What Is a Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) Service?
Non-destructive testing (NDT) services are tests to determine the presence, size, shape, distribution, etc., of scratches on a surface or interior surface without destroying the object being tested.
Destructive testing is a testing method in which pressure, temperature, vibration, etc., are applied to an object until it is destroyed, and the permissible limit of defect generation is directly examined. NDT service is an indirect testing method and has the disadvantage of not being able to reliably determine the conditions under which defects can occur. It can detect defects without damaging the shape or function of the object. This makes it possible to test buildings, plants, railways, aircraft, etc., while they are in operation.
Uses of NDT Services
NDT services are used in a wide variety of fields.
Depending on the type of NDT Services, the purpose of use and the materials that can be used will vary. For example, eddy current testing can detect flaws on the surface of conductors without contact and at high speed. However, it cannot be used on non-conductive materials and can only detect internal flaws to a limited extent. Therefore, it is necessary to select the appropriate test for the intended use.
Principles of NDT Services
Various NDT services exist, each with different principles. The following is a description of the principles of typical NDT Services:
1. Radiation Transmission Testing
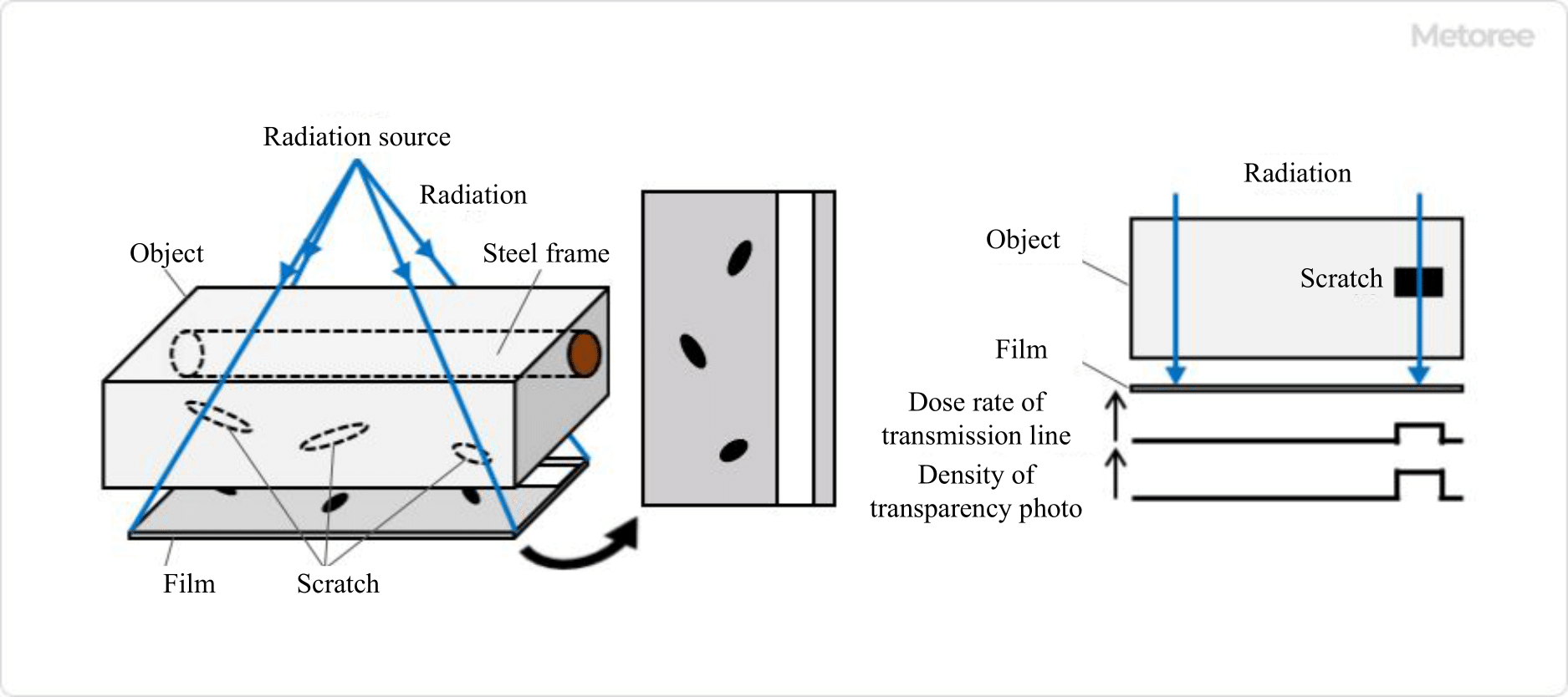
Figure 1. Principle of radiation transmission testing
In a radiation transmission test, an object is exposed to X-rays or γ-rays, and the images projected on a film or image plate are used to determine the internal state of the object.
