What Is an Air Nozzle?
An air nozzle is a nozzle attached to the end of a pneumatic pipe. It is used to inject or supply compressed air by specifying the direction, amount, and strength of the gas flow. Note that the shape of the jet from the nozzle depends on the application.
Since the flow rate and spray angle also change as the operating pressure changes, the standard operating pressure and appropriate pressure are defined for each nozzle. The flow rate and spray angle according to these pressures are presented as catalog values.
Applications of Air Nozzles
Air Nozzles are used to remove oil, water droplets, chips, etc. to reduce cleaning time and to heat, cool, or dry heated objects by supplying temperature-controlled air to the surface. In the industrial field, they are often incorporated into mass-production equipment or installed on conveyor belts for cleaning, heating, and cooling. They are also attached to air curtains and air showers installed at the entrances to clean rooms in testing laboratories, food factories, etc.
Principle of Air Nozzles
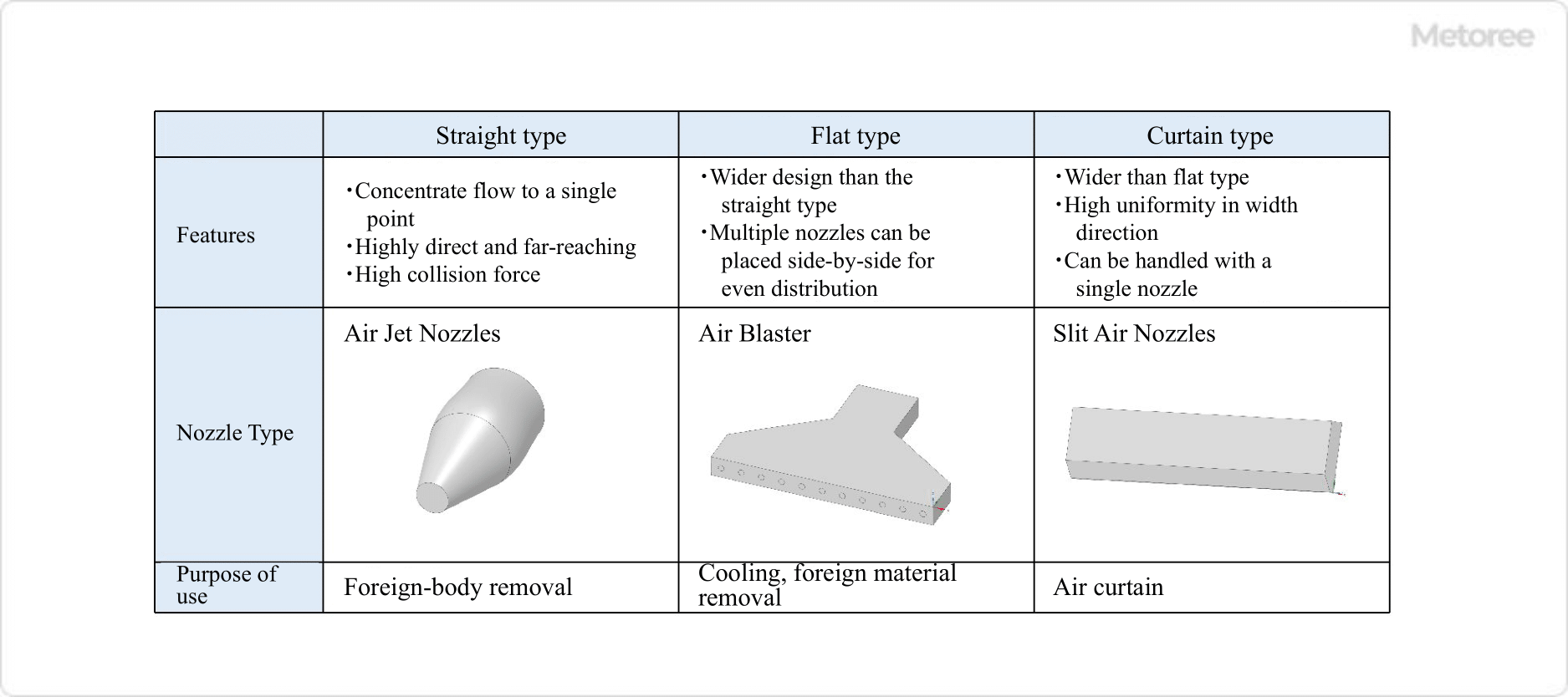
Figure 1. Types and characteristics of air nozzles
The principle of Air Nozzles is simple. By attaching it to the end of a compressed air pipe, it defines the direction in which the compressed air flows and prevents loss due to shear with the outside air, so that compressed air energy can be sprayed onto the object without wasting it.
