What Is an Electrolyte?
 Electrolytes are liquids that contain dissolved electrolytes which allow electrical current to flow.
Electrolytes are liquids that contain dissolved electrolytes which allow electrical current to flow.
Electrolytes are dissolved as cations and anions, which can carry electric charges, thus electrolytes are ion conductive. Electrolytes are mainly used in storage devices, such as batteries and in plating.
In addition, although protic aqueous solvents are often used as electrolytes, non-protic solvents are commonly used in electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries.
Uses of Electrolytes
Electrolytes are used in a wide range of battery applications, whether for primary batteries or secondary batteries that can be charged and discharged. Specifically, electrolytes are used in lead-acid batteries, alkaline manganese batteries, nickel-metal hydride batteries, nickel-cadmium batteries, primary lithium batteries, secondary lithium-ion batteries, aluminum electrolytic capacitors, electric double layer capacitors, and lithium-ion capacitors.
Electrolytes are one of the materials that make up a battery, and a battery can generate electromotive force through chemical reactions at its electrodes. It is also an indispensable material for electrolysis to generate redox reactions on electrodes. In plating, it is a source of metal to be plated.
Principle of Electrolytes
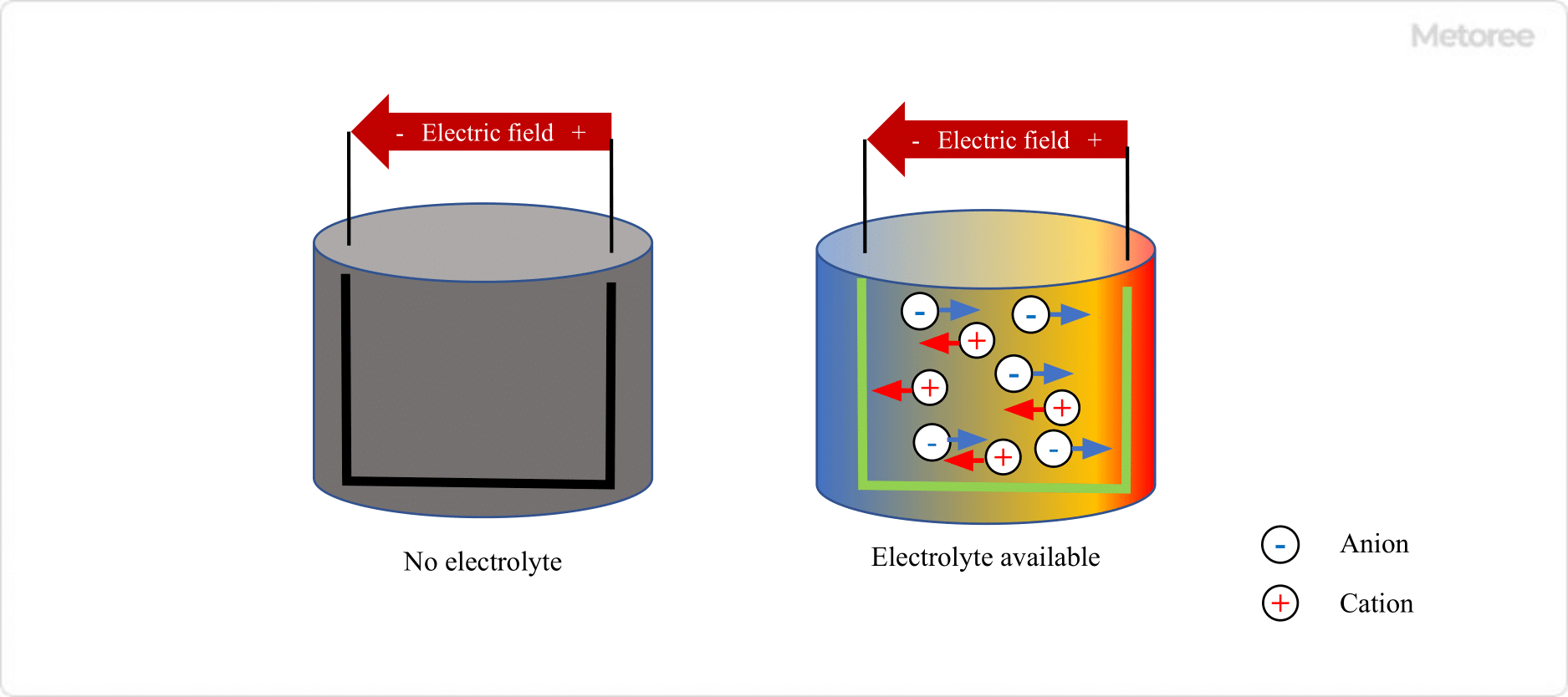
Figure 1. Principle of electrolyte
Electrolytes are solutions containing dissolved electrolytes used in batteries and electrolysis. The electrolyte is ionized into cations and anions in a solution, and these ions act as charge carriers. The composition of electrolytes varies depending on the application, and the development of electrolytes with superior properties is constantly underway.
