What Is Diethylenetriamine?
Diethylenetriamine is an organic compound with the chemical formula C4H13N3 and structural formula HN(CH2CH2NH)2. It falls under the category of primary amines and is known by several names, including 2,2′-iminodiethylamine, 2,2′-diaminediethylamine, and bis(2-aminoethyl)amine. Its CAS number is 111-40-0.
Chemically akin to ethylenediamine, it finds use in similar applications. The molecular structure is often compared to that of diethylene glycol.
Uses of Diethylenetriamine
Diethylenetriamine is utilized in various applications, such as paper wetting and strengthening agents, epoxy resin curing agents, chelating agents, ion exchange resins, fiber treatment agents, and the synthesis of synthetic organic materials. Among these, its most significant use is as a paper wet strengthener.
This compound is integral to the production of polyamide resins through the reaction with adipic acid, further treated with epichlorohydrin. As a fiber treatment agent, it is used in anti-wrinkle agents, surfactants, and dye-fixing agents.
Additionally, it serves roles in agrochemicals as a fungicide, insecticide, and herbicide, and is notably used in epoxy resin-based adhesives and curing agents for thermosetting resins, facilitating cross-linking through reaction with epoxide groups.
Properties of Diethylenetriamine
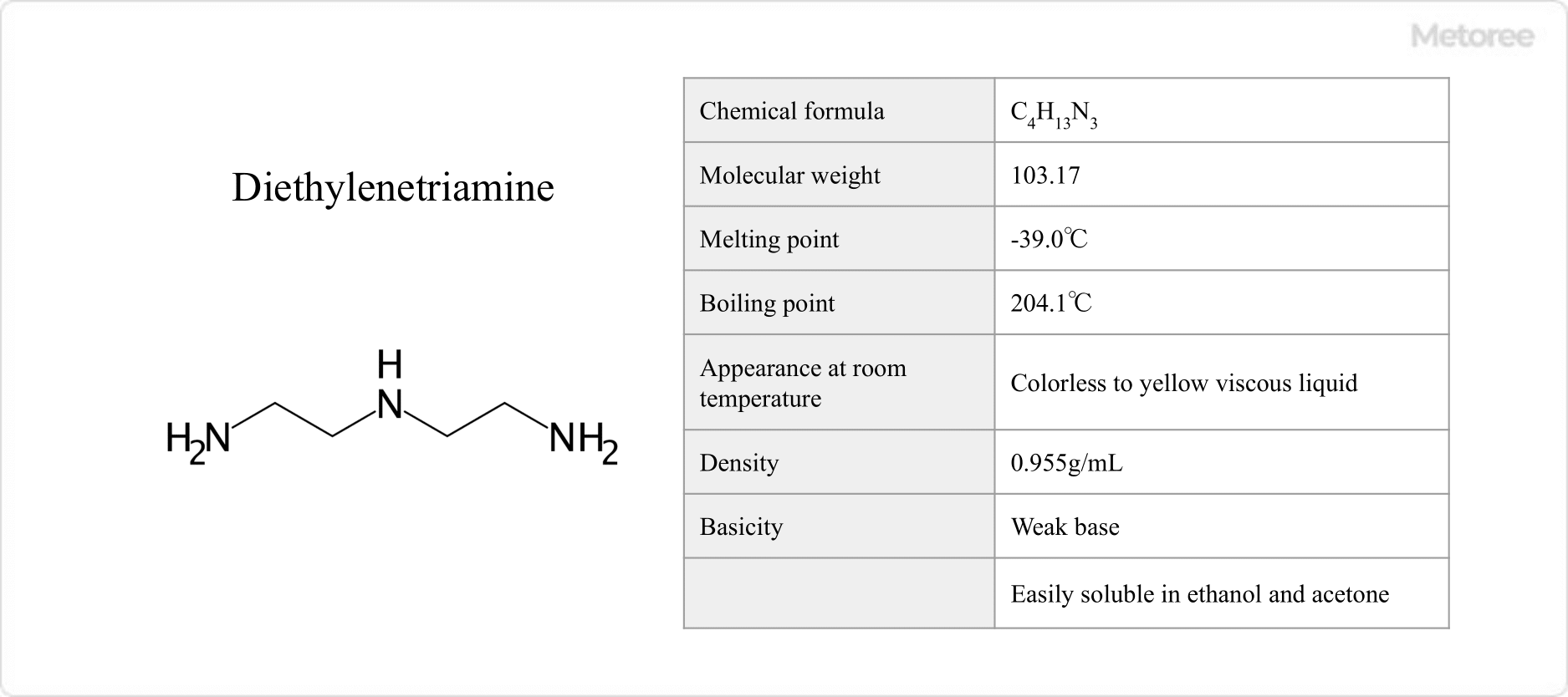
Figure 1. Basic Information on Diethylenetriamine
With a molecular weight of 103.17, diethylenetriamine has a melting point of -39.0°C and a boiling point of 204.1°C. At room temperature, it appears as a colorless to yellow viscous liquid and emits an amine odor.
