What Is a Turbine Pump?
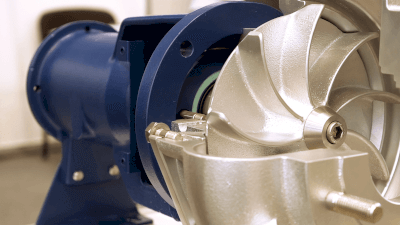
A turbine pump, also known as a diffuser pump, is a type of centrifugal pump equipped with guide vanes for handling high pressures. Commonly used in liquid transport, turbine pumps are efficient in increasing fluid pressure, suitable for high-head applications. They are known for their robustness, reliability, and long service life, but are less effective with viscous fluids or those containing solids.
Uses of Turbine Pumps
Turbine pumps have diverse industrial applications:
1. Power Plants
Used in pumped-storage power plants and thermal power plants, these pumps handle high heads for water pumping and boiler feedwater supply.
2. Water Distribution Systems
In urban and industrial water distribution, turbine pumps efficiently transport water to reservoirs and supply systems.
3. Fire Fighting Systems
For fire suppression, turbine pumps deliver water to elevated or distant locations, offering compact design and high-pressure capabilities.
4. Seawater Desalination Plants
Essential in desalination plants, they provide the necessary high pressure for seawater processing through membrane filters andevaporators.
Principle of Turbine Pumps
Turbine pumps operate by rotating an impeller, creating a pressure difference that propels the liquid centrifugally. Equipped with guide vanes, these pumps effectively convert kinetic energy into pressure energy, allowing high-pressure discharge.
How to Select a Turbine Pump
Key factors in turbine pump selection include flow rate, head, liquid characteristics, and efficiency:
1. Flow Rate and Head
Choose based on the required liquid transfer amount, elevation differences, pressure, and pipe length to the destination.
2. Liquid Characteristics
Consider the type and viscosity of the liquid, impacting material selection and pump design.
3. Efficiency
Opt for high-efficiency models to reduce energy costs and environmental impact, with larger capacities generally offering better efficiency.