What Is Morpholine?
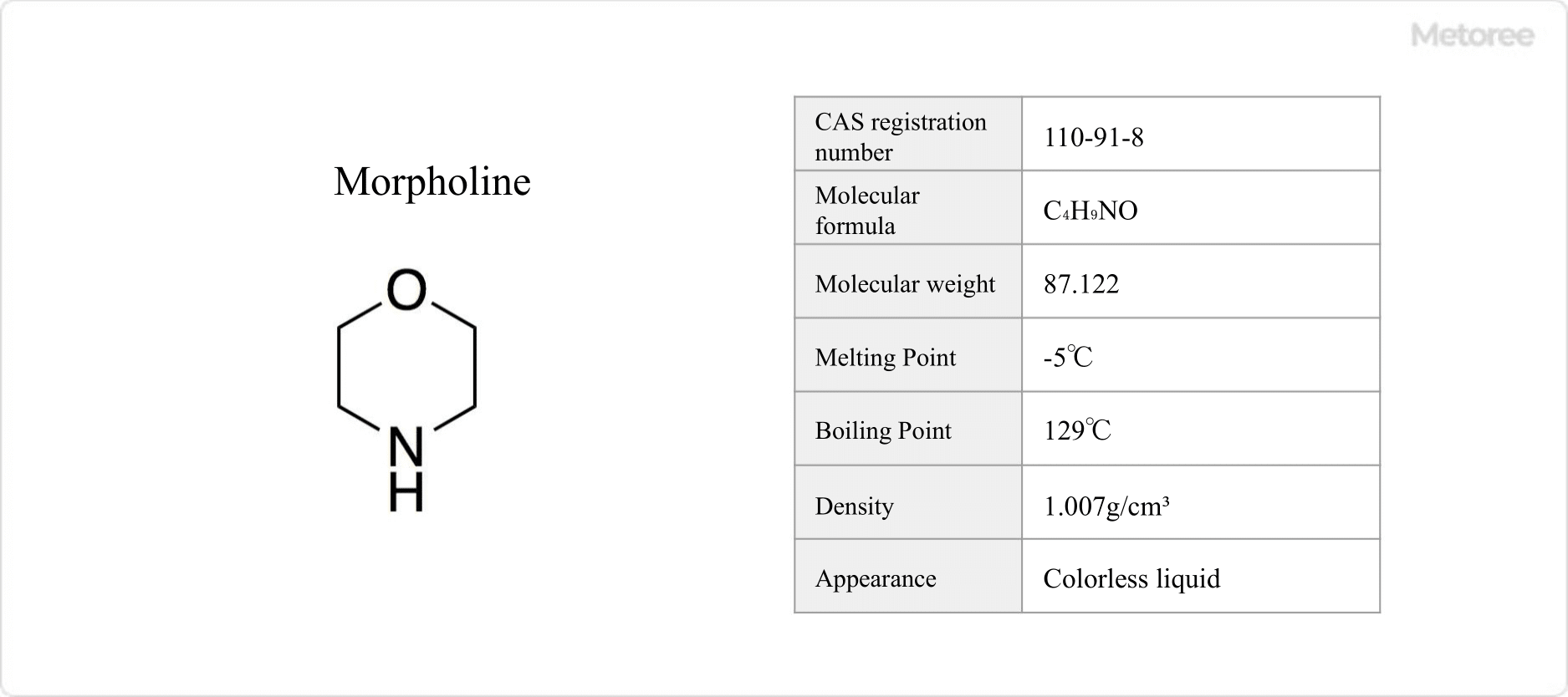
Figure 1. Basic Information on Morpholine
Morpholine, an organic compound with the molecular formula C4H9NO, also known as tetrahydro-2H-1,4-oxazine, is a colorless liquid at room temperature. As a skin irritant and flammable substance, it requires careful handling due to potential adverse effects on the kidneys and liver from long-term exposure.
It is classified as a hazardous and flammable substance under various laws, requiring caution in its handling.
Uses of Morpholine
Primarily, morpholine serves as a vulcanization accelerator in synthetic rubber manufacturing. Due to carcinogenic nitrosamines produced during vulcanization, regulations have tightened, prompting the development of safer accelerators. Additionally, morpholine forms the backbone of various pharmaceuticals, including analgesics, sedatives, and local anesthetics.
