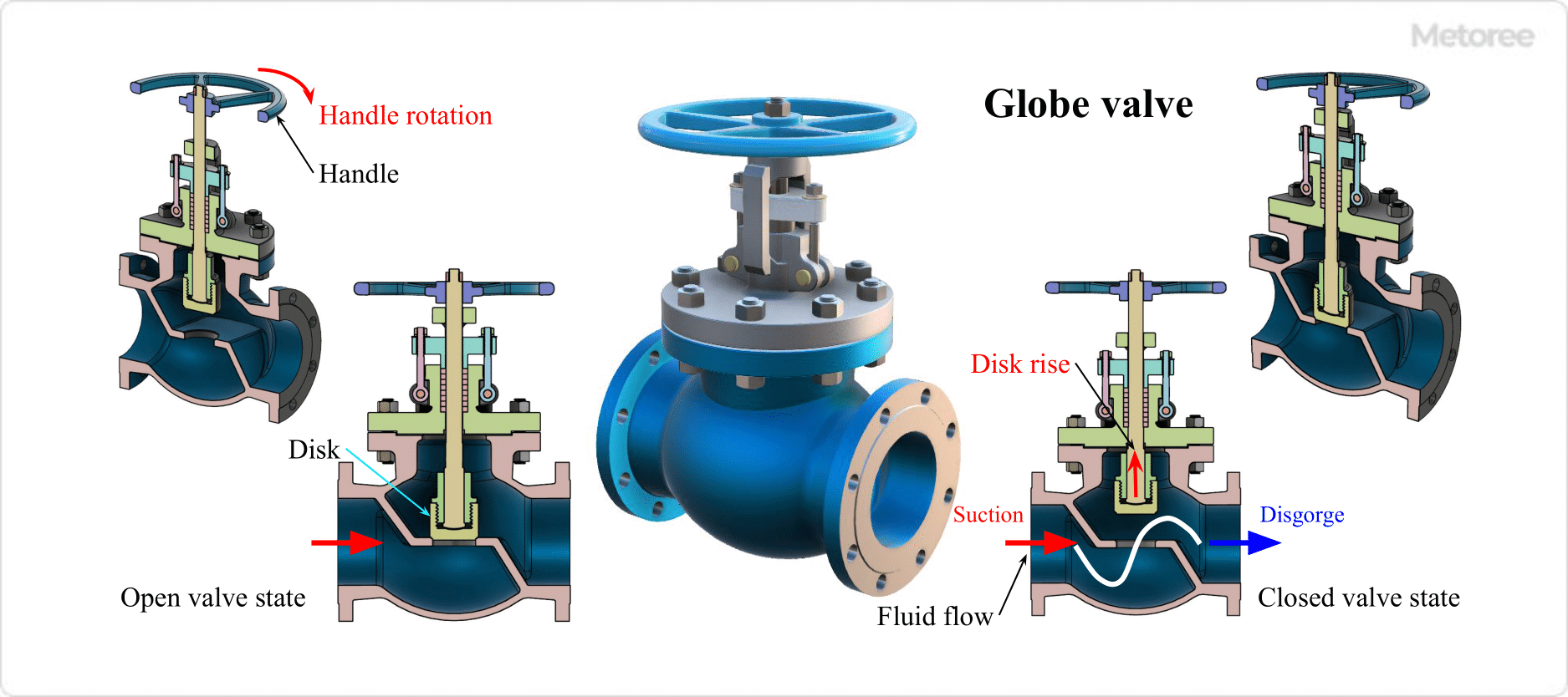
Figure 1. Structure of globe valve
Uses of Globe Valves
Globe valves are excellent for shutting off fluids and regulating flow and pressure, so they are used as stop valves when you want to shut off fluids without leakage. However, due to their high pressure drop, gate valves, ball valves, and butterfly valves with low pressure drop may be used for “always open” applications.
Globe valves are used in utility-related water, steam, and air piping in factories and power plants in general industry, and are often used in facilities and equipment where pipes are laid. It is also used in piping around water meters, gas meters, and water heaters in homes.
Because they are suitable for many applications, including high temperature, high pressure, and large-diameter use, they are used in a very wide range of applications. However, needle valves are best suited for use in small-diameter piping for minute flow rate control. The valve plug is tapered and needle-shaped, making it possible to adjust a minute amount of flow. The basic structure of the needle valve is the same as that of a globe valve, as it is opened and closed by moving the needle valve up and down.
Principle of Globe Valves
The valve plug (disc) in the valve housing (body) of a globe valve is rotated and moved up and down by a handle or actuator (drive unit) attached to the valve stem (stem). This causes the plug to contact the seat (valve seat) and shut off the fluid.
