What Is Taping Machinery?
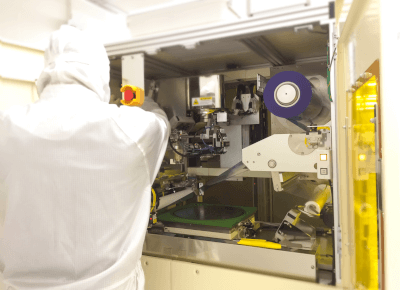
Taping machinery is a machine that fixes electronic components to tape with a heat seal and winds the tape onto a reel. It is mainly used in the process of surface mounting semiconductor chips on substrates. In this process, the electronic components embedded in the tape are sequentially removed to ensure a stable supply.
There are two types of taping machinery: the automatic type, which performs the entire process automatically, and the semi-automatic type, which seals the electronic components with a cover tape and winds them onto a reel. A rolling drum is required to wind the tape onto the reel, and a drum with high surface accuracy is necessary to reduce the runout of the drum.
Uses of Taping Machinery
In semiconductor production lines, taping machinery is used either by incorporating it into the surface mounting process or by off-line winding tape embedded with electronic components onto reels and supplying the reels to the mounting line. This allows for a stable, high-speed supply of electronic components.
Taping machinery is also used that combines the normal function of embedding electronic components and other parts into the tape with a cover tape with the function of inspecting and re-taping only good products or aligning and taping disparate parts.
Principle of Taping Machinery
Taping machinery is used to make continuous tapes as one of the packaging methods to enable the use of microscopic electronic components for surface mounting. A series of concave indentations, called pockets, are placed on a plastic or paper tape called an embossed carrier tape. Then, electronic components, etc., are placed one by one in each pocket covered with a cover tape, and sealed. Thermal tape is generally used for the cover tape, which is then wound onto a reel.
In addition to single-function taping machinery, there are also taping machines that are combined with the processes before and after the mounting process. For example, LEDs are fed from a parts feeder, inspected on a turntable, placed in a pocket on the carrier tape, and checked for posture with an image camera. It then seals them with cover tape and winds them on a reel. Many complex machines are also used. For example, small switches for mobile devices are fed through a parts feeder, and after characteristic inspection, good switches are taped and defective switches are ranked.