Radiation has the property of penetrating through materials, but the ease of penetration depends on the condition of the object’s interior. For example, a damaged part of an object is generally more easily penetrated by radiation than a healthy part, resulting in a darker appearance on the film. The shading of the film is caused by the reaction of the emulsion that makes up the film to radiation.
Radiation transmission tests are classified into several methods, depending on the method of photography and other factors. For example, image data is obtained by using an image plate instead of a film.
2. Ultrasonic Testing
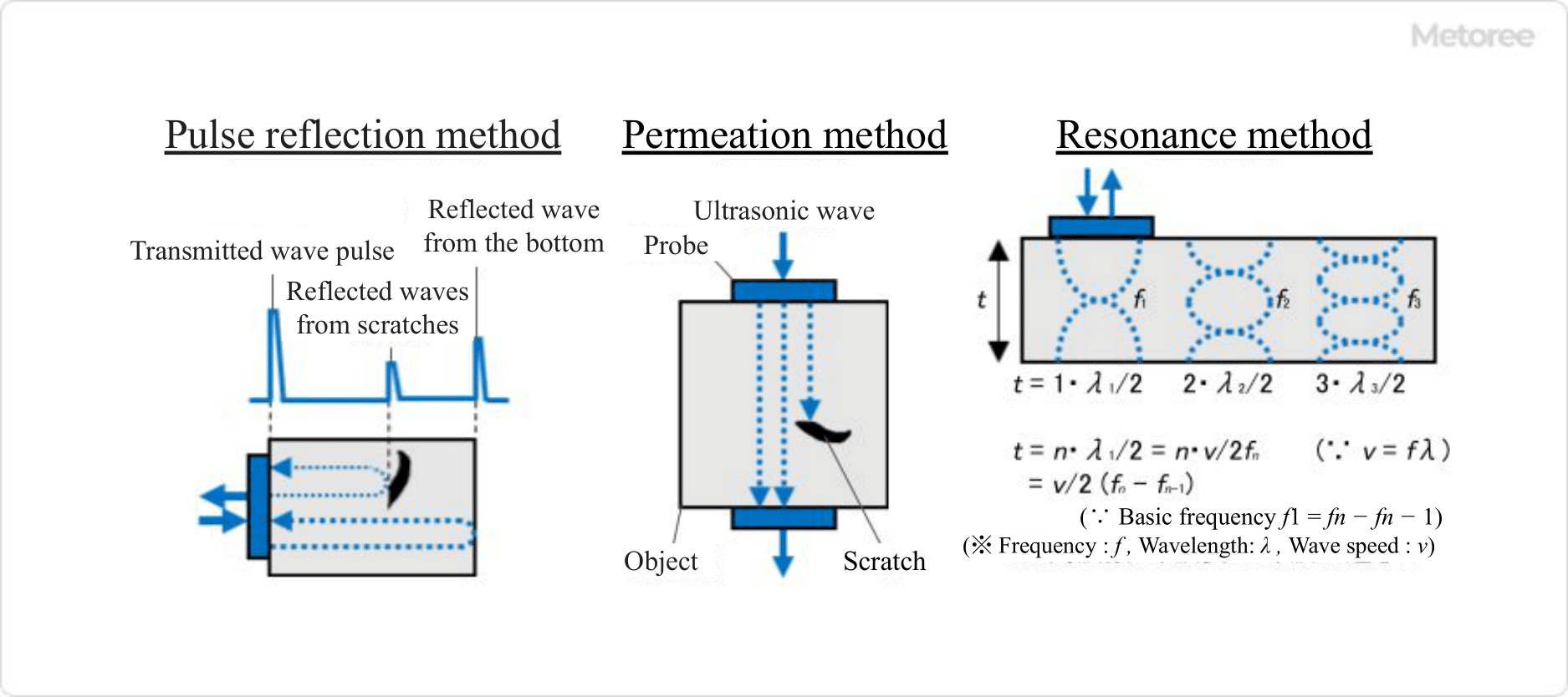
Figure 2. Principle of ultrasonic testing
Ultrasonic flaw testing is a test used to estimate the internal condition and thickness of an object by applying ultrasonic waves to the object.
