What Is a Ferrite Core?
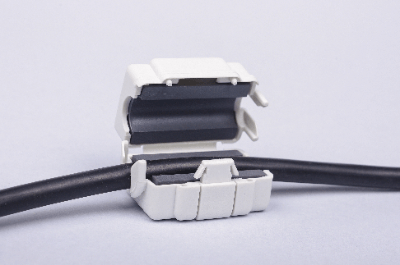 A ferrite core is a ceramic magnetic material called ferrite, which is mainly composed of iron, and is processed according to the application.
A ferrite core is a ceramic magnetic material called ferrite, which is mainly composed of iron, and is processed according to the application.
The use of ferrite as a magnetic core can block high-frequency currents, and is therefore effective as a noise suppressor. Ferrites are classified into different systems according to their composition, but Ni-Zn ferrites are mainly used for noise reduction.
The reasons for this are that the Ni-Zn type does not require insulation processing and has excellent high-frequency characteristics. Noise can be eliminated by passing a cable through a ring-shaped ferrite core.
Uses of Ferrite Cores
Ferrite cores are used for noise reduction in electronic equipment. The noise-reducing effect of ferrite cores is not limited to noise entering the cable from the outside, but can also eliminate noise generated by the cable itself.
Ferrite cores are simple, inexpensive noise suppression components and are characterized by their easy handling. Therefore, noise suppression can be implemented without the need for design changes to the board or circuitry. Therefore, they can be used as an experimental method before finalizing the final specifications or as an emergency noise suppression measure.
Principle of Ferrite Cores
There are two main principles by which ferrite cores can eliminate noise: First, they act as a filter to cut high-frequency frequencies and eliminate noise caused by high-frequency currents.
When electricity flows through the hole in the ferrite core, the cable becomes an inductor, and the impedance of the cable changes according to the magnetization of the ferrite core. At this time, the impedance becomes higher in the high-frequency band, enabling attenuation of high-frequency currents that are noise components.
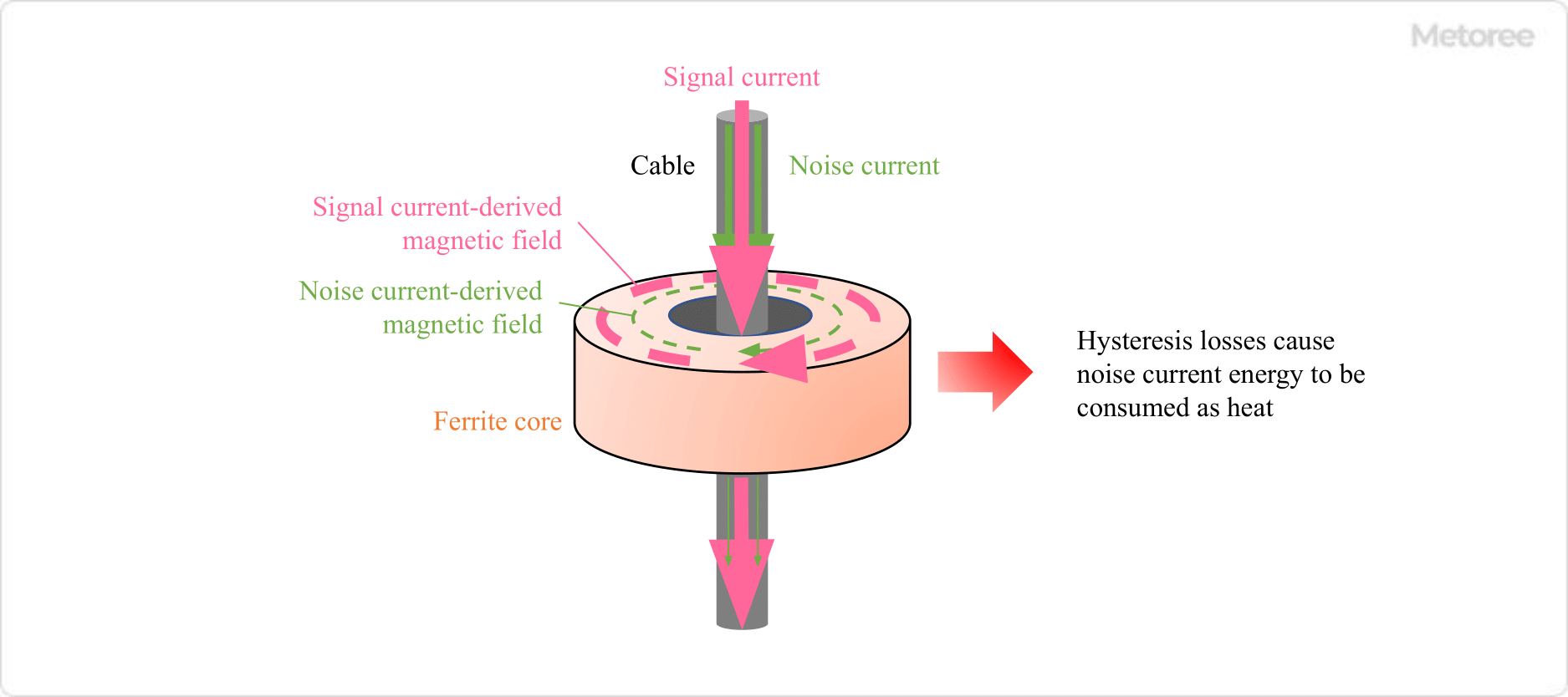
Figure 1. Ferrite Core Noise Removal
Second, hysteresis loss allows noise current to be dissipated as thermal energy. When an inductor is configured by a ferrite core and an alternating current flows through it, the generated magnetic field fluctuates in direction and magnitude with time in a certain period.
The magnetization of the ferrite core making one cycle is called a hysteresis loop, and the loss of energy that occurs during this process is called hysteresis loss.
