What Is a Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) System?
Non-destructive testing (NDT) systems inspect an object’s interior or surface without destroying or damaging it.
The purpose of the inspection is to check for scratches, defects, cracks, voids (bubbles), etc., inside or on the surface of the inspected object. This inspection allows us to examine manufactured products without destroying them and to provide reliability and assurance.
Many types of non-destructive testing (NDT) systems are based on various principles. These systems can be used for multiple purposes. A certification test for NDT systems determines whether a person is proficient in using NDT systems and meets the inspection techniques for each of the six inspection categories as specified.
Uses of Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) Systems
The equipment is used to determine the presence or absence of melts and weld defects inside welds, cracks, voids, and other imperfections and defects inside materials, as well as scratches and cracks on the surface of materials that cannot be identified visually.
Non-destructive testing does not always require equipment (visual inspection, penetrant testing, etc.), but there are many situations where equipment is needed. For example, non-destructive inspection is used for aging steel frames inside concrete buildings, bridges, tunnels, and elevated bridges; in-process inspection of steel, copper, and aluminum pipes; aircraft fuselage inspection; and inspection of containers and pipes inside nuclear power plants. X-ray imaging, CT scans, and magnetic resonance imaging used for inspecting the human body are also forms of non-destructive testing (NDT) systems.
Principles of Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) Systems
