What Is a Threaded Connection?

A threaded connection (threaded joint, screw joint, screwed fitting) is a type of pipe fitting.
A pipe fitting is a component used to connect, branch, and close pipes. There are four major types of pipe fittings: threaded connection, welded connection, flanged connection, and ferrule connection.
Threaded connection is one of the four types that can be connected without using special tools or equipment. As a relatively inexpensive piping joint, it is used in a wide range of fields, including power generation and chemical plants, factories, building facilities, and general households.
Applications of Threaded Connection
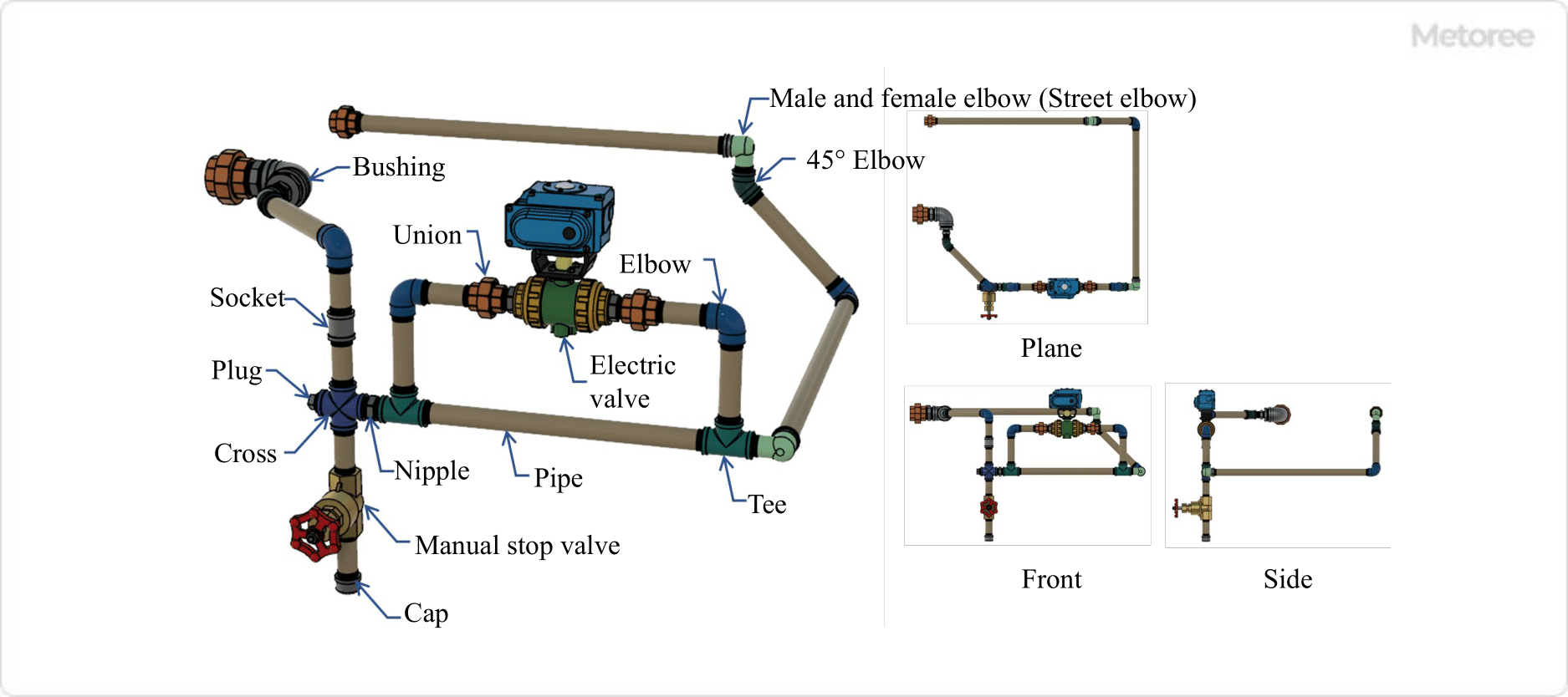
Figure 1. Example of screwed joint use
Threaded connection is mainly used to connect, branch, and close pipes during piping installation. In most cases, piping routes do not follow a straight line along their entire length, and there are cases in which a pipe route is curved up, down, left, or right, or a single pipe route is branched into two to four pipes, or vice versa, and then assembled. In such cases, threaded connections are required.