It exhibits high solubility in water, ethanol, and acetone, and is soluble in polar solvents but insoluble in simple hydrocarbons. Its density is 0.955 g/mL. Being a weak base, its aqueous solutions display weak alkalinity.
Types of Diethylenetriamine
Available primarily for research and development, diethylenetriamine is sold in various volumes, including 5mL, 25mL, 100mL, 1L, 2.5L, and 18L, accommodating both laboratory use and larger-scale applications affordably.
Other Information on Diethylenetriamine
1. Synthesis of Diethylenetriamine
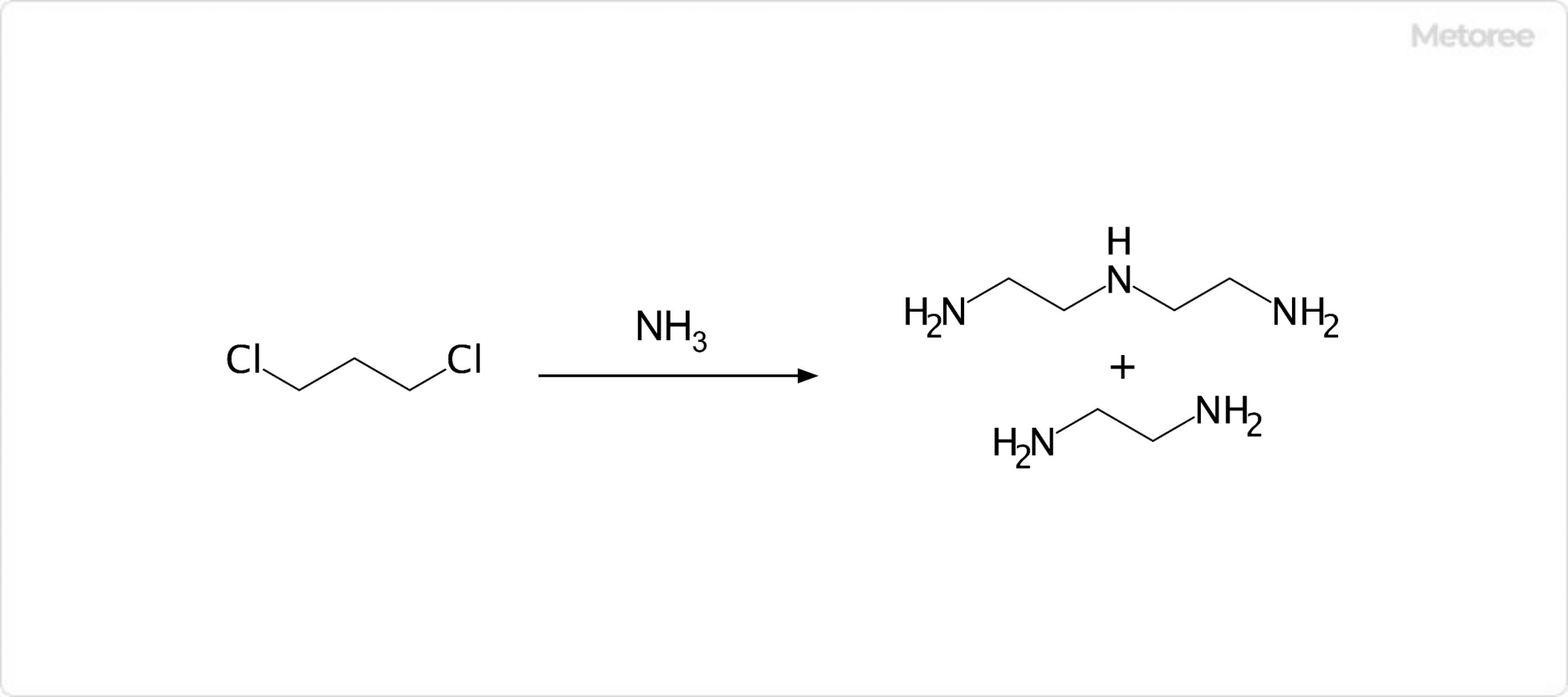
Figure 2. Synthesis of Diethylenetriamine
Diethylenetriamine can be synthesized by reacting 1,2-dichloroethane with ammonia, or monoethanolamine with ammonia under hydrogenated catalysts. Industrially, it is primarily obtained as a byproduct in the production of ethylenediamine from 1,2-dichloroethane.