Ultrasonic testing can be broadly classified into three methods: transmission, pulse reflection, and resonance. The methods are further classified according to the type of ultrasonic wave and the method of application. They are used in different ways depending on the intended use.
Transmission method
The transmission method estimates internal conditions by comparing the strength of transmitted and received ultrasonic waves.
A probe is positioned on the surface of the object to introduce ultrasonic waves, and another probe is placed at the bottom of the object to receive these waves. The ultrasonic waves, initiated by the surface probe, penetrate the interior of the object and reach the probe at the bottom. If there is a flaw within the object, the ultrasonic wave is unable to pass beyond it, resulting in a weakening of the wave. This attenuation of ultrasonic waves reveals internal defects through the formation of ultrasonic shadows.
Pulse Reflectometry
The pulse reflection method uses the reflection of ultrasonic waves to identify the presence, location, size, etc. of a flaw.
A probe capable of transmitting and receiving ultrasonic waves is placed on the surface of the object. Ultrasonic waves incident inside the object from the probe reflect off the bottom surface and return to the probe. Ultrasonic waves are also reflected if there are scratches or other defects inside the object. The internal condition of the object is estimated by receiving the transmitted pulse, the reflected wave from the scratch, etc., and the reflected wave from the bottom surface.
Resonance Method
The resonance method is a method to measure the thickness of an object by utilizing the resonance of the object.
When ultrasonic waves are injected into an object while continuously changing the wavelength, the object resonates when an integer multiple of half wavelength equals the thickness of the object. The vibration energy for resonance is supplied by the oscillator, and the occurrence of resonance can be confirmed by detecting the increase in current. The thickness of the object is estimated from the sound velocity, frequency, and resonance order at resonance. It is also possible to estimate the presence or absence of scratches inside the object from the strength of the resonance.
