What Is a Timing Pulley?
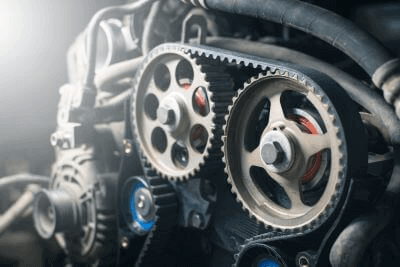
A timing pulley is a mechanical element used to precisely synchronize multiple parts of an internal combustion engine or automobile engine.
It is a type of pulley used to transmit power with a belt. Basically, timing belts and timing pulleys are used as a set.
Specifically, they are used to precisely synchronize the camshaft and crankshaft in the engine and to control the timing of valve opening and closing. Timing pulleys are gear-shaped components that drive the timing belt connecting the camshaft and crankshaft, which rotates at a precise angle.
It must be manufactured from high-quality materials and accurately designed because it has a significant impact on engine performance and fuel economy. In addition, timing pulleys are generally replaced at the same time when timing belts are replaced.
Uses of Timing Pulleys
A familiar application for timing pulleys is in automobile engines. The engine has intake valves to intake the air mixture into the cylinders and exhaust valves to exhaust the exhaust gases after combustion. These valves are opened and closed by camshafts, and timing pulleys are used to drive the camshafts.
The intake and exhaust valves must open and close in accordance with the timing of the pistons, which repeat their up-and-down motion at high speed. If the timing is off, the engine will malfunction or fail.
In order for the engine to produce power, it is very important to match the piston movement, valve opening and closing, and ignition timing. Timing belts and timing pulleys play this role.
They are sometimes used in machines other than automobiles when the timing of the internal components must be matched. Timing pulleys are also used in production lines for industrial products such as printing and textile machinery.
Principle of Timing Pulleys
Timing pulleys are intermeshing transmissions. Like a gear, it has a set number of teeth, and the timing can be adjusted by setting the number of teeth. If the number of teeth on the drive timing pulley is 20 and the number of teeth on the transmission side is 40, two revolutions on the drive side will result in one revolution on the transmission side.
If the number of teeth is incorrectly set, the timing will be off each time the pulley rotates, causing damage to the machine or equipment. Otherwise, the tooth profile and pitch of the pulley are used in conjunction with the timing belt.
Timing pulleys come in a very wide variety of types and are available in many different types for mounting on a shaft. Keyway, shaft hole, crimp type with threaded holes, and keyless type (with integrated fasteners) are available, allowing for installation in any location.
Types of Timing Pulleys
There are various types of timing pulleys, which are classified by tooth shape and size standard.
1. Inch Type
In the inch series, trapezoidal type MXL, XL, L, and H are available. They are used for general transmission and light-load conveyance.
2. Millimeter Series
The millimeter series includes trapezoidal T, AT, S and R types for high-torque transmission, and H type for high-precision positioning. The S and R types are often used for positioning because of their low backlash, while the H type is used in situations that require particularly high accuracy. The trapezoidal type is often used for conveyance, and AT has 1.3 times the allowable tension of T, enabling high-load conveyance.
How to Select a Timing Pulley
Because of the great variety of types and standards, care must be taken when selecting a timing pulley. Timing pulleys should be selected by calculating the load, safety factor, and other factors based on the conditions under which they will be used.
1. Confirmation of Usage Conditions
First, clarify the conditions of use. Determine the transmission power from the rated power of the prime mover, and determine the correction factor based on the conditions of use. The method for determining the correction factor is described in the manufacturer’s literature.
For example, the correction factor is determined based on the presence of repetitive loads, vibration, and daily operating hours. The transmission power multiplied by the correction factor is called the design power, which is the transmission power used in the selection process.
2. Determination of Tooth Profile and Belt Width
Next, a simplified selection table is used to select a belt type (tooth profile) based on the pulley rotation speed and design power. A simplified selection table is provided in the selection documents of each manufacturer.
Once the tooth profile is determined, use the standard transmission capacity table to determine the standard transmission capacity based on the pulley rotation speed. Calculate the required belt width from the design power, standard transmission capacity, standard belt width, and engagement coefficient.
3. Mounting Method and Belt Length
Select the mounting conditions, such as whether a flange should be attached and how many shafts should be spaced. The belt tensioning mechanism is also designed, and the mounting dimensions and belt length are determined.
4. Material
Pulley materials include aluminum and iron, which must be selected according to the application. Iron or stainless steel is used when strength is required. Aluminum is often used for precision positioning that requires a low moment of inertia.