Generally speaking, electrolytes are for batteries. There are several types of electrolytes for batteries, and their composition varies greatly depending on the type of battery.
Types of Electrolytes
Electrolytes are important materials that are responsible for carrying the electric charge between the positive and negative electrodes of a battery, for example. The following is a description of electrolytes for each application.
1. Electrolytes for Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries use 30~35% dilute sulfuric acid as electrolytes. Lead-acid batteries use lead dioxide as the positive electrode and sponge lead as the negative electrode. When charging, the lead is converted to lead dioxide by passing current through the cathode, and converted to lead by passing current through the anode.
During discharge, lead dioxide from the positive electrode and lead from the negative electrode are dissolved in dilute sulfuric acid to produce electricity. Lead-acid batteries are used in automobiles, UPS (uninterruptible power supply), etc., and are widely used because they are inexpensive and easy to manufacture.
2. Electrolytes for Alkaline Batteries
Alkaline battery electrolytes are strongly alkaline aqueous solutions containing potassium hydroxide as the main component. Since the electrolytes of alkaline batteries are aqueous solutions, self-discharge occurs even when the batteries are not in use.
In the event of leakage, contact with the skin, or contact with the eyes, immediately rinse with large amounts of clean water and seek medical attention. Alkaline batteries are widely used as primary batteries and are suitable for long-term storage.
3. Electrolytes for Nickel-Metal Hydride Batteries
Concentrated potassium hydroxide solution is used as electrolytes for nickel-metal hydride batteries. Nickel-metal hydride batteries use a nickel oxide compound for the anode and a hydrogen storage alloy for the cathode. Nickel-metal hydride batteries have a high charge-discharge cycle performance and are used in hybrid cars and home appliances.
4. Electrolytes for Lithium-Ion Batteries
Organic electrolytes containing dissolved lithium salts such as LiBF4 (lithium tetrafluoroborate), LiPF6 (lithium hexafluorophosphate), and LiFSI (lithium bis-fluorosulfonyl imide) are used in lithium ion batteries. Electrolytes for batteries must not decompose during charging and discharging, not denature when heated, and not ignite when heated.
Lithium-ion batteries are lightweight, high-power, and long-lasting, and are used in smartphones, electric vehicles, and household storage batteries.
5. Electrolytes for Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitors
Electrolytes for aluminum electrolytic capacitors are made by dissolving salts of tertiary amines or amidines with carboxylic acids in solvents such as lactone or glycol. Aluminum electrolytic capacitors are used in a wide variety of products with electronic substrates in a wide range of fields, including the automotive, home appliance, and industrial equipment fields, because of their low cost.
6. Electrolytes for Electric Double-Layer Capacitors
Electrolytes for electric double-layer capacitors are made by dissolving electrolytes such as quaternary ammonium salts and imidazolium salts in organic solvents. A rechargeable battery is a capacitor that uses activated carbon as the active material for the positive and negative electrodes, and is suitable for applications that require a lot of energy. Where rapid charging and discharging is required and durability is required, electric double-layer capacitors are the capacitor of choice.