2. Chemical Reaction of Diethylenetriamine
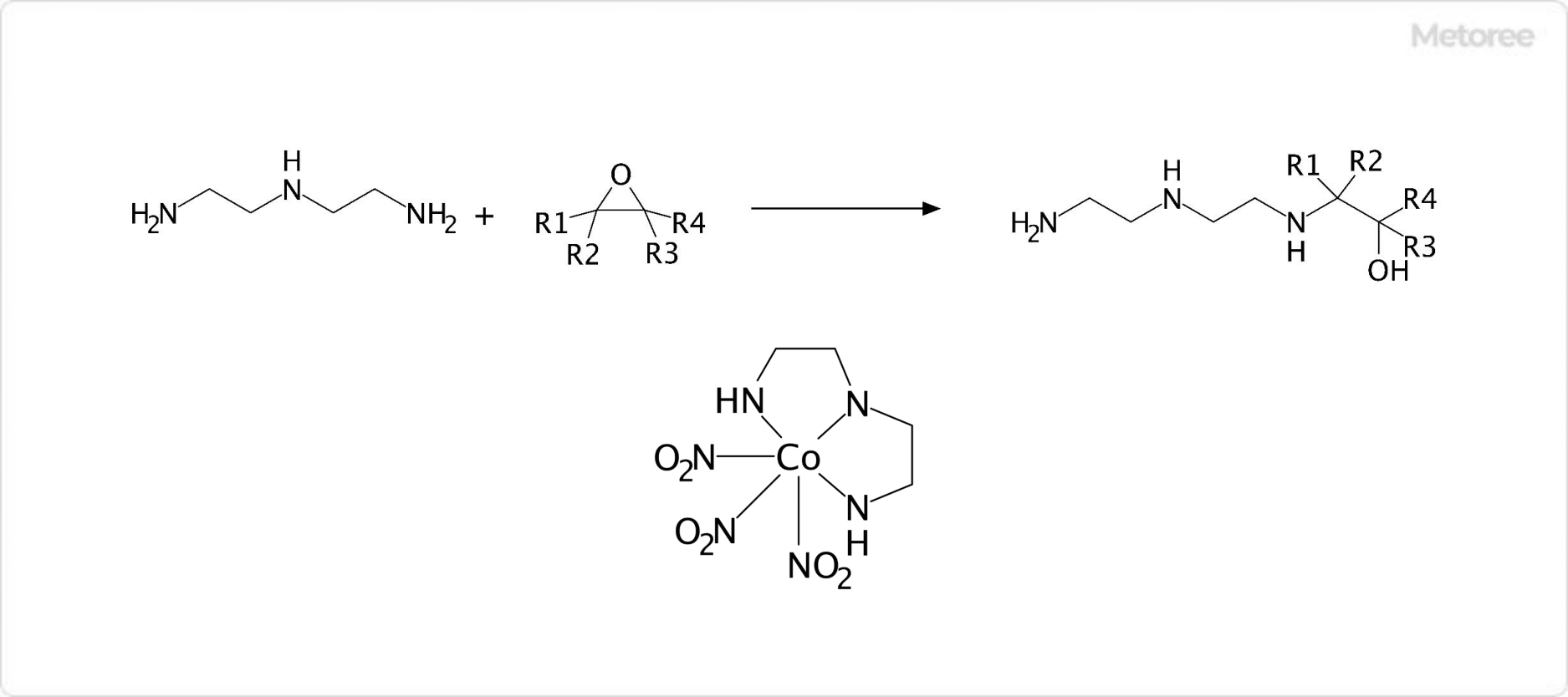
Figure 3. Reaction of Diethylenetriamine with Epoxide Groups
It reacts with epoxide groups to form N-alkylated crosslinks, a reaction pivotal in the use of curing agents for epoxy resin adhesives. Diethylenetriamine also acts as a tridentate ligand in coordination chemistry, forming complexes with metals such as in Co(Dien)(NO2)3.
3. Toxicological Information on Diethylenetriamine
Recognized as a hazardous substance, diethylenetriamine exhibits various toxicity levels under the GHS classification, including acute toxicity (oral, dermal, inhalation), skin corrosion/irritation, serious eye damage/eye irritation, respiratory and skin sensitization, and reproductive toxicity.
4. Regulatory Information on Diethylenetriamine
Due to its hazardous properties, diethylenetriamine is subject to regulatory oversight under various laws.