What Is a Solenoid Valve?
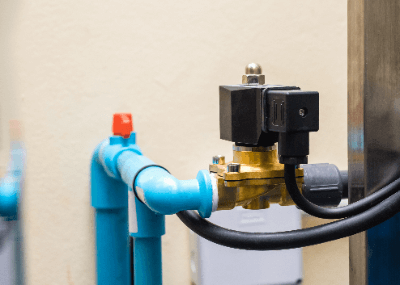 A solenoid valve is a valve that opens and closes by means of an electromagnetic coil.
A solenoid valve is a valve that opens and closes by means of an electromagnetic coil.
Solenoid valves are indispensable devices for everyday life as well as industrial applications.
Uses of Solenoid Valves
Solenoid valves can be used to control the flow of a wide range of fluids, including oil, water, steam, compressed air, and fuel.
1. Machine Oil
Solenoid valves are used to control the flow in hydraulic units. Machines that require strong pressure are often driven by hydraulic pressure, typical examples being automobiles and hydraulic presses. In automobiles, hydraulic pressure has been used for power steering, but in recent years, electric power steering has become the mainstream.
2. Water
Solenoid valves are used to control the flow of drinking water and industrial water. A typical example is water level control in water storage tanks, where solenoid valves are sometimes used in addition to ball taps. Solenoid valves are also used for automatic water sprinkling in agriculture.
3. Steam
Solenoid valves can distribute steam depending on the product. They are used for flow control in large clothes dryers that use steam. They may also be used to control steam tracing for freeze protection.
4. Compressed Air
Solenoid valves are primarily used to control pneumatic equipment. Compressed air is used to control pneumatic valves and pneumatic cylinders, which are controlled by solenoid valves. Compressed air may also be used for automatic drainage of compressed air.
5. Fuel
Atomization of gaseous or liquid fuel is controlled by a solenoid valve. Used for city gas (propane gas) flow control for water heaters, etc. Used in gas engines and light oil burners and may also be used to produce steam and electricity.
6. Solenoid Valve Principle
Solenoid bubbles are divided into a solenoid section and a valve section.
The main component of the solenoid section is an electromagnetic coil, which, when voltage is applied, excites the fixed iron core to move the movable iron core. The movable iron core is interlocked with the valve section and converted to the open/close motion of the valve. The valve section is divided into a valve disc and a valve seat, and fluid flow is controlled by the valve disc. The valve plug will move in conjunction with the movable iron core.
Types of Solenoid Valves
There are three types of solenoid valves:
1. 2-Way Solenoid Valve
A solenoid valve with two ports (inlet and outlet) which controls two operations: fluid stop or fluid flow.
2. 3-Way Solenoid Valve
This solenoid valve has three ports: supply, cylinder, and exhaust. The cylinder port is connected to either the supply or exhaust port. It is used to change the fluid flow or to operate a single-acting cylinder.
3. 4-Way Solenoid Valve
A 4-way solenoid valve is a solenoid valve with 4 or 5 ports. It has one supply port, two cylinders, and one or two exhaust ports. It is used, for example, to control double-acting cylinders. It is divided into a closed center, exhaust center, and pressure center according to the center position.
How to Select a Solenoid Valve
The following is an example of selection criteria for choosing a solenoid valve.
1. Target Fluid and Temperature
Solenoid valves are designed to handle a specific type of fluid. Typical fluids are listed in the “intended use” section, and selection is based on the target fluid. The temperature at which Solenoid Valve can be used is also determined by the product, so it should be selected according to the temperature of the target fluid.
2. Number of Ports
Select the number of ports for the solenoid valve. For fluid flow control, select 2 or 3 ports. For cylinder operation control, 3 ports or 4 or 5 ports are generally selected.
3. Operating Pressure and Connection Method
Select the pressure to be used. If a product with lower pressure resistance than the operating pressure is selected, it will burst, which is very dangerous. Therefore, it is best to select a product with higher pressure resistance than the working pressure.
Once the operating pressure is determined, select the connection method and bore size. Generally, flanged or screwed connections are used. For large bore sizes, most products have flange connections, while most products for small bore sizes have screw connections.
4. Power Supply Voltage
Select the voltage to be used for the power supply. Generally, voltages such as 5 VDC to 24 VDC or 100 VAC to 200 VAC are used and selected according to the control voltage. 100 VAC/200 VAC dual-use products also exist, in which case either one is selected according to the wiring method.