Threaded connections are used in many situations in factories, machinery, and homes. However, threaded connections are generally used in piping for low-pressure fluids. For fluids such as high-pressure, high-temperature steam, etc., the possibility of accidents or damage due to leakage exists, so fittings such as plug-in fittings or welded fittings should be used.
As an example, in JIS B2301 threaded malleable iron pipe connection, the maximum working pressure is specified as follows:
| Fluid state | Max. working pressure |
| Static water at 120°C or less | 2.5 MPa |
| Steam, air, gases, and oil up to 300°C | 1.0 MPa |
Principles of Threaded Connection
Threaded connection has a pipe thread machined on one or both ends of the part. The thread shape is specified by various standards, and the typical types are as follows.
| Standard | Standard No. | Standard Name |
| ISO | 228-1 | Pipe threads where pressure-tight joints are not made on the threads – Part 1: Dimensions, tolerances and designation |
| 7.1 | Pipe threads where pressure-tight joints are made on the threads – Part 1: Dimensions, tolerances and designation | |
| ANSI / ASME | B1.20.1 | Pipe threads or general -purpose inch |
| NPS: American National Standard Straight Pipe Threads | ||
| NPT: American National Standard Taper Pipe Threads |
Tapered pipe threads have a thread outside diameter that decreases toward the tip for male threads and toward the depth of the hole for female threads. For parallel pipe threads, the thread outside diameter is the same over the entire length of the thread for both male and female threads.
Threaded connection prevents leakage of fluid by ensuring that the male and female threads are tightly fitted together. Generally, when used as a fitting for piping, tapered pipe threads are used in many cases because they are more tightly sealed than parallel pipe threads. Sealing tape can be wrapped around the threads or sealing material can be applied to further improve sealing. See figure 2 below for a close fit of the male and female threads.
