What Is a Chip Resistor?
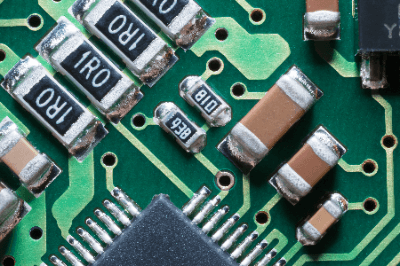 Chip resistors, also called surface mount resistors, are rectangular resistors with a metal film as a resistive element on a small ceramic substrate.
Chip resistors, also called surface mount resistors, are rectangular resistors with a metal film as a resistive element on a small ceramic substrate.
In general, chip components refer to all small surface-mount passive components. Chip components are made of capacitors, resistors, fuses, coils, transformers, etc., all of which are characterized by having fixed electrodes.
In older resistors, flexible lead wires were used as electrodes to be inserted into holes in printed circuit boards, but chip resistors have fixed electrodes that are soldered directly to the surface of the printed circuit board.
Uses of Chip Resistors
Resistors, along with capacitors and coils, are the most basic passive elements in electronic circuits. Chip resistors are used in all kinds of electronic devices, playing various roles, such as limiting current, detecting voltage, and setting bias voltage.
In recent years, demand for chip resistors has been growing rapidly, especially in the field of mobile communications, particularly for cellular phones and smartphones. Chip resistors are sold in a variety of products to suit different purposes and applications, so it is necessary to determine the performance and characteristics of the resistor according to the required performance.
Principle of Chip Resistor
Chip resistors are classified into the following three types depending on the resistive element to be formed on the ceramic substrate.
1. Thick-Film Chip Resistor
Thick-film chip resistors employ metal glaze as a resistive element and form a film several μm thick. They are called thick-film chip resistors because they are thicker than the thin-film chip resistors described below.
Resistance can be adjusted by trimming a part of the resistive element after the metal-glaze film is formed. Since the metal-glaze film can be formed on a ceramic substrate at once using the screen printing method, these resistors are relatively inexpensive and versatile. Various constants and sizes are available.
2. Thin-Film Chip Resistor
The structure is almost the same as that of thick-film chip resistors, but the resistive element is a metal alloy, and the resistive element is formed on a ceramic substrate using the vacuum evaporation method. The thickness of this resistive element is extremely thin, about several nm. That is why they are called thin-film chip resistors.
Thin-film chip resistors have a small error (±1% or less) with respect to the nominal resistance value and a small temperature coefficient, so they are employed when accurate resistance values are required. Another feature of thin-film chip resistors is that they show little change in resistance value over time.
3. Metal Plate Chip Resistors
Metal plate chip resistors use a metal plate as a resistive element, enabling the production of resistors with small resistance values. Resistors of 1 mΩ or less are also available for current detection. Also, because of its excellent heat dissipation and large thermal capacity, it can carry a relatively large current.
On the other hand, its disadvantage is that it is difficult to produce high resistance values and is expensive. The ceramic substrate on which the resistor is based is mainly made of alumina, an oxide-based ceramic, and has excellent strength, thermal conductivity, and insulation properties.
Types of Chip Resistors
The following high-performance products are available for chip resistor according to the market needs.
1. Sulfur-Resistant Chip Resistor
Silver is used for the internal electrode of general chip resistors, and if left in an atmosphere containing sulfur, the silver reacts with sulfur to form silver sulfide, which is an insulator, and this growth is likely to cause poor conductivity of the internal electrode.
Therefore, resistors with sulfurization countermeasures should be used in environments where sulfur components are present in the atmosphere, such as near active volcanoes or in the vicinity of materials containing sulfur.
Specifically, a resistor has been developed in which the internal electrode is changed to a material that does not react with sulfur, instead of silver.
2. Surge/Pulse Resistant Chip Resistors
When surge voltages or pulses are frequently applied to resistors, such as in switching circuits or circuits prone to electrostatic discharge, it is necessary to use resistors that are not easily damaged even when large amounts of instantaneous power are applied. For this reason, anti-surge and anti-pulse chip resistors are also available.
3. Chip Resistors With High Measurement Accuracy
Precision equipment, such as measuring and control instruments, requires high-precision resistors with small resistance error (resistance tolerance) and resistance change with temperature (temperature coefficient of resistance).
4. Chip Resistors for Current Detection
Chip resistors for current sensing applications have a small resistance value. Metal plate chip resistors are mainly used for current sensing to detect overcurrent and remaining battery charge.
There is also a growing need for lower resistance to reduce power consumption in circuits and for high-precision resistors that ensure excellent resistance temperature coefficient even in harsh temperature environments.
5. Chip Resistors With Long Electrodes
Chip resistors originally had electrodes laid out on the short side. Since the resistive element itself has low heat dissipation, heat dissipation through the electrodes greatly affects the rated power of Chip Resistor.
Therefore, several resistors makers have introduced products with electrodes on the long side of the chip resistor to increase the electrode area and improve heat dissipation. These chip resistors are called “long side electrode type” or “long side chip resistor.”
Conventional chip resistors are sometimes called “short side electrode type” to distinguish them.
Other Information on Chip Resistors
Size of Chip Resistors
Typical sizes of chip resistors are as follows:
- 6.mm x 3.mm
- 5.0mm x 2.5mm
- 4.5mm x 3.2mm
- 3.2mm x 2.5mm
- 3.2mm x 1.6mm
- 2.0mm×1.25mm
- 1.6 mm x 0.8 mm
- 1.0 mm x 0.5 mm
- 0.6 mm x 0.3 mm
- 0.4 mm x 0.2 mm
- 0.3 mm x 0.15 mm
However, the rated voltage and power rating are restricted by size, and the larger the size, the more advantageous, so the size cannot be freely determined. On the other hand, small resistors can be selected for circuits that operate at relatively low voltages, but the mounting equipment (mounter, etc.) that can handle them may be restricted.
The size with the largest shipment volume for chip resistors is “1005 (1.0mm x 0.5mm),” while the previous mainstay “1608 (1.6mm x 0.8mm)” size is decreasing in volume. On the other hand, “0603: 0.6mm x 0.3mm” size, which will be the mainstream in the future, is increasing in volume.
In addition, “03015: 0.3mm x 0.15mm” size was commercialized as a small chip resistor in October 2011, and “0201: 0.2mm x 0.125mm” size is under development by resistor manufacturers.