What Is a Memory Module?
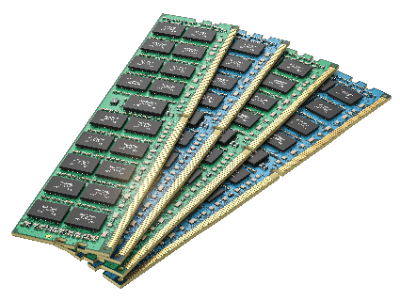 A Memory Module is a multiple number of memory chips mounted on a substrate.
A Memory Module is a multiple number of memory chips mounted on a substrate.
It is inserted into the memory slot on the motherboard. It is an electronic component used to temporarily store computer programs and processing contents.
Memory modules are mainly classified into DIMM and SO-DIMM according to size.
Uses of Memory Modules
Memory Modules are used with CPUs in desktop and notebook PCs, servers, and industrial equipment. Memory is configured in memory modules so that the memory capacity can be easily increased depending on the intended use.
For example, you can add a memory module to the same model of PC that you use for office document creation and for simple photo editing.
Principle of Memory Modules
Most memory modules consist of a substrate on which several DRAM memory chips are mounted. A DRAM consists of a memory cell, which consists of a capacitor that stores an electrical charge, a pair of field effect transistors (FETs) that act as switches, a memory cell array of memory cells, bit lines, word lines, etc.
A bit of logic information is stored with or without charge in the capacitor of the DRAM. Since the charge disappears over time, the charge must be refreshed several times per second. When a voltage is applied to the word line, the FET of the memory cell conducts between the capacitor and the bit line, and one bit of logic information “0” or “1” is read or written by the capacitor’s charge transfer.
The memory capacity of a memory modules is expressed in terms of memory capacity. It is determined by the number of DRAM memory chips mounted on the board, and the larger the number, the more operations and simultaneous operations can be performed. Memory standards and data transfer rates are collectively referred to as memory clock specifications, with a higher data transfer rate meaning faster data transfer.
Types of Memory Modules
There are several types of memory modules, depending on their shape. There are SIMMs, which became popular before DIMMs, DIMMs with more efficient signal output, and RIMMs developed independently by companies, but in general, high-speed, high-capacity DIMMs are widely used.
1. SIMM (Single Inline Memory Module)
SIMMs are a memory module designed to output the same signals on both sides of the board, and consists of 4 or 8 DRAM memory chips. They have fewer pins than DIMMs and are smaller in size.
2. DIMM (Dual Inline Memory Module)
DIMMs are a memory module designed to output different signals on the front and back sides of the board, and uses the SDRAM memory chip standard. DIMMs are further divided into two types according to size:
- DIMM: For desktop PCs.
- SO DIMMs: for notebook PCs and hardware such as printers and routers, about half the size of DIMMs.
3. RIMM (Rambus Inline Memory Module)
RIMMs are a special type of memory module called direct RDRAM developed by Rambus, Inc. It is made with a proprietary technology different from DIMMs and has a relatively high latency (CL) and high cost instead of high bandwidth.
Other Information on Memory Modules
1. Memory Chip Standards
There are standards for memory chips. The name of the standard is DDRn (n is a number indicating the generation). Currently, there are four generations available on the market: DDR2, DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5.
Memory modules must be composed of memory chips of the same standard. And since there is no interchangeability between generations, it is not possible to use DDR4 memory modules in place of the DDR3 memory modules that have been used up to now.
The data transfer rate of memory becomes faster with the latest generation, but the CPU and motherboard must support it.
2. Dual Channel
Dual channel is a method of doubling the data transfer rate by using two memory modules of the same standard and capacity in one set. The motherboard must support dual channel, but many models do.