Non-destructive testing involves a variety of methods based on several principles. This section describes the inspection methods and principles that require NDT systems.
1. Ultrasonic Testing Equipment

Figure 1. Principle of ultrasonic testing systems
Ultrasonic testing equipment emits high-voltage ultrasonic waves from an ultrasonic probe. It receives echoes when vibrations propagate or are transmitted through the surface or interior of an object and are reflected by internal defects or surface flaws, thereby identifying the location and size of internal defects or surface flaws.
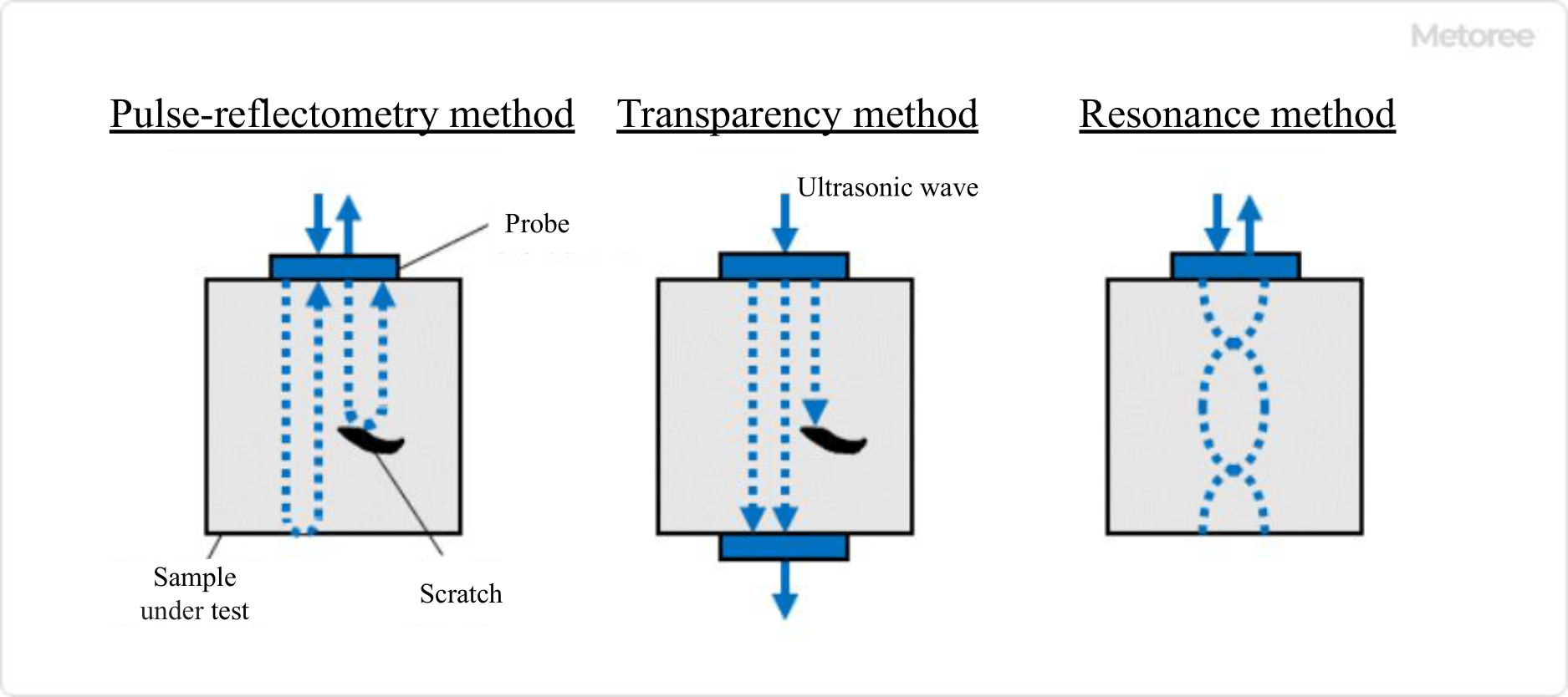
Figure 2. Types of ultrasonic testing systems
There are three types of ultrasonic inspection methods: the pulse reflection method, the transmission method, and the resonance method.
2. Magnetic Particle Inspection System
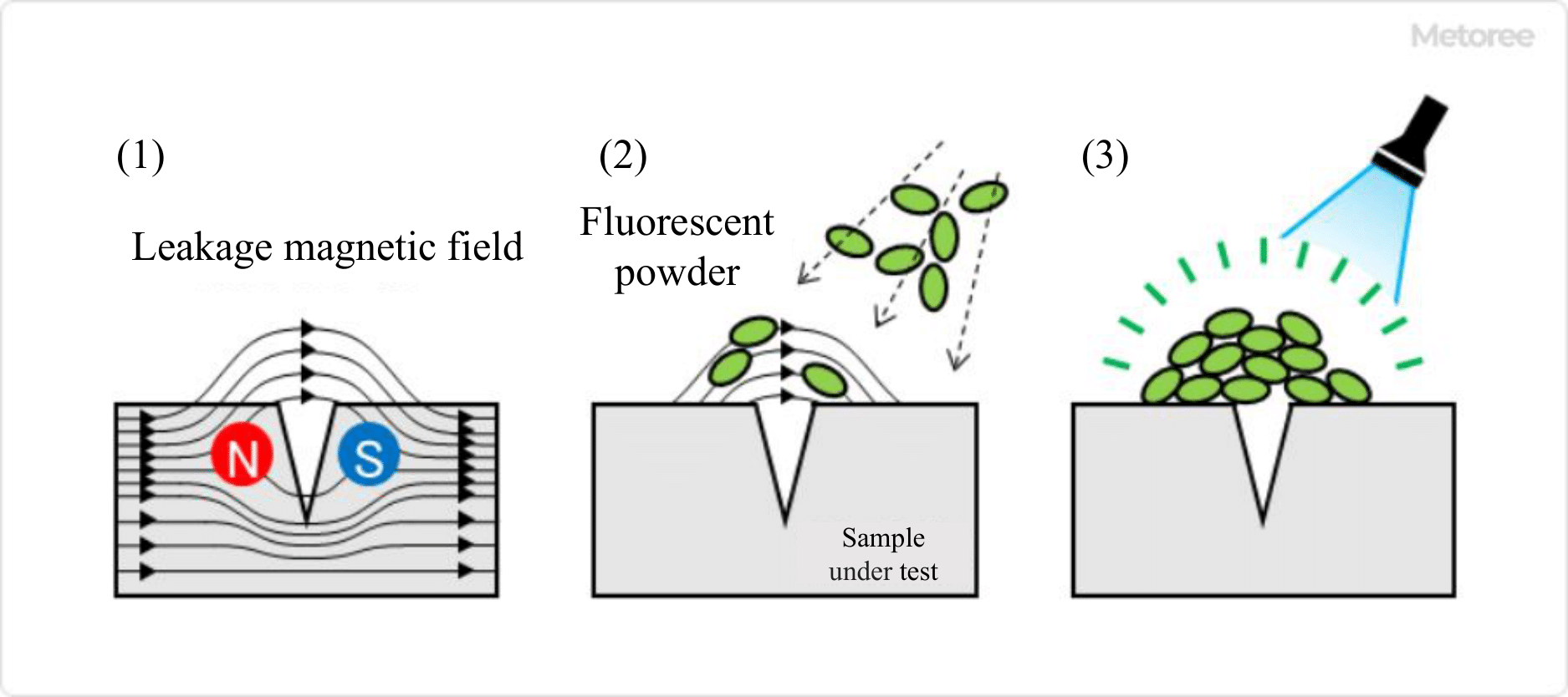
Figure 3. Principle of magnetic particle inspection systems
Magnetic particle inspection equipment is a method that utilizes the magnetic flux disorder generated in the surface flaw area.
When a strong magnetic field is applied to a magnetic object to be inspected, a disturbance of the magnetic flux is generated in the area where the surface flaw is located. When colored iron powder or fluorescent magnetic powder is sprinkled on the inspected object, the iron powder or fluorescent magnetic powder aligns with the shape of the magnetic flux leakage at the surface defects, making them visible as a pattern or a set of lights.
Typically, this method is mainly used for visual inspection without equipment, but automatic magnetic particle inspection equipment equipped with an image recognition device is also used.
3. Eddy Current Flaw Detector
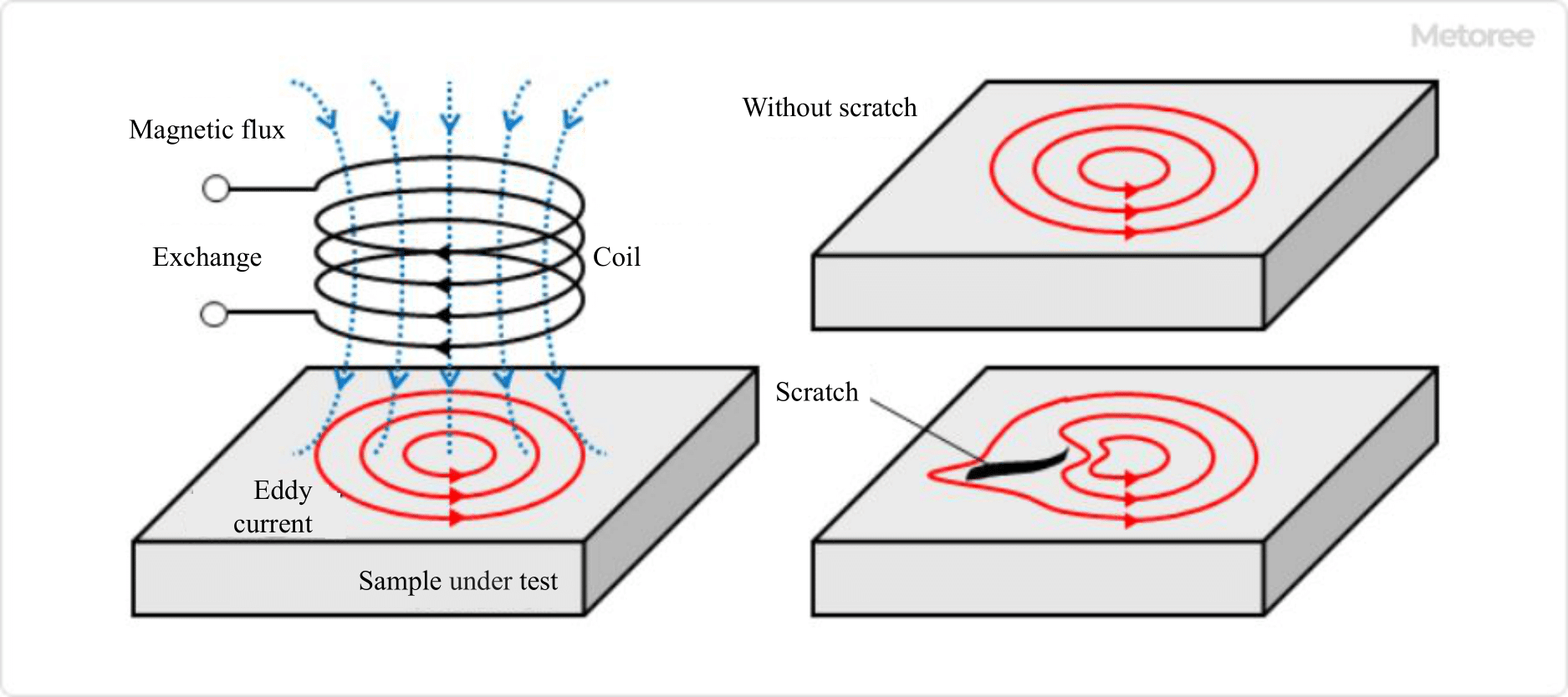
