What Is an Air Release Valve?
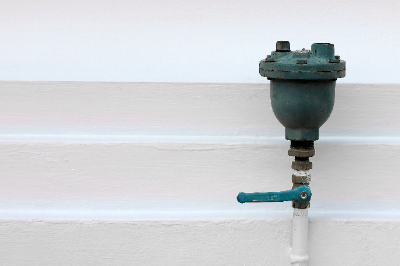
An air release valve, often referred to as an air vent, is a valve designed to discharge air that becomes trapped in liquid pipelines, such as those used for water or oil transport.
These valves are equipped to automatically release air from the system when a certain quantity of air becomes entrapped within the fluid. Air release valves operate seamlessly without requiring any manual intervention.
The primary function of air release valves is to eliminate trapped air in liquid pipelines. This not only enhances the efficiency of fluid transport but also prevents issues such as pipeline vibrations, abnormal noise in pipes and joints, and potential pump malfunctions caused by air entrapment.
Uses of Air Release Valves
Air release valves find application in various scenarios where it is necessary to remove air from the flow path of a fluid, such as air or oil. They are typically installed in locations where the mixing of air within the fluid path is expected or where such air mixing would be inconvenient.
Common instances where air entrapment is likely to occur include systems like hot water boilers and solar heating systems, where the air inside can expand when heated. Additionally, air often accumulates at the high points of pipes and storage tanks. Another critical application is at the inlet of pumps, where it’s essential to prevent air interference in the pump’s operation.
Principle of Air Release Valves
Air release valves consist of several components, including a valve disc, a valve seat, and a float connected to the disc. When the amount of air mixed in the fluid is minimal, the float remains in a high position, causing the valve disc to make contact with the valve seat, effectively sealing the outlet. As the volume of air in the fluid increases, the float descends along with the decreasing water level. Eventually, the valve disc disconnects from the valve seat, allowing the outlet to open. This permits the trapped air to be discharged under the pressure of the fluid. After a sufficient amount of air has been released, the float rises again, closing the valve. This automatic process ensures the efficient removal of air without the need for manual operation or external power sources.
Some air release valves are equipped with an intake function in addition to their air release capability, and these are known as intake and exhaust valves. In situations where negative pressure occurs within the fluid path, such as during temporary water cutoffs, intake, and exhaust valves rapidly introduce air to alleviate the negative pressure, preventing backflow within the pipeline.
It’s important to note that air release valves are designed for specific fluid types and minimum specific gravity requirements. They may not function as intended for fluids with specific gravities below the specified minimum. While most air release valves are compatible with water, if they are to be used with oil or other fluids, careful selection is necessary to ensure compatibility.