What Is Phosphorus Trichloride?
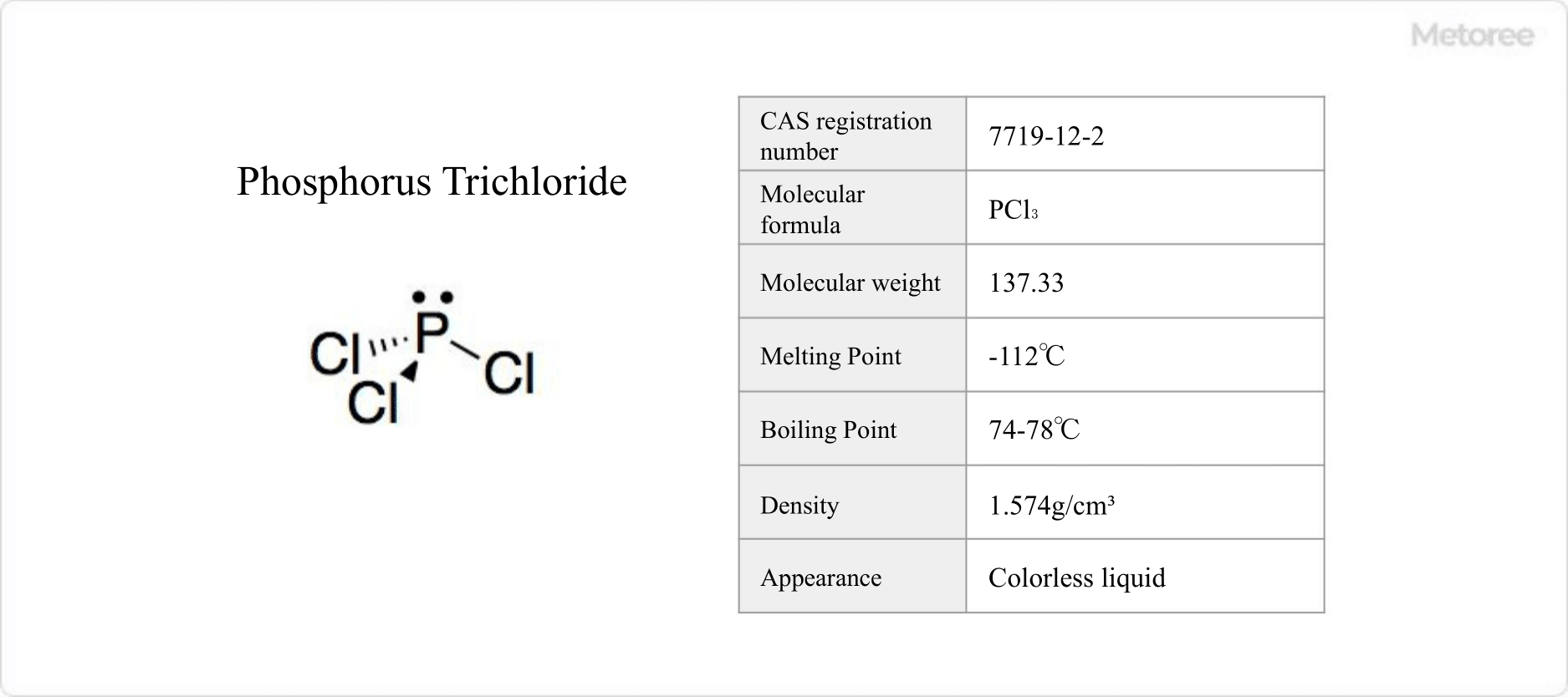
Figure 1. Basic Information on Phosphorus Trichloride
Phosphorus trichloride (PCl3) is a phosphorus chloride, known for its toxicity and hazardous nature, capable of causing fatal exposure at concentrations as low as 600 ppm. It is recognized for its irritant properties and acute toxicity by global safety standards and is regulated under various health and safety laws.
Uses of Phosphorus Trichloride
As a versatile trivalent phosphorus compound, phosphorus trichloride is used in a myriad of applications including as a flame retardant, antioxidant, plasticizer, in water treatment, and in the synthesis of organophosphine ligands and pharmaceutical intermediates. It serves as a precursor for many phosphorus-based compounds, including phosphoryl chloride and phosphorus pentachloride.