3. Magnetic Powder Flaw Testing
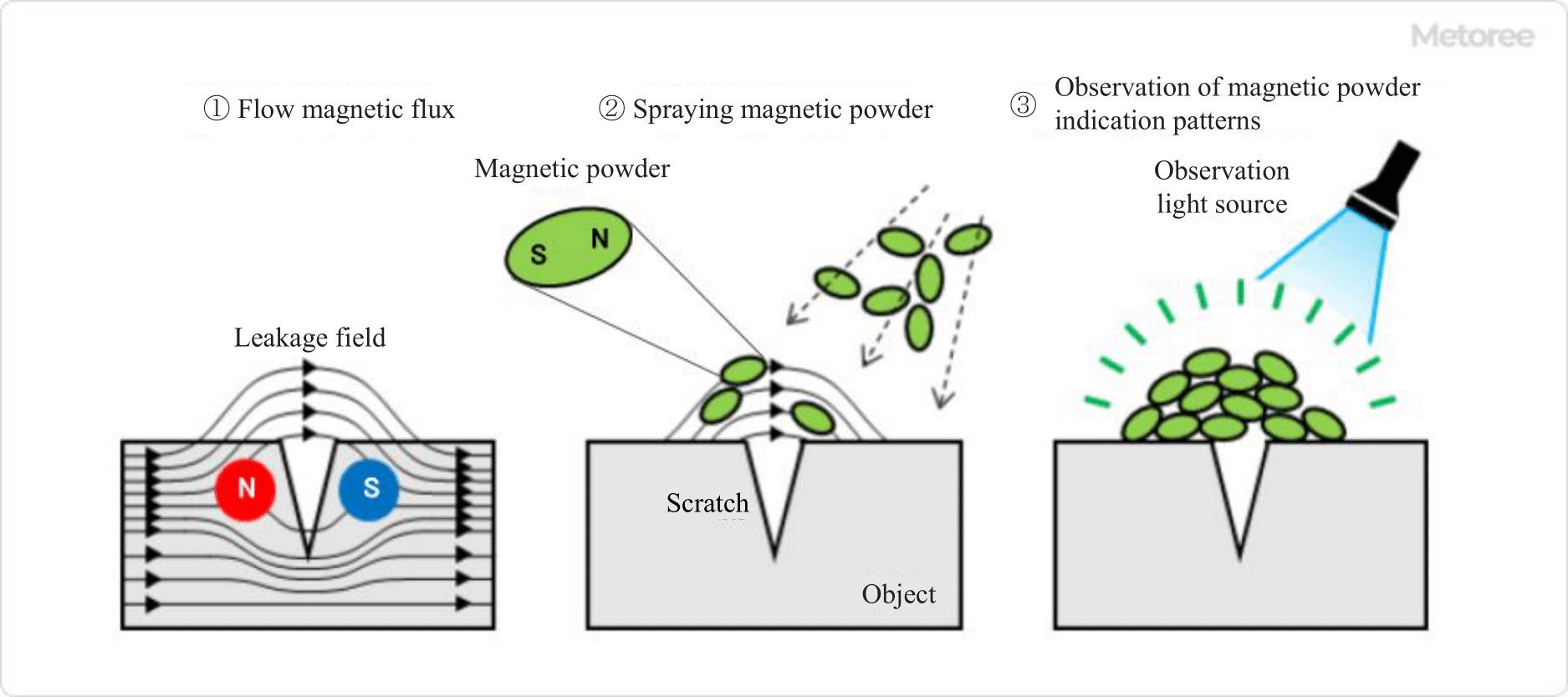
Figure 3. Principle of magnetic particle inspection testing
The magnetic particle flaw test is a test used to visually check for flaws near the surface of an object using a leaking magnetic field.
As the magnetic flux flows through the ferromagnetic object and increases, a portion of the flux leaks into the external space in the area where the flaw is located. When the magnetic powder is sprinkled in this leaking magnetic field, the magnetic powder adheres to the area around the flaw and a magnetic powder indication pattern appears. By observing this pattern, even minute scratches can be detected.
Magnetic powder testing is directional in detecting flaws and is classified as a method to magnetize the flaw detection point in the appropriate direction. It can also be classified into several methods, depending on the magnetic powder used and the light source for observation. These methods should be used appropriately depending on the shape of the object and the flaw to be detected.