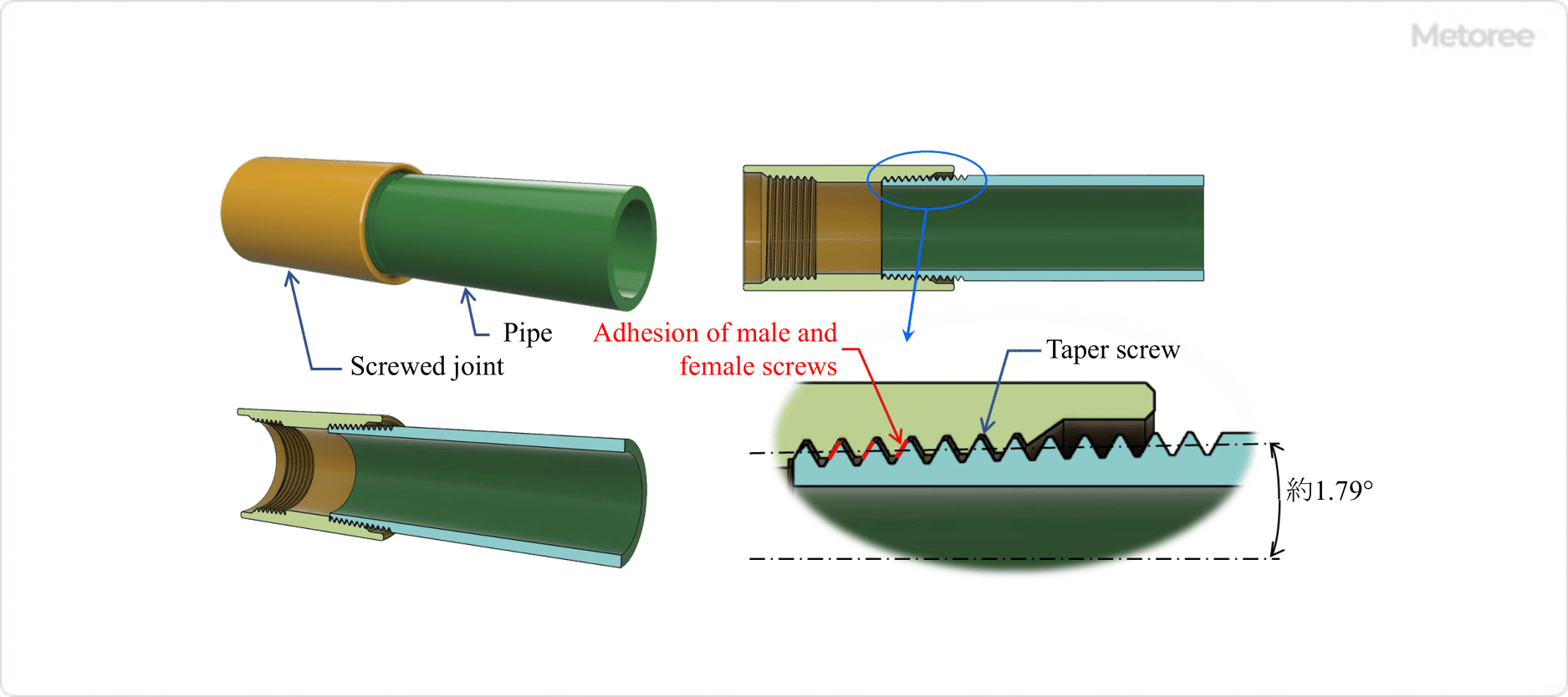
Figure 2. Principles of taper screw
The two types of parallel pipe threads and tapered pipe threads are selected in the following combinations according to the application and required tightness.
| Combination of threads | Male thread | ||
| Tapered pipe thread (R) | Parallel pipe thread (G) | ||
| Female thread | Tapered pipe thread (Rc) | ◎ | ×2 |
| Parallel pipe thread (Rp) | ◎ | ×2 | |
| Parallel Thread for Pipe (G) |
×1 |
〇1 | |
Symbol Description
◎: Can be combined with sealing tape for tight joints such as piping.
〇1: Mechanical joints can be combined by using packing or gasket together.
×x1: Combination is not possible due to the possibility of leakage caused by damage to the parallel threads or packing.
×x2: Depending on the screw manufacturing tolerance, it may not be possible to screw in, so sealing cannot be achieved, and the combination is not possible.
Types of Threaded Connections
There are several types of threaded connections depending on the application and direction.
1. Threaded Connections Standards
Standard threaded connections are specified in terms of dimensions, shape, material, and range of application in each standard. Refer to the table below for the various standards of threaded connections.
| Standard | Standard No. | Standard Name |
| JIS | B2301 | Threaded malleable cast iron pipe fittings |
| B2302 | Threaded connections for steel pipes | |
| B2303 | Threaded drainpipe joints | |
| B2308 | Stainless steel threaded connections | |
| ISO | 4144 | Pipework – stainless steel fittings threaded in Accordance with ISO 7-1 |
Types of JIS B2301
There are many types of threaded connections, and examples of JIS B2301 are shown in the table below. Refer to figures 2 and 3 for their shapes.
