What Is a Synchronous Motor?
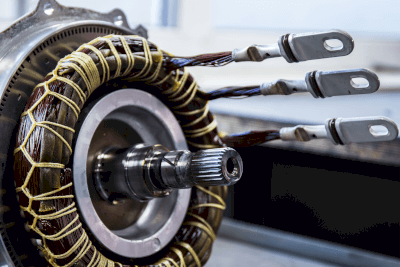
A synchronous motor is an electrical motor that operates in sync with the frequency of the supply power. These motors are known for their ability to maintain constant speed, regardless of power supply frequency or load fluctuations, due to the synchronization of rotor and stator magnetic fields.
For example, a 4-pole synchronous motor supplied with 50 Hz power will rotate at 1,500 RPM. They are preferred for their high efficiency and reduced mechanical losses, enhancing energy efficiency. However, they tend to be costlier than standard induction motors, and those using permanent magnets have higher maintenance costs.
Uses of Synchronous Motors
Synchronous motors are employed in various sectors for applications requiring constant speed and high torque:
1. Manufacturing Industry
They drive pumps, fans, and compressors in factories, offering energy efficiency and constant performance.
2. Processing Machines
Used in machining centers such as milling machines, synchronous motors provide the necessary stable speed for precise operations.
3. Electric Vehicles
These motors are increasingly used in electric vehicles for their efficiency and high torque, contributing to better vehicle performance.
Principle of Synchronous Motors
Synchronous motors consist of a stator, rotor, and enclosure, operating based on magnetic field interactions:
1. Stator
The stator, with its coils, creates a constant magnetic field when excited by three-phase power.
2. Rotor
The rotor rotates in response to the stator’s magnetic field, often containing a hero magnet and winding magnetized by DC.
3. Enclosure
Encased in a robust enclosure, often made of steel, these motors are designed for durability and efficient heat dissipation.
Types of Synchronous Motors
Synchronous motors come in various designs:
1. SPM (Surface Permanent Magnet) Motors
SPM motors have permanent magnets mounted on the rotor’s surface, providing high efficiency and torque density, making them ideal for electric vehicles and industrial applications.
2. IPM (Interior Permanent Magnet) Motors
IPM motors feature permanent magnets embedded within the rotor, offering stability and suitability for high-load conditions.
3. Electromagnet Type Synchronous Motors
These motors use electromagnetic coils in the rotor, allowing for a wide speed range and flexible magnetic characteristic control.