4. Penetration Flaw Detection Test
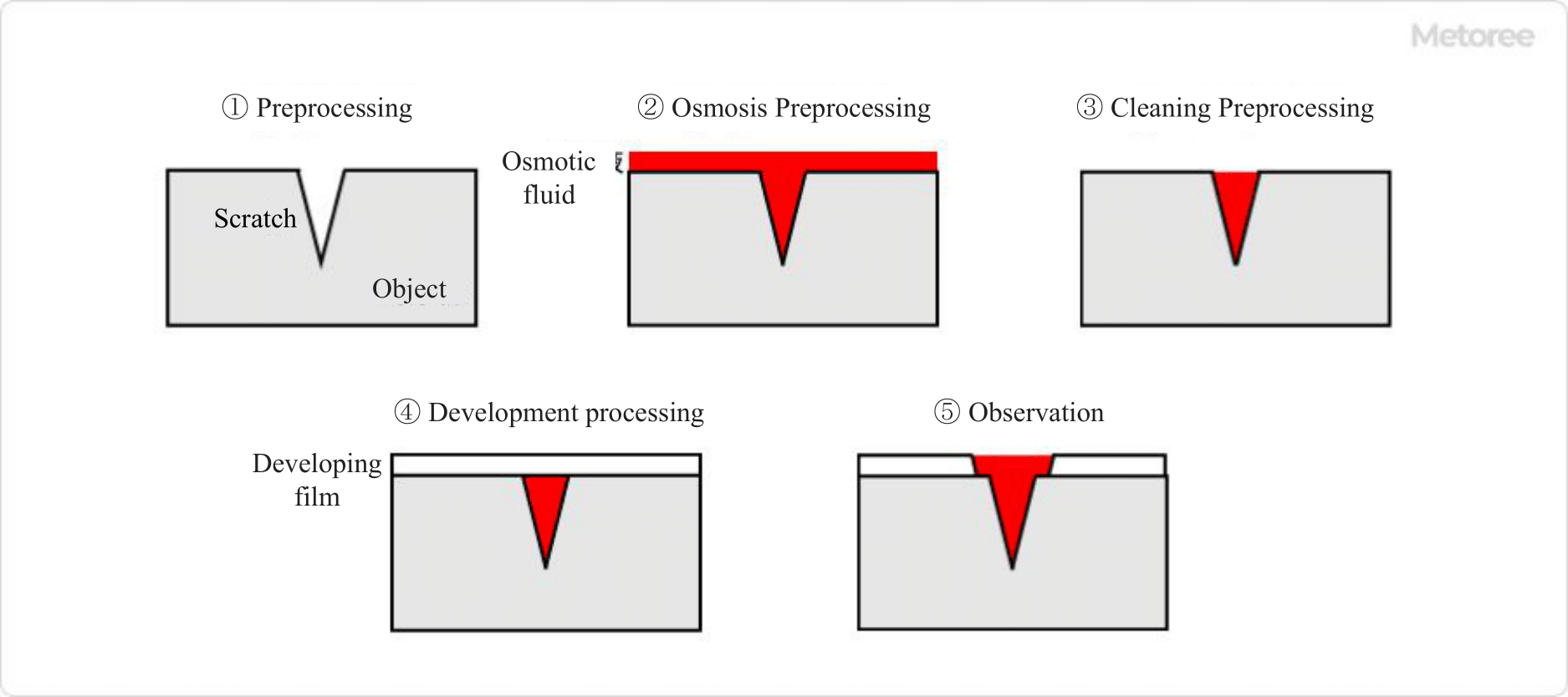
Figure 4. Principle of penetrant testing
Penetration testing is a test used to detect flaws on the surface of an object using a penetrant.
First, the surface of the object is cleaned as a pretreatment, and the inside of the flaw is opened and dried. Next, the penetrant is applied to the surface of the object, and the excess penetrant is removed. Finally, a developing film is applied to absorb the penetrant that has penetrated into the flaw, and the enlarged penetrant indication pattern is observed.
There are two types of observation methods, three types of penetration fluid removal methods, and four types of development methods in the penetration test, and the appropriate combination is selected according to the application.
