What Is Heat Shrinkable Tubing?
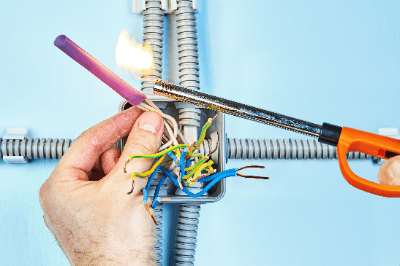 Heat shrinkable tubing is tubing that has been processed to shrink when heat is applied.
Heat shrinkable tubing is tubing that has been processed to shrink when heat is applied.
It is a molded resin tube that has undergone radiation treatment and is widely used mainly to protect and insulate electric wires. To use, simply pass the wires through the heat shrinkable tubing and apply heat with a heat gun or similar device. The process is simple and can be used in any work environment.
Uses of Heat Shrinkable Tubing
Heat shrinkable tubing is a material that shrinks to fit the covered wires, and is mainly used to protect, insulate, waterproof, and prevent corrosion of wires and parts.
Specific applications are as follows:
- Internal wiring used in home appliances
- Internal wiring used in electronic products
- Power feed wiring for industrial equipment
- Wiring harnesses for automobiles
- Surgical equipment for laparoscopic surgery
Principle of Heat Shrinkable Tubing
Heat shrinkable tubing is made of high molecular polymers such as polyethylene and various elastomers. These materials have the property of shrinking under heat while retaining their flexibility.
The above polymer polymers are irradiated with electron beams to induce a cross-linking reaction during the tubing manufacturing stage. When the tubing after the cross-linking reaction is heated and stretched, it solidifies while remaining elongated, and when heated again, the tubing shrinks and returns to the size it was before being stretched. This is the principle of Heat Shrinkable Tubing.
Types of Heat Shrinkable Tubing
Heat shrinkable tubing can be classified into single-layer Heat Shrinkable Tubing and double-layer Heat Shrinkable Tubing, depending on the difference in structure.
When heat is applied, the tubing shrinks in the diameter direction, and the shrinkage ratio is approximately 2:1 to 3:1. Materials include rubber-based, PE-based, fluoroplastic-based, and silicone resin-based. There are many types of Heat Shrinkable Tubing, so proper selection is essential.
1. Single Layer Heat Shrinkable Tubing
One-layer heat shrinkable tubing is a common type of tubing and is divided into “thin-wall,” “medium-wall,” and “thick-wall” types based on the thickness of the tubing. The purpose of single-layer Heat Shrinkable Tubing is to provide insulation or partial protective guarding. Each color of tubing is sold in different colors and can be used for identification.
2. Two-Layer Heat Shrinkable Tubing
Two-layer heat shrinkable tubing consists of two layers, an inner layer and an outer layer. It is used for electrical insulation and mechanical protection. Due to the thicker layers, it may be used to protect against humidity and corrosive environments. Like single-layer heat shrinkable tubing, it is sold in various colors for identification purposes.
Other Information on Heat Shrinkable Tubing
1. How to Use Heat Shrinkable Tubing
Heat shrinkable tubing is selected so that the inner diameter after shrinking is thinner than the object. The length will also shrink slightly, so select and cut a slightly longer length. Shrinkage rates also vary depending on the material, so check the heating conditions before working with it. When cutting, it is important to align the cut surface neatly, as the cut surface may break.
Heat shrinkable tubing generally shrinks from about 120℃, so a heat gun should be used as the heating device. Low-temperature types shrink from about 80°C, so they can be worked with a hair dryer. A soldering iron can also be used in place of a soldering iron for small diameters and small quantities. In this case, care should be taken to prevent the tip of the iron from touching the surrounding area.
2. Cautions for Heat Shrinkable Tubing
Heat shrinkable tubing requires the use of a heating apparatus. To use it safely, it is essential to be careful of burns and to use the apparatus properly. In particular, when using an open flame such as a gas burner, the tube will melt due to overheating, so the flame must be turned off at the appropriate time.
In addition, when wrapping items with good heat conductivity, such as metals, it is difficult to shrink them because they easily lose heat during heating, and this can be handled by applying heat for a longer period of time than usual. Never use it for electrolytic capacitors, secondary batteries, etc. This is because they may burst due to heating. Therefore, working near them should also be avoided as much as possible.