Properties of Phosphorus Trichloride
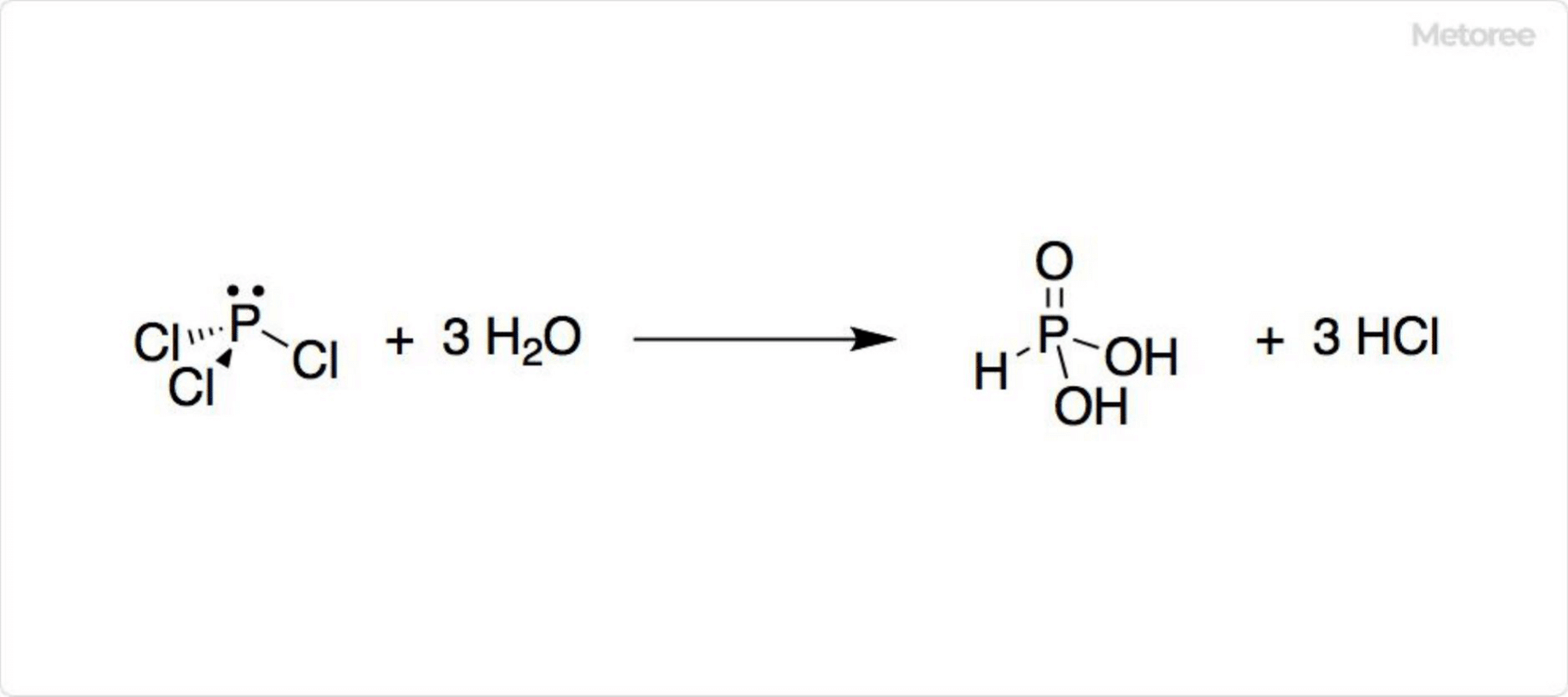
Figure 2. Hydrolysis of Phosphorus Trichloride
A colorless or yellow fuming liquid at room temperature, phosphorus trichloride has a pungent odor and reacts violently with water to produce hydrochloric acid and phosphonic acid, showcasing its corrosive nature towards metals.
Structure of Phosphorus Trichloride
With a molecular weight of 137.33 g/mol and a trigonal pyramidal structure, phosphorus trichloride exhibits significant chemical characteristics, including a specific dipole moment and a defined angle between its chlorine atoms, indicative of its reactive nature as a strong Lewis acid.
Other Information About Phosphorus Trichloride
1. Synthesis of Phosphorus Trichloride
Phosphorus trichloride can be industrially synthesized by chlorinating phosphorus under controlled conditions, with laboratory methods favoring red phosphorus for safety.
