What Is a Heat Sink?
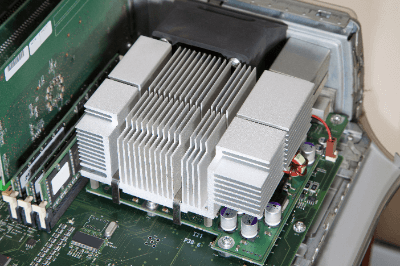
A heat sink is a component attached to a device for the purpose of cooling. It is mainly used in electronic equipment to prevent excessive temperature rise.
It is very simple in principle, structure, and does not require physical operation. Therefore, it has the advantage that it is not prone to breakdowns.
Uses of Heat Sinks
Heat sinks are used in combination with electronic components that generate heat. A typical example is CPU cooling in personal computers.
Electronic components, such as CPUs, will use semiconductors and conductors inside their housings. These parts constantly generate heat during operation, and if left unchecked, the temperature inside electronic products rises, melting the surrounding varnish or burning out semiconductor parts. Heat sinks dissipate the heat from these heat-generating parts and help prevent failures due to overheating.
In a normal CPU, a heat sink is installed and then cooled using a fan. These are called CPU coolers, as a set.
Principle of Heat Sink
A heat sink is made up of metal parts arranged in the shape of a comb. The comb is called a fin, and the comb shape increases the surface area for enhanced heat dissipation performance. The principle of heat sink is the second law of thermodynamics. This is an extremely simple principle that heat always flows from high-temperature materials to low-temperature materials.
Therefore, if a heat sink is operated alone, it cannot lower the temperature below the atmospheric temperature. Hence, it is used for small electronic components and equipment with a high-heat resistance requirement. Cooling efficiency can be improved by using a fan or pump in conjunction with the heat sink to provide forced circulation.
If the heat generation is high, using a device with even higher cooling efficiency, such as a Peltier element or heat pump is advised.
Other Information on Heat Sinks
1. Performance of Heat Sink
Heat sink performance is mainly measured by “thermal resistance.” Thermal resistance is a value that indicates the resistance to heat transfer, meaning “how many degrees the temperature rises when one watt of heat is applied to an object. The unit of thermal resistance is “K/W” or “°C/W”.
Thermal resistance depends on the surface area of the Heat Sink and the material used. The lower the value, the better the performance will be. Heat sinks are designed in a comb or bellows shape because a larger surface area reduces thermal resistance most efficiently.
Another value that indicates the performance of a heat sink is the pressure drop. Pressure drop is a measure of the resistance of air or cooling water passing through a heat sink; the lower the value, The better the performance will be.
2. Heat Sink Material
Heat sinks are made of metals with high thermal conductivity. Aluminum alloys, copper materials such as brass and bronze, and metals such as silver and iron are used. Copper is the best thermal conductor, but it is heavy and expensive. Therefore, it is rarely used as a material for heat sinks.
Aluminum, on the other hand, is lightweight and Low-cost. Aluminum also has high self-dissipation properties, making it more suitable than copper in some environments where airflow is low.
Aluminum is the primary material used for heat sinks. However, other materials are considered when aluminum does not meet the required specifications.