The distance between the valve plug and the valve seat changes to the extent that the handle or actuator is rotated, and the cross-sectional area of the flow path changes, making it possible to adjust flow and pressure. This type of valve is used to adjust the volume of utilities such as steam, cooling water, hot water, compressed air, and vacuum lines that require flow and pressure adjustment.
The valve box is ball-shaped, and the flow path from the inlet, through the valve seat, to the outlet is S-shaped. Inside the valve, the flow direction is changed and the flow path rapidly expands and contracts, resulting in a very large pressure drop.
However, when the valve is closed, the valve plug is pressed against the seat from above, resulting in low leakage and high shutoff performance. In addition, the valve plug position can be finely adjusted, allowing fine control of the flow rate.
Other Information on Globe Valves
1. How to Open and Close the Globe Valve
Globe valves can be opened and closed manually or automatically.
Manual Operation Type
In the manual operation type, the valve is opened and closed by rotating the round handle and moving the valve stem up and down.
Automatic Operation Type
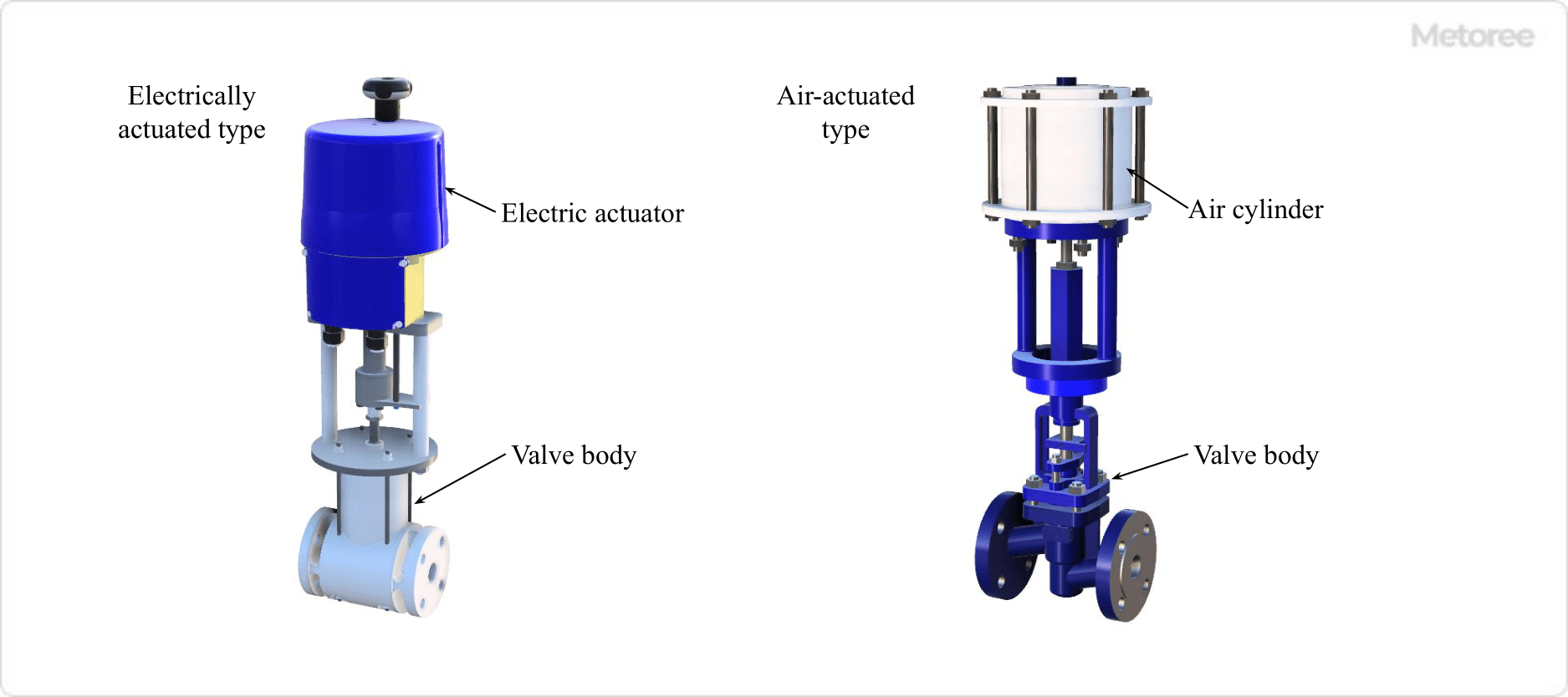
Figure 2. Self-operated globe valve
For self-operated valves, there are two types of actuators (drive units): electrically actuated and pneumatically actuated. Electric actuators use a combination of an electric motor (motor) and reduction gear to move the valve stem up and down to open and close the valve.
