What Is a Helisat Screw?
A Helisat screw is one of the thread inserts used to repair or strengthen the female threads in threaded fasteners.
In the Japanese industrial world, threaded inserts are widely used under the name of Helisert. Helisert is also one of the threaded inserts, but it is a registered trademark of Tsugami Corporation. In addition, the name was changed to E-sert in 2001.
Applications of Helisat Screws
The Helisat screw is used to strengthen threaded holes in various plastic materials such as nylon, plastic, and Duracon, and other soft metals such as die-cast and aluminum. Heliserts can also be used to strengthen female threads when tapping into the base material alone will not provide tightening force, or to repair female threads that have been destroyed due to over-tightening torque.
The Helisat screw is widely used in automotive parts, transportation equipment, space industry, electronics, medical equipment, imaging equipment, agricultural machinery, playground equipment, musical instruments, etc.
Principle of Helisat Screws
Screw inserts, not limited to the Helisat screw, are used to strengthen a threaded hole or to rebuild a damaged threaded hole by screwing and embedding a threaded hole made of a strong material into the target threaded hole.
In other words, in order to use a Helisat screw, a pre-drilled hole of a larger size than the screw used for fastening is required. For example, a M8x1.25 Helisat screw has a M10x1.0 male thread on its outside diameter. Therefore, a M10x1.0 pre-drilled hole is required for the threaded hole to be strengthened.
To insert a Helisat screw, a special jig is used. There are two types of jigs: manual and electric. The electric jig uses an electric screwdriver to improve work efficiency.
Both manual and electric jigs require a special jig that matches the size of the Helisat screw to be inserted. A dedicated jig is also used to remove Helisat screw.
Other Information About Helisat Screws
The Helisat screw is a spring made of stainless steel wire with a diamond-shaped cross section, while Helisat screw is an integral part made by cutting from a steel bar. The advantages over Heliserts are as follows:
1. No Need to Fold the Tongue After Insertion
Heliserts have a tang, which is used for screwing in the insert, and requires a folding operation to remove the tang after insertion. Helisat screw, on the other hand, has no tongue, so there is no need to remove it after insertion.
2. No Pitch Jump
When the spring of a helical insert is stretched, the pitch of the thread is lost and the screw cannot be inserted, resulting in pitch jumps. Helisat screws, on the other hand, are one piece, so pitch jumps do not occur.
3. No Change in Shape
When a screw is inserted and removed repeatedly using a helical insert, the spring at the mouth of the screw may stretch and prevent the screw from being tightened. The one-piece Helisat screw does not change its shape in this way.
4. Good Insertion Workability
Insertion of helical inserts requires a certain degree of skill and takes about 20 seconds. Helisat screw, on the other hand, requires no skill for insertion, which is said to take only 4 to 5 seconds.
5. Pre-holes Can Be Drilled With Commercially Available Taps
The bottom hole of a helical insert is drilled with a dedicated tap. With a Helisat screw, a commercially available tap can be used for the pre-hole.
6. Adhesives Can Be Used
With the Helisat screw, adhesives can be used to secure the screw inserts firmly. Because of the spring structure of the helical insert, the adhesive will leak into the inside of the insert through gaps. Helisat screw is a one-piece unit, so no adhesive will leak into the insert.
 An X-ray CT machine is a device that irradiates X-rays to examine the materials and structure inside an object.
An X-ray CT machine is a device that irradiates X-rays to examine the materials and structure inside an object.