| Type | Uses | |
| Elbow | 90° elbow | For changing the piping route to 90° or 45° |
| 45° elbow | ||
| Different diameter elbow | ||
| Male and female elbows (street elbows) | ||
| 45° Male and female elbows (45° street elbows) | ||
| Male elbow with different diameter (different diameter street elbow) | ||
| Tee (cheese) | Tee with the same diameter | Branching (or gathering) piping routes in three directions |
| Different-diameter tee | ||
| Three-way different-diameter tee | ||
| Cross | Same diameter cross | When branching (or assembling) piping routes in 4 directions |
| Different diameter cross | ||
| Sockets | Sockets with the same diameter | When joining pipes with male threads |
| Different diameter sockets | ||
| Female male socket | ||
| Bushing | When joining female threaded connections and pipes of different diameters | |
| Nipple | Same diameter nipple | For joining threaded connections with female threads |
| Different diameter nipple | ||
| Cap | To close a pipe with male threads | |
| Plug | To close a female threaded connection | |
| Union | Same diameter union | When female threaded connections are joined and need to be separated |
| Female male union | ||
| Union Elbow | ||
| Male Male union elbow | ||
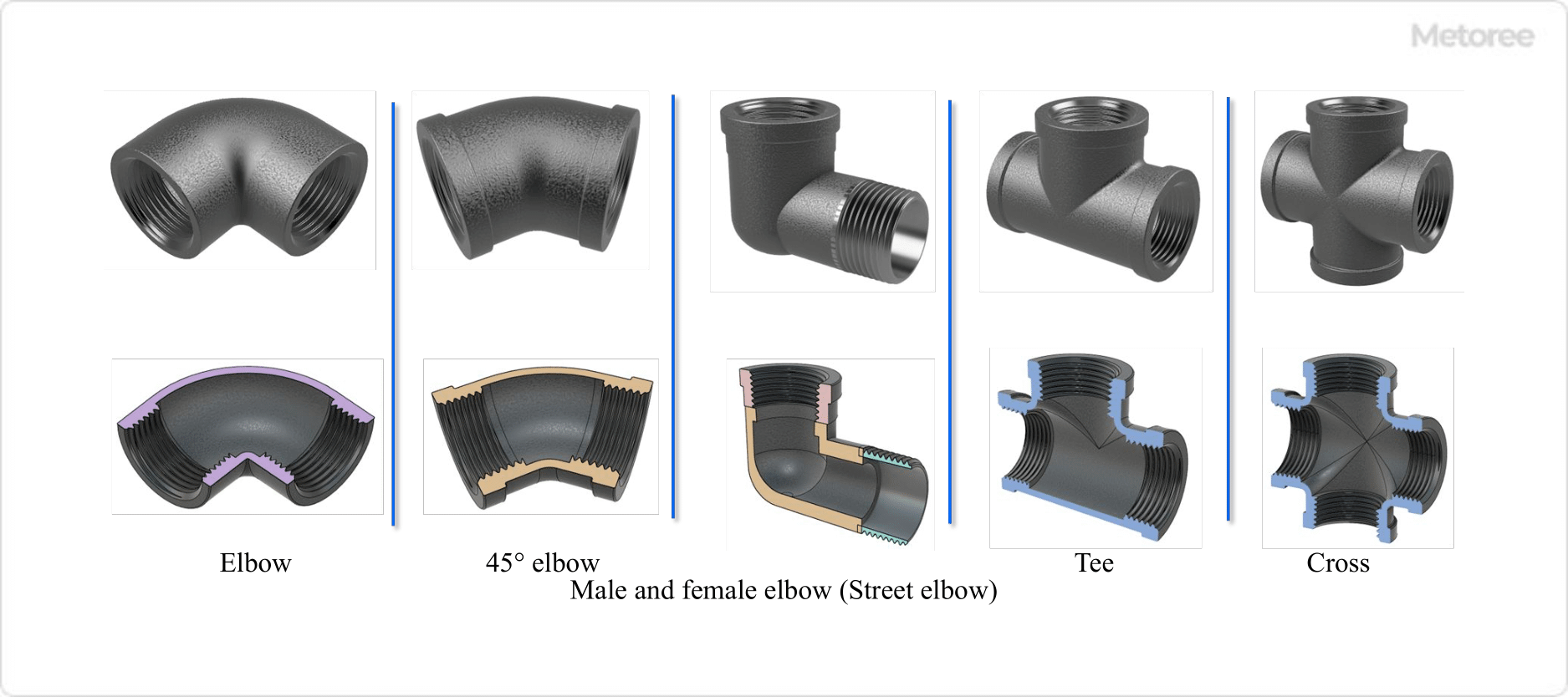
Figure 3. Types of screwed joints (1)
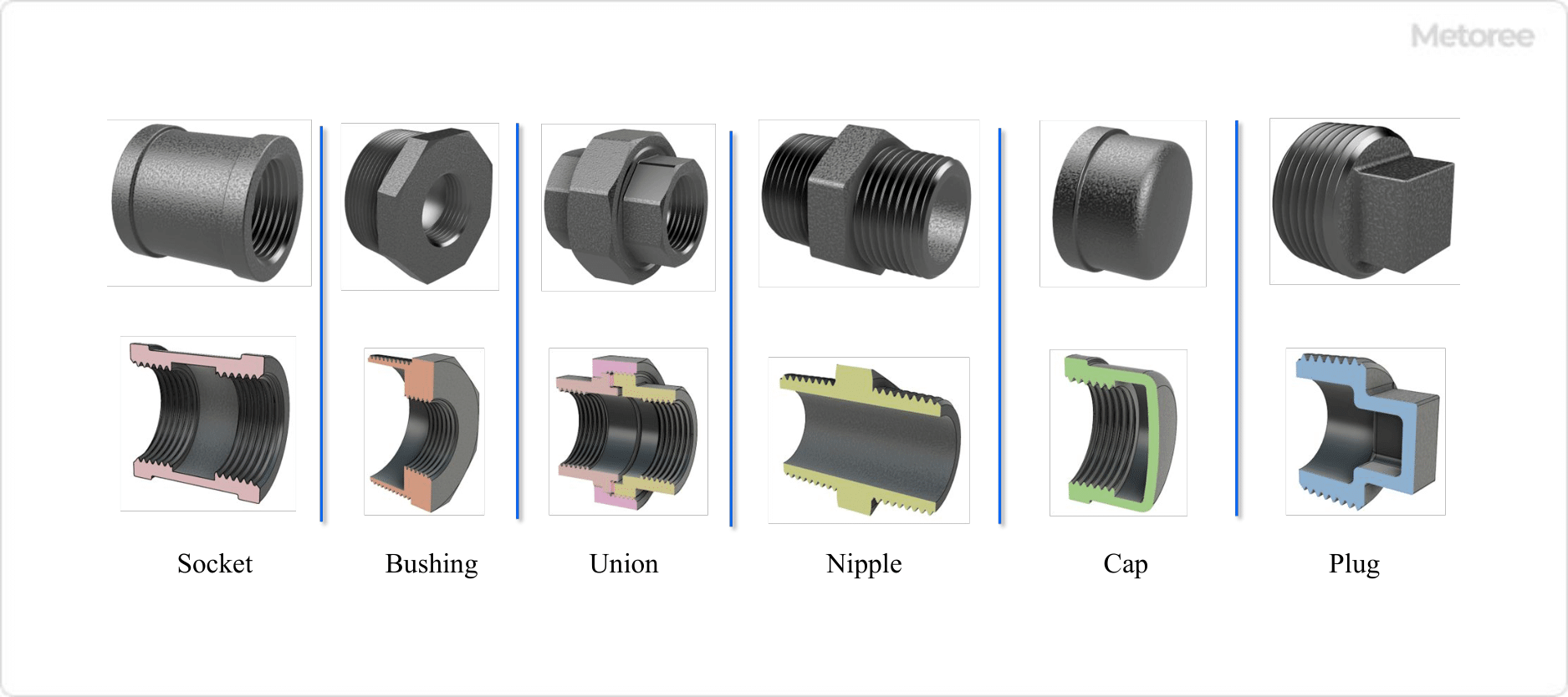
Figure 4. Types of screwed joints (2)
Various sizes are available for each type, and are selected according to the pipe nominal diameter.
2. Specifications and Sizes of Threaded Connections
Product specifications and sizes of threaded connections are defined by JIS standards and are indicated as follows.
| Standard No. or Standard Name | Type | Shape | Surface condition | Joint nominal | |
| Example 1 | JIS B 2301 | Type I | Male and female elbows, different diameter | black | 2 x 3/4 |
| Example 2 | Threaded malleable iron pipe fitting | Type I | 45° elbow | plated | 1-1/2 |