Some Air Nozzles also take advantage of outside air being entrained by the compressed air being injected at high speed and the pressure drop caused by Bernoulli’s theorem. There are many other types, such as those that aim to draw in outside air and increase the flow rate.
How to Select an Air Nozzle
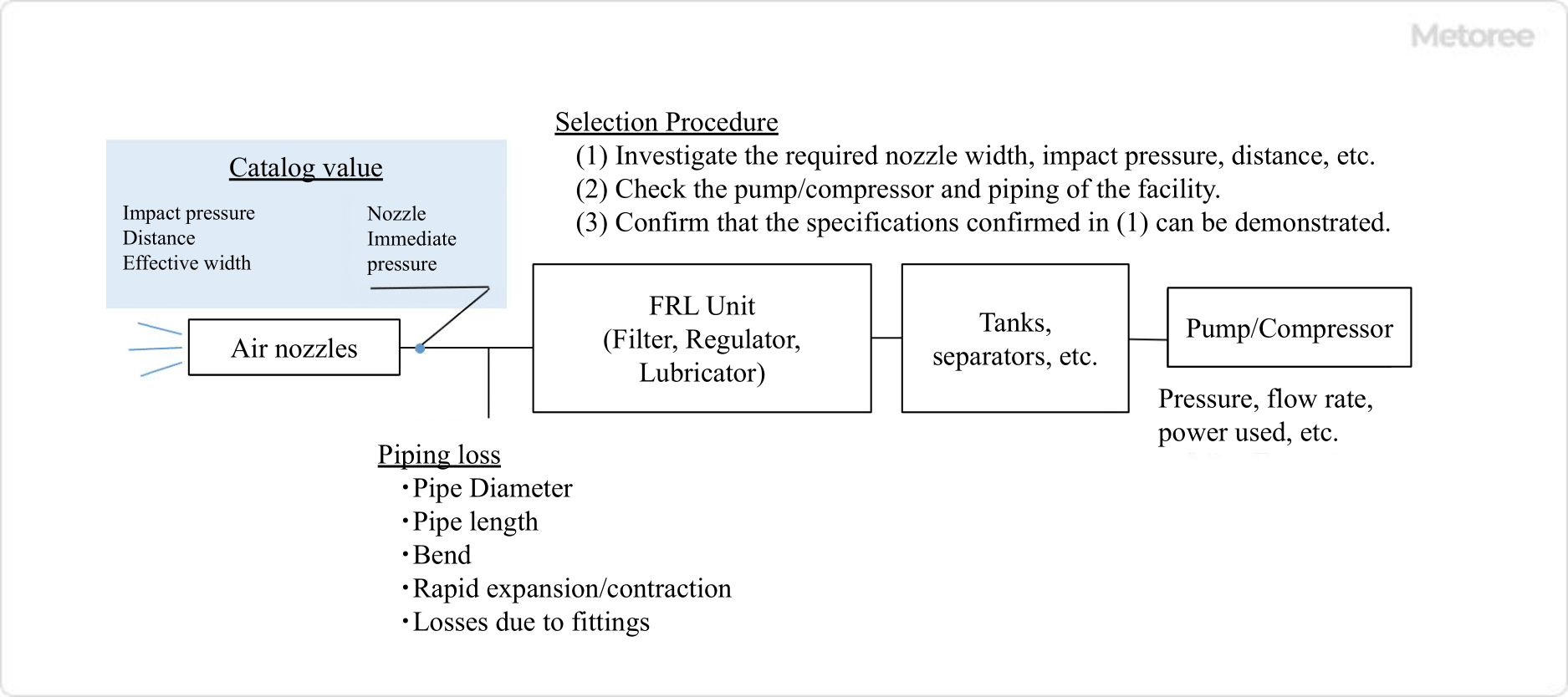
Figure 2. Selection of air nozzle
Air Nozzle selection can be divided into three main steps.
1. Checking Distance, Width, and Length
First, it is necessary to experiment to ascertain the distance, width, and length required for blowing air. Naturally, the farther, wider, and stronger the air is blown, the greater the required pressure and air volume.
These values are listed in the catalog specifications for Air Nozzles, so it is possible to select an Air Nozzle based on these values.
2. Confirmation of Piping and Pneumatic Circuit
Next, check the piping and pneumatic circuit where the Air Nozzle will be installed. Note that if the piping from the pump to the Air Nozzle is long, or if there are many bends or branches, or if the piping thickness varies, the pressure at the end of the piping will also vary.
The pressure to be used should be predicted according to the piping plan, and the pump, compressor, piping, and Air Nozzle should be capable of supplying the required flow rate. Even if Air Nozzles meet the specifications, they will not be able to demonstrate their performance unless the piping and pneumatic circuits are capable of fully demonstrating their performance.