Figure 4. Principle of eddy current testing systems
In the eddy current flaw detector, a probe with an embedded coil of copper wire is brought into proximity to the surface of the object to be inspected by passing an alternating current through it, and the presence of flaws is determined by measuring the turbulence of the overcurrent generated on the object’s surface.
Since the accuracy and sensitivity of flaw detection require a coil shape that matches the object to be inspected, this type of equipment is often used when inspecting many objects of the same shape.
4. Radiation Transmission Testing Equipment

Figure 5. Principle of radiation transmission testing systems
X-rays penetrate the object to be inspected using high-energy X-rays, which have the highest penetrating performance among all types of radiation. A detector receives the transmitted radiation, and the signal is used for drawing or image recognition to detect defects inside the inspected object.
In the past, defects were determined visually by sensitizing a film with radiation, as in the X-ray inspection of the human body. Still, more and more equipment automatically identifies defects by image recognition.
Other Information on Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) Systems
1. Disadvantages of Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) Systems
Non-destructive testing (NDT) systems are very useful, but it is essential to understand that each measurement principle has disadvantages.
Ultrasonic Testing
Spherical flaws and cavities are difficult to detect because echoes are reflected in all directions. It is also not suitable for inspecting complex shapes or coarse-grained materials. This is because minute echoes generated randomly at each tissue’s boundaries spread randomly and are superimposed as noise on the echoes to be detected.
Magnetic Powder Inspection
Not applicable for the inspection of non-magnetic materials.
Eddy Current Inspection
It is difficult to inspect nonconductive materials and detect internal defects. It is also not suitable for objects with complex shapes.
Radiation Penetration Test
Special equipment is required to inspect thick objects because of the extremely high-energy radiation required. It is also not good at detecting surface defects and closely adhered cracks. Above all, radiation safety control requires careful attention.
2. Market Size of Non-destructive Testing (NDT) System
The market size of non-destructive testing in Japan is estimated to be 200~300 billion yen when adding the inspection service market to equipment sales.
Increasingly, manufacturers are not only conducting inspections in-house but are also outsourcing to inspection companies. As cities and industries become more sophisticated, safety, security, and quality control are becoming more important, and non-destructive testing is playing an increasingly important role. From the perspective of safety and consideration for the natural environment, the market for non-destructive testing is expected to grow further.
Construction Industry
In the construction and civil engineering industries, the market for non-destructive testing and diagnosis of concrete structures will continue to grow. This is due to the growing importance of extending the service life of concrete structures and the need to perform preventive maintenance before deterioration becomes pronounced.
Other Industries
Non-destructive testing is also expected to expand in the energy and heavy industry sectors, promising markets for future growth.