What Is a Proximity Switch?
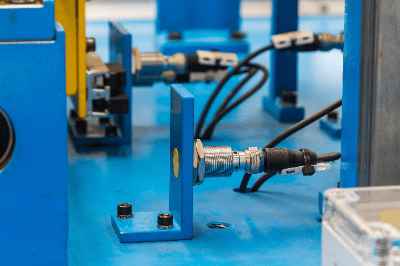
Proximity switches are used to determine the proximity of an object in various processes, such as turning things on and off.
They operate by detecting infrared rays, microwaves, magnetism, light, vibration, and pressure. A switch may be activated by mechanical contact or by a change in electrons or resistance emitted when a built-in proximity switch detects light or other stimuli.
Uses for Proximity Switches
Proximity switches are used in stores, residences, products, production plants, and laboratory equipment. When selecting proximity switches, it is necessary to consider size, detection accuracy, noise immunity, and durability.
The following are examples of proximity switches in use:
- Systems that use infrared rays to detect a person approaching an automatic door and activate the door.
- Systems in factories that detect passing objects and sound alarms.
- Detection systems for IC cards and magnetic stripe cards at entrance gates.
Principle of Proximity Switch
Proximity switches detect proximity by various methods, including direct contact, magnetism, light, and temperature change.
1. Contact
When sensing contact, pressure changes are measured by the amount of change in resistance of the proximity switch using a diaphragm or other sensing element. Other methods include operation by mechanical contact.
2. Magnetic
Proximity switches, Hall elements, and magnetoresistive elements are used to detect the amount of change in magnetism and drive the switch. Depending on the type of proximity switch used, some switches do not require a power supply, switches that can respond quickly, and switches with high sensitivity.
3. Light
Proximity switches are operated by detecting light using a sensing element called a photodiode. A photodiode is a sensing element that converts light into electricity.
4. Temperature
These proximity switches are operated by using a thermal resistive element, whose resistance changes with temperature, as a sensing element. A diaphragm or something similar is used to detect the amount of resistance changed by temperature.
Types of Proximity Switches
There are two broad categories of proximity switches: contact and non-contact.
Contact Proximity Switch
A contact proximity switch relies on physical force. Since the sensing body directly contacts the switch to the circuit, detection is highly accurate, but the physical contact can cause the proximity switch to malfunction and deteriorate over time.
Non-Contact Proximity Switch
Non-contact proximity switches use magnetism or light to detect proximity without direct contact and are characterized by a longer service life than contact-type proximity switches.
Proximity switches are classified as Form A, Form B, or Form C depending on the type of internal circuit.
- Form A
The Form A contact type has no circuit connected when the switch is in the off state, and the circuit is connected when the proximity switch reacts.
- Form B
The Form B contact type is the opposite of Form A: the circuit is connected in the switched-off state, and the circuit is disconnected when the proximity switch reacts.
- Form C
Note that non-contact proximity switches are also suitable for use outside of machines and around water because of their low risk of failure and excellent durability, even with a larger sensing body. Additionally, using a waterproof proximity switch can help prevent faulty signals caused by water intrusion from the main body of the proximity switch and the harness connector.
Waterproofing of Proximity Switches
Proximity switches may need to be waterproof depending on the environment in which they are used. Examples include electrical appliances in the vicinity of water, parts of in-vehicle equipment that may come into contact with water, and machines used outside.
1. Waterproof Detection of Electrical Appliances
Waterproof proximity switches used for driving electrical appliances are mainly contact-type, compact proximity switches.
However, it is not enough to simply select a waterproof proximity switch. Attention must also be paid to the water resistance of the harness connector.
2. Waterproof Detection for Outdoor Use
Equipment used outside may have a large sensing element, and small proximity switches have a high risk of failure. Therefore, depending on the situation, a non-contact, waterproof proximity switch should be selected.