Properties of Morpholine
With a melting point of -5°C and a boiling point of 129°C, morpholine exhibits hygroscopic properties and has a distinctive amine odor. Its flash point is 38°C. Soluble in water, its basic nitrogen atom contributes to the formation of morpholinium ions in solution, with a pKa of 8.33.
Structure of Morpholine
Morpholine features both amine and ether functional groups, resembling cyclohexane with two opposing carbon atoms replaced by an oxygen and a nitrogen atom. This heterocyclic amine has a molecular weight of 87.12 and a density of 1.007 g/cm3.
Other Information on Morpholine
1. Synthesis of Morpholine
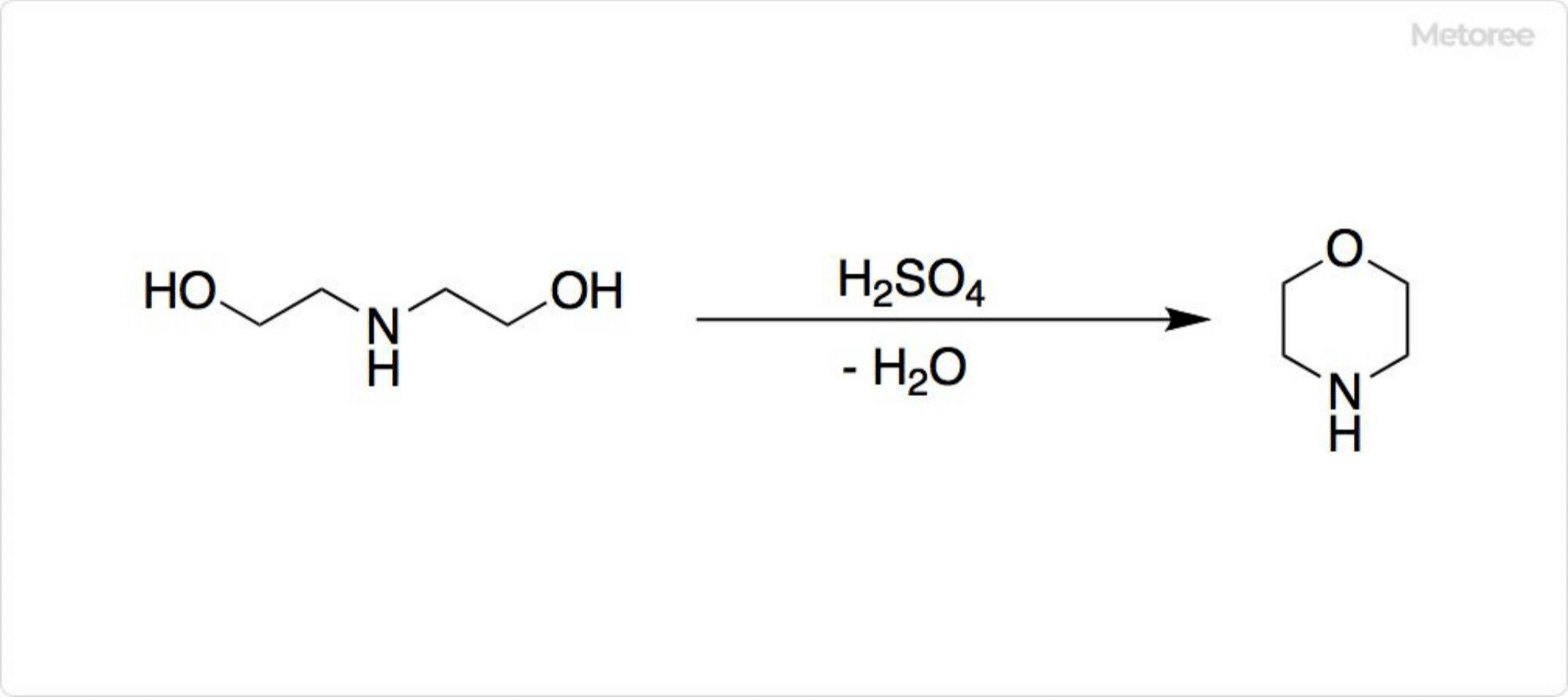
Figure 2. Synthesis of Morpholine
Morpholine is industrially synthesized through the dehydration of diethanolamine (DEA) using sulfuric acid. DEA is a compound combining features of diols and secondary amines.
