What Is a Circuit Board Heat Sink?
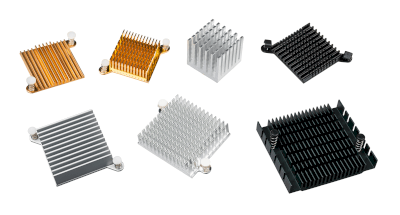
A circuit board heat sink is a cooling device attached to the circuit boards of electronic equipment and computers.
They are used to stabilize circuit operation by dissipating heat generated by electronic and electrical components mounted on printed circuit boards. Semiconductor components in various circuits tend to generate large amounts of heat when large drive power is required.
With the evolution of semiconductor processes, large-scale integrated circuits have been realized in extremely small sizes. In devices that realize such complex and advanced functions and performance, the amount of heat generated is also often large.
To reduce the amount of heat generated, various efforts are being made on the semiconductor device side to reduce power consumption. However, in most cases, heat sinks are required to maintain stable operation when used in various environments.
Circuit Board Heat Sink Applications
Circuit board heat sinks are cooling devices that are primarily used on electronic equipment and computer circuit boards. The following are some of their main uses:
1. CPU
The CPU is an important component responsible for computing and controlling the computer. A high-performance CPU performs many calculations and generates a lot of heat as a result. Overheating may cause performance degradation or damage.
Circuit board heat sinks are attached to the CPU to absorb the heat generated by the CPU. Heat exchange with the surrounding air is facilitated through the fins of the heat sink. This allows the CPU to maintain proper operating temperature and maximize performance.
2. GPU
The GPU is responsible for graphics-related tasks such as processing 3D graphics and decoding video. The GPU also often generates a lot of heat during graphics-intensive situations such as high-resolution games and video editing. Circuit board heat sinks are attached to the GPU to provide proper cooling and maintain high performance.
3. Power Electronics
Power electronics are electronic components that control or convert power. Inverters and motor drivers are examples.
These components handle high power and generate a large amount of heat. Circuit board heat sinks are attached to these components to provide efficient cooling. As a result, damage due to overheating can be prevented.
Principle of Circuit Board Heat Sink
The cooling principle of circuit board heat sinks is to effectively remove the heat generated on electronic device boards by using the processes of thermal conduction and thermal radiation.
1. Material and Shape
Circuit board heat sinks use aluminum, iron, and copper as their materials because of their good thermal conductivity. In addition, to increase the heat dissipation capacity of heat sinks, they are often designed to increase their surface area.
One example of such a device is to increase the surface area of a heat sink by placing many thin plates side by side on the surface of the heat sink with space between them. Products with many rod-like structures bonded to the surface are another way to increase surface area. In addition, when heat is to be dissipated efficiently, forced air cooling may be used to lower the ambient temperature.
2. Fixing Method
There are various ways to secure a heat sink to a PCB, including double-sided tape, pins, and clips. In some cases, double-sided thermally conductive tape is used to secure the heat sink.
In this method, double-sided adhesive tape with high thermal conductivity is placed between the heat sink and the heating element. This method is often used for small and lightweight heat sinks. Another method is to fix the heat sink and board with push pins.
The heat sink is held in place by spring tension. Another method is to secure the heat sink to the board with stepped screws, which makes it easy to replace the heatsink.
The Z-shaped clip method uses two anchors on the board and a Z-shaped wire clip to secure the heatsink in place. It is characterized by ease of attachment and removal.
Types of Circuit Board Heat Sinks
Circuit board heat sinks can be classified into two types depending on the cooling method: natural air cooling and forced air cooling.
1. Natural Air Cooling
Natural air cooling is a method that relies solely on heat dissipation from the heat sink. It is more advantageous in an open space with no enclosure.
2. Forced Air Cooling
Forced air cooling is a cooling method that uses a fan. Forced-air cooling is more efficient when there is an enclosure. This system controls the air velocity inside the chassis by the size of the duct opening to dissipate heat.
In forced air cooling, too large a flow path reduces air velocity, and too small a flow path reduces airflow. To maintain proper air velocity and air volume, the minimum cross-sectional area of the flow path must be equal to or greater than the minimum cross-sectional area of the fan.