5. Eddy Current Testing
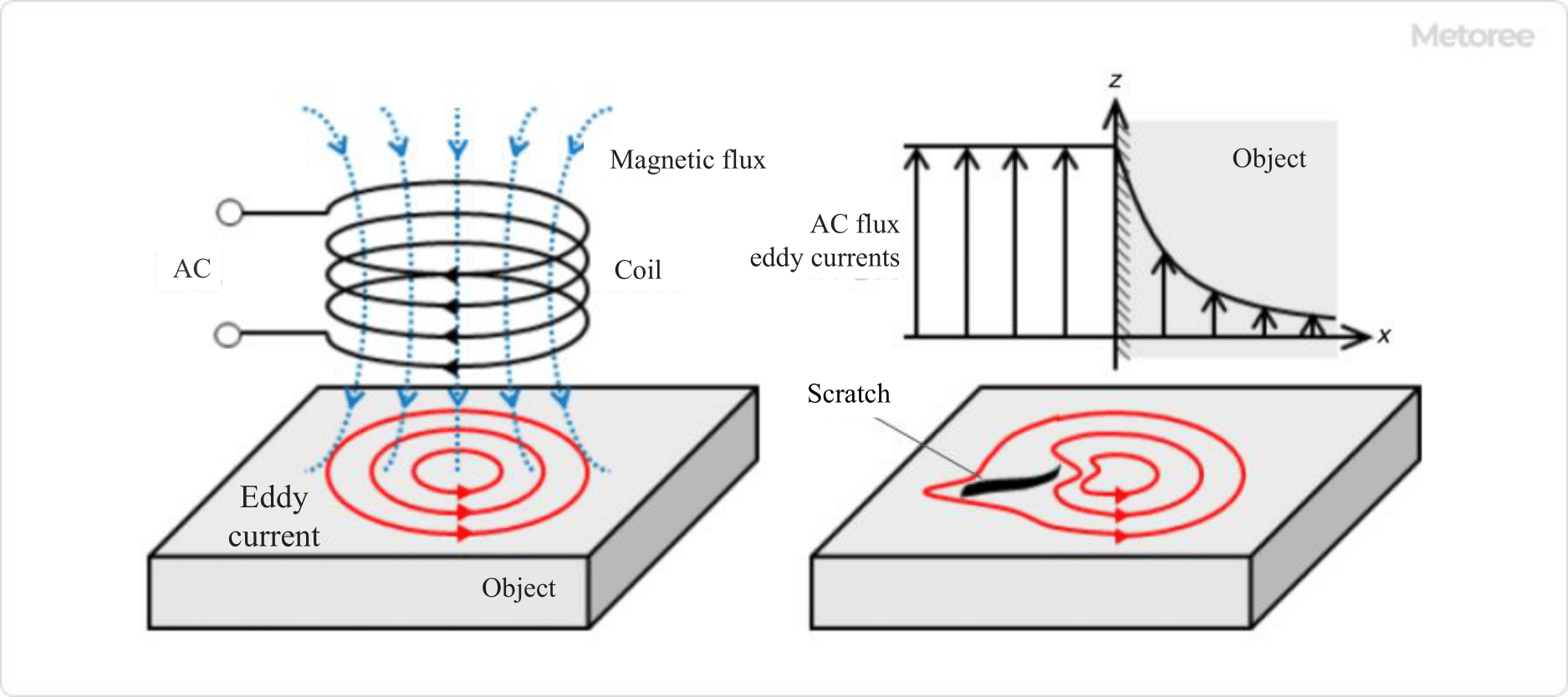
Figure 5. Principle of eddy current testing
The eddy current test induces eddy currents on the surface of a conductive object and detects the turbulence of the eddy currents to determine whether a flaw exists.
When a coil with alternating current is brought close to the object, eddy currents are generated near the surface of the object due to electromagnetic induction. If the surface of the object is scratched, the eddy currents are disturbed. The disturbance of the eddy currents causes a change in the magnetic flux inside the coil, resulting in a change in the electromotive force of the coil, and by detecting this change in electromotive force, the disturbance of the eddy currents, in other words, the presence or absence of a scratch, can be confirmed.
Since eddy currents are induced intensively only near the surface of an object and hardly ever inside the object, eddy currents are mainly used for flaw detection on the object’s surface. The phenomenon in which eddy currents decay rapidly inside an object is called the skin effect. However, the depth of the flaw can sometimes be estimated by using the properties of the eddy current phase.