2. Basicity of Morpholine
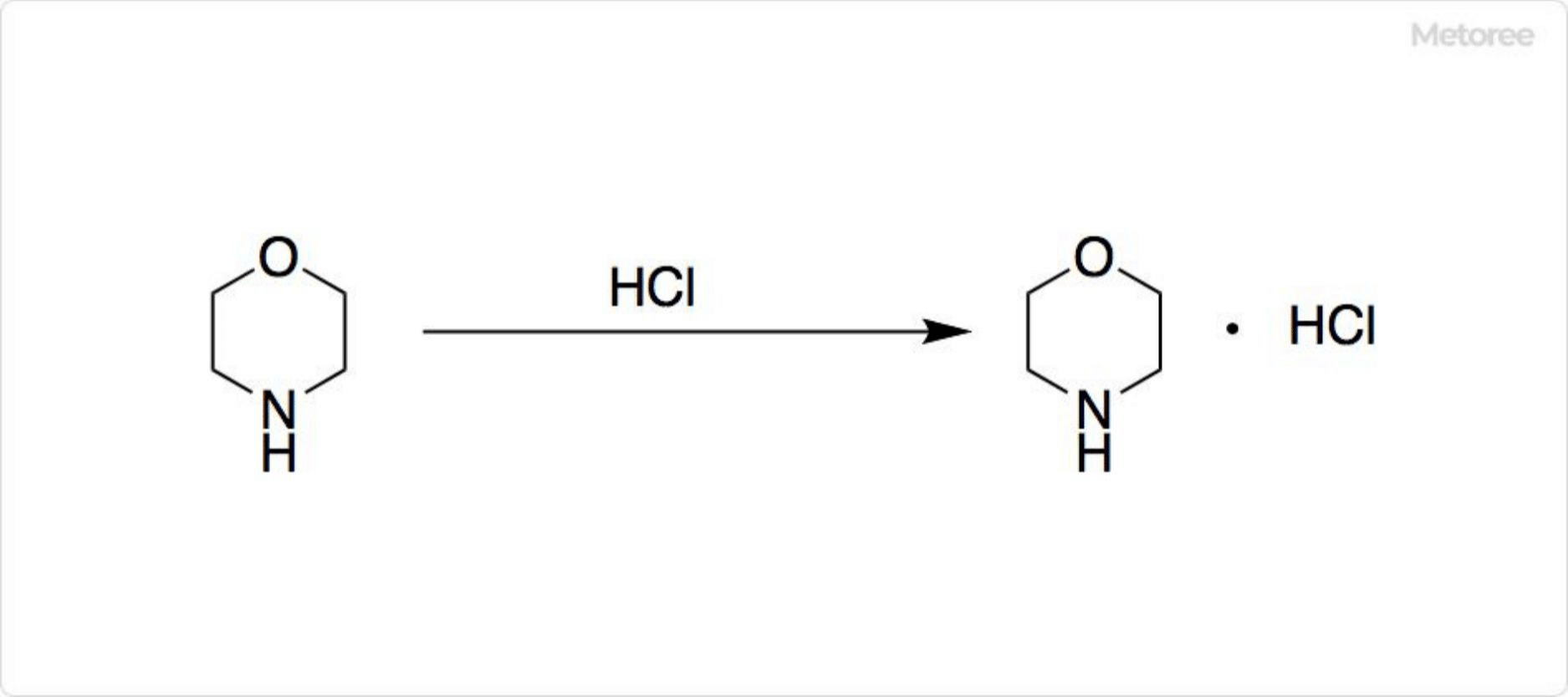
Figure 3. Reactions of Morpholine
Morpholine’s conjugate acid, morpholinium, forms through the reaction with hydrochloric acid, producing morpholine hydrochloride, a colorless liquid with a weak ammonia-like odor. Named by Ludwig Knorr, morpholine was once mistakenly associated with morphine. Its ether oxygen lowers the nitrogen atom’s electron density, reducing its nucleophilicity and basicity compared to similar secondary amines.
3. Reactions with Morpholine
In organic synthesis, morpholine is instrumental in producing the antibiotic linezolid, the anticancer drug gefitinib, and the analgesic dextromoramide. It also facilitates enamine production, serving as a versatile synthetic intermediate and solvent in various industrial applications.