2. Synthesis of Phosphine Using Phosphorus Trichloride
It serves as a starting point for the synthesis of a wide array of organophosphine compounds, highlighting its importance in organic chemistry.
3. Reaction of Phosphorus Trichloride With Alcohols
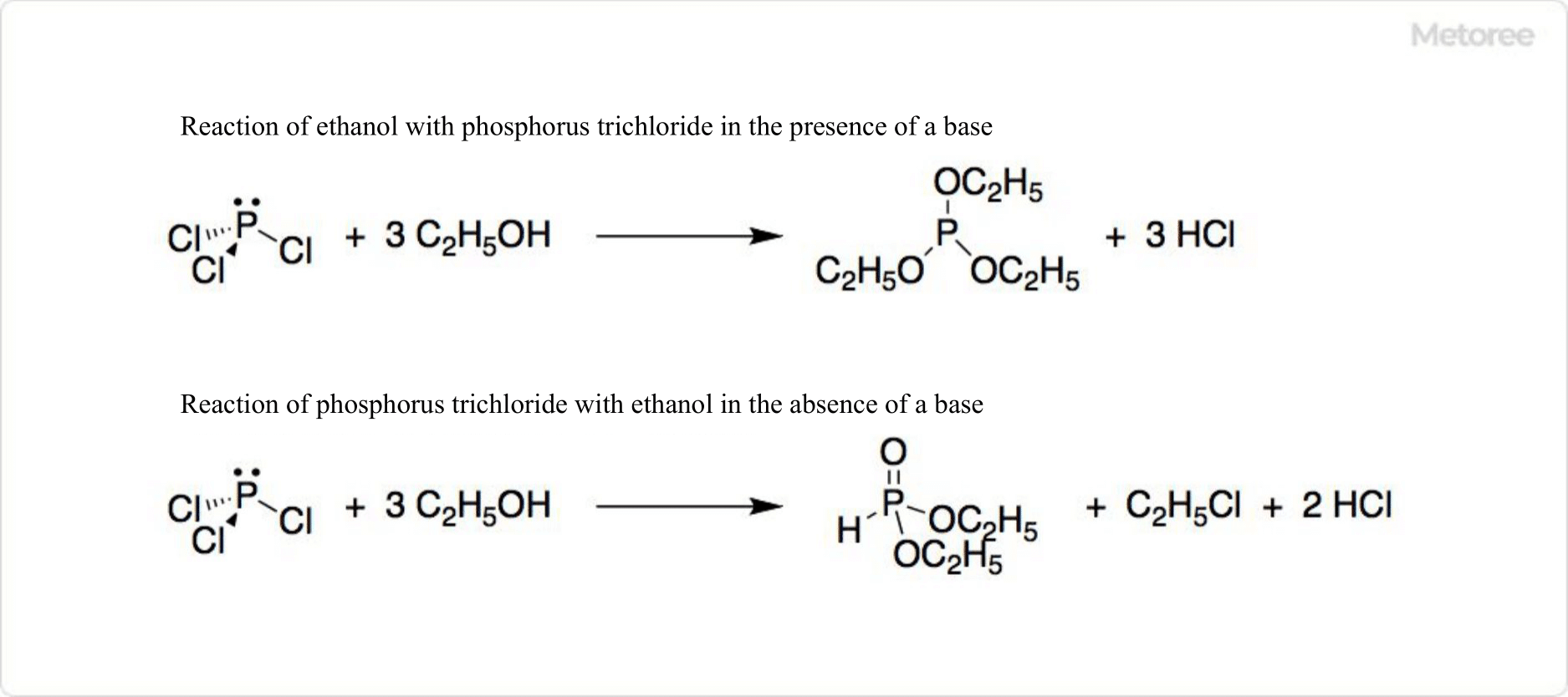
Figure 3. Reaction of Phosphorus Trichloride
Phosphorus trichloride’s interaction with alcohols, depending on the presence of a base, can yield various phosphorus-containing organic compounds, demonstrating its role in synthetic organic chemistry.
4. Reaction of Phosphorus Trichloride With Amines
This compound’s reactions with amines and thiols further underline its utility in producing specialized chemicals for industrial applications.
5. Other Reactions of Phosphorus Trichloride
Its capability to undergo substitution reactions and act as a Lewis base illustrates the broad reactivity and application of phosphorus trichloride in chemical synthesis and industry.