3. Prediction of Pressure and Flow Rate
Pressure is defined based on the nozzle attachment point of the piping. Therefore, when measuring the working pressure, the pressure near the Air Nozzle should be used as a reference.
Flow rate is defined in JIS B 0100 as the volume or mass of fluid flowing in unit time, and the unit is l/min in the SI unit system. if the flow rates at two locations are Q1 and Q2 and their pressures are P1 and P2, the relationship is as follows.
Q1: Q2 = √P1: √P2
In other words, the higher the pressure, the higher the flow rate. Therefore, the required flow rate can be predicted in advance according to the intended use, and the number of air nozzles and tip shape can be selected based on that prediction. Note, however, that the above formula does not take into account the compressibility or viscosity of air.
Other Information on Air Nozzles
If You Want to Be More Particular in Selecting Air Nozzles
If you want to be even more particular in selecting an Air Nozzle, aim to minimize the flow rate used by the Air Nozzle. Compressed air is not inexpensive and has a large electrical cost. Using a structure that has as little loss as possible in the Air Nozzle can save on the flow rate used.
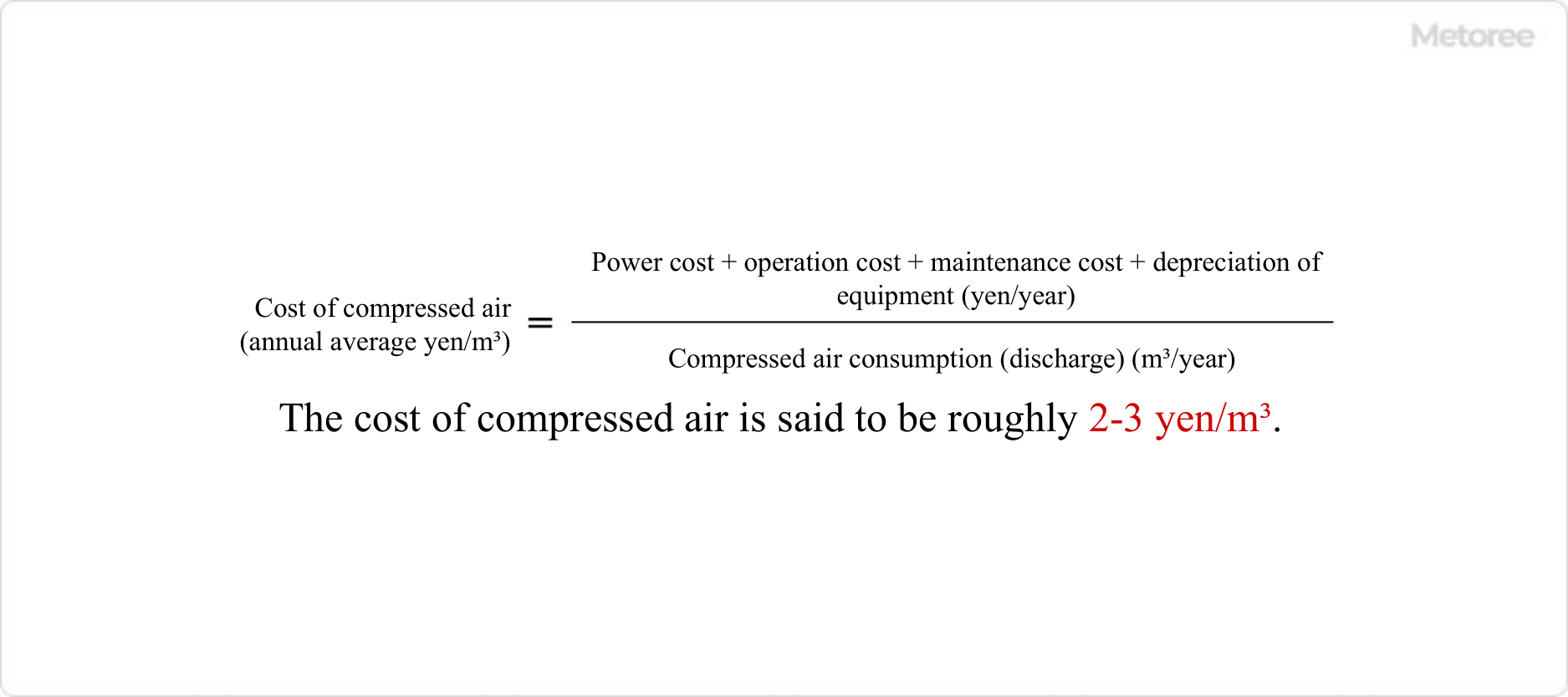
Figure 3. Cost of compressed air
In addition, noise is reduced by decreasing losses due to turbulence. By closely checking the performance of the Air Nozzles offered by various companies while satisfying the required striking force and flow rate, the best nozzle can be selected.