On the other hand, the pneumatic actuated type uses compressed air injected into the air cylinder to move the cylinder and valve stem up and down to open and close the valve.
2. Comparison With Other Types of Valves
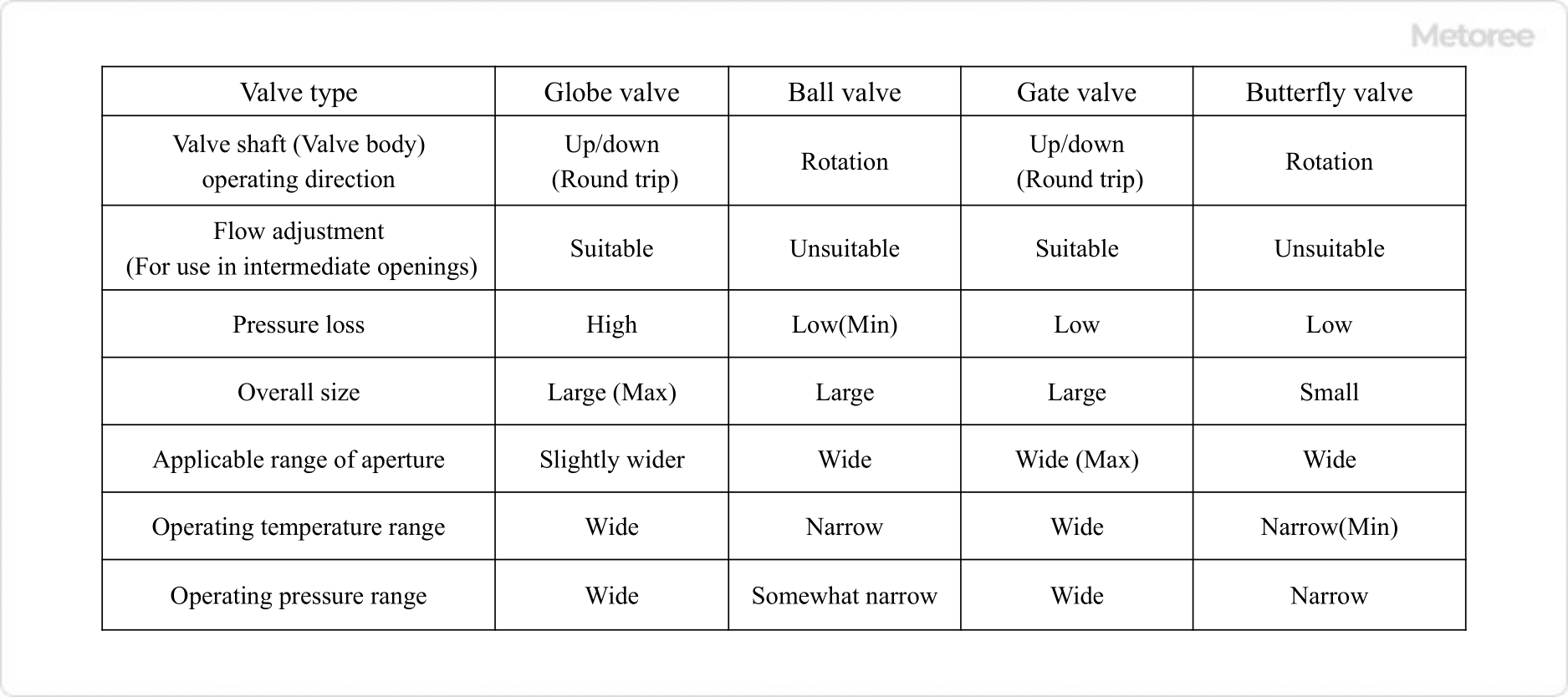
Figure 3. Comparison of valve features
Ball Valve
Ball valves can adjust the flow rate when used in the intermediate opening position. However, when used at the middle opening position, fluid can accumulate between the valve seat (ball seat) and the ball, causing leakage and possible damage to the valve seat.
Therefore, ball valves should be used in fully open and fully closed applications. In particular, ball valves can be easily operated fully open or fully closed by simply turning the handle. However, some manufacturers sell ball valves that can be used in intermediate opening positions.
In general, globe valves are used when both shutoff and flow control functions are required, while ball valves are used when shutoff is the main purpose and full opening and closing can be easily accomplished.
Gate Valves
Gate valves can be used in the middle opening position, but the valve plug may vibrate, so they should be used in the fully open or fully closed position. As with ball valves, globe valves are generally used when both shutoff and flow control functions are required, and gate valves are used when shutoff is the main purpose and full opening and closing can be easily accomplished.