How to Select a Ferrite Core
When selecting a ferrite core, there are some things to keep in mind.
1. When Cutting Noise in the High-Frequency Band Above 150 Mhz as a Rough Guide
- The inner diameter of the ferrite core should match the cable, and the outer diameter should be as large as possible and the length should be as long as possible.
- Use the cable without turning
- Obtain good impedance characteristics due to the shape factor of the ferrite core
2. When Used to Cut Noise in the Sea Frequency Range Lower Than 150MHZ or as a Noise Suppressor for Cables in Equipment
- Select a type of ferrite core with a larger inner diameter and shorter length
- Use cable with turns
- Obtain good impedance characteristics depending on the number of turns
Other Information on Ferrite Cores
1. Ferrite Core Material
A soft magnetic material called soft ferrite is used for ferrite cores. Oxides of transition metals such as nickel, iron, zinc, and copper are the main raw materials. Since the permeability of soft ferrite can be changed by its composition, the impedance can be tuned by the ratio of the main raw materials.
Impedance has two components, namely reactance and resistance. The material composition of a ferrite core for noise rejection contains a large amount of resistance component. Therefore, noise rejection is more effective in dissipating the energy of noise current as heat due to hysteresis loss than in filtering to cut high frequencies.
2. Noise Rejection Performance of Ferrite Cores
The noise rejection performance of a ferrite core is evaluated by its impedance. Impedance is determined by material properties, shape factor, and number of turns.
The material properties are determined by the composition of the soft ferrite. The shape factor is the cross-sectional area of the ferrite core divided by the average magnetic path length. Therefore, a ferrite core with a large cross-sectional area and a small inner diameter performs better. For better noise rejection, wrapping the cable around the ferrite core multiple times is also effective.
However, when a conductor is wound more than once, the beginning and end of the winding are close to each other, creating stray capacitance between them. Since this stray capacitance reduces the effectiveness of countermeasures against high-frequency components, it is necessary to wind the cable while keeping an eye on the frequency band for which noise reduction is desired.