What Is Anisole?
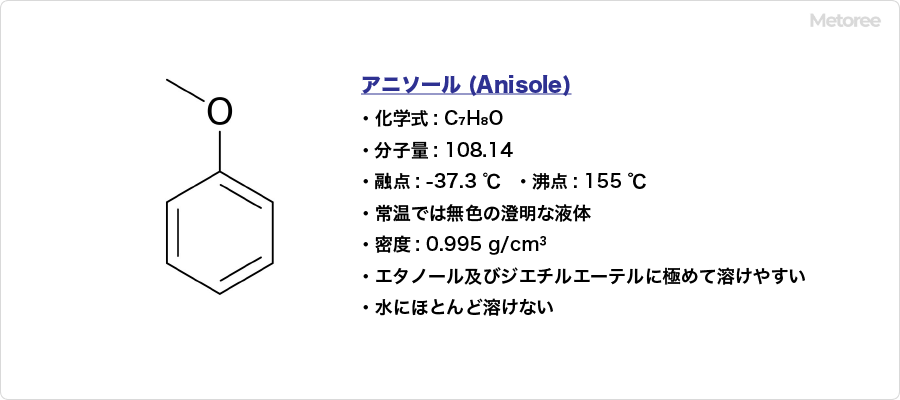 Anisole is an organic compound with C7H8O and CH3OC6H5.
Anisole is an organic compound with C7H8O and CH3OC6H5.
It is known in the IUPAC nomenclature as methoxybenzene (although “anisole” is also an acceptable common name). It has other names such as methylphenyl ether. The CAS registration number is 100-66-3.
It has a molecular weight of 108.14, a melting point of -35 °F (-37.3 °C), and a boiling point of 311 °F (155 °C). It is a clear, colorless liquid at room temperature. It has a density of 0.995 g/mL and is extremely soluble in ethanol and diethyl ether and is almost insoluble in water.
Uses of Anisole
Anisole is one of the aromatic ethers, and as an ether solvent, it is widely used as a solvent and diluent for various paints, including lacquers.
Anisole is also used as a flavoring agent. It is said to have a sweet aroma that goes well with sweets, such as aniseed.
Since it is also a type of insect pheromone, it is also used as a pharmaceutical ingredient in anthelmintics, which kills or expels parasites found in the body.
Properties of Anisole
In the structure of anisole, the electron density of the benzene ring is high because the methoxy group is electron-donating due to resonance effects. Therefore, in electrophilic reactions, it shows ortho- and para-orientation. For example, the reaction of acetic anhydride with anisole yields p-methoxyacetophenone.
Types of Anisole
Anisole is sold as R&D reagents and industrial chemicals. As a reagent product for research and development, anisole is used as a raw material for organic synthesis and as a solvent.
It is also sometimes used as a substitute for the main tar of lignin in pyrolysis experiments. The volume types include 1 mL, 25 mL, 500 mL, 1 L, 2 L, etc. It is a reagent product that can be handled at room temperature.
For industrial use, it is commonly used for fragrances, solvents, etc. It is available in capacities to meet demand at factories, etc.
Other Information on Anisole
1. Synthesis of Anisole
Anisole is synthesized by the methylation reaction of sodium phenoxide with dimethyl sulfate or methyl chloride.
2. Chemical Reaction of Anisole
Many chemical reactions of anisole are known. For example, the reaction of anisole with diphosphorus pentasulfide (P4S10) yields the Lawson reagent. Lawson reagent is a potent sulfidizing agent that exchanges oxygen for sulfur on organic compounds.
In the reaction of the Lawson reagent, for example, a carbonyl group is converted into a thiocarbonyl group, and an amide is converted into a thioamide. The methyl group of anisole is relatively stable but reacts against hydriodic acid to remove it, yielding phenol.
3. Anisole Handling and Regulatory Information
Anisole should be stored in a cool, well-ventilated area away from high temperatures, direct sunlight, heat, flames, sparks, and static electricity. Miscibility with strong oxidizers should be avoided.
In addition, due to its low flash point of 125.6°F (52°C), anisole is a substance subject to various legal restrictions. It is necessary to handle it correctly in compliance with the laws and regulations.