Butterfly Valves
Butterfly valves can adjust the flow rate when used at an intermediate opening position. Butterfly valves have a smaller pressure drop than globe valves, but their disadvantage is that they are prone to unbalanced torque and water hammer due to the plate-shaped valve plug.
Butterfly valves have a smaller valve box and shorter face-to-face dimensions (distance between fluid inlet and outlet), and they have superior shutoff performance. In general, globe valves are used when both shutoff and flow control functions are required and full open/close time can be afforded, while butterfly valves are used when full open/close time is required in a short period and the face-to-face distance is short.
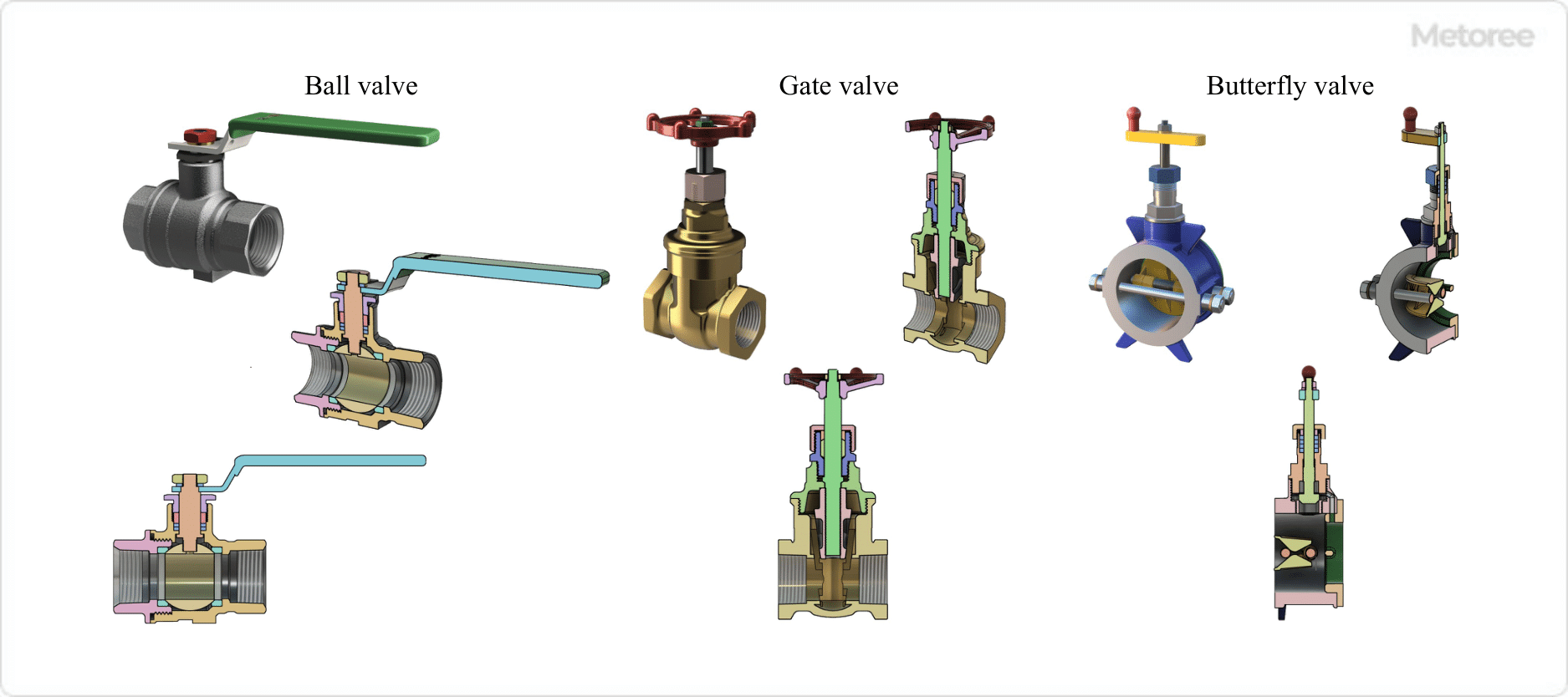
Figure 4. Structure of each valve type
3. Advantages and Disadvantages of Globe Valves
The advantages and disadvantages of globe valves can be briefly summarized as follows.
Advantages
- Low leakage and excellent shut-off performance
- Excellent flow control
Disadvantages
- Time-consuming, requiring multiple turns of the handle or actuator for full-close to full-open operation
- Large pressure loss in the valve box
 A globe valve is a valve used in process piping.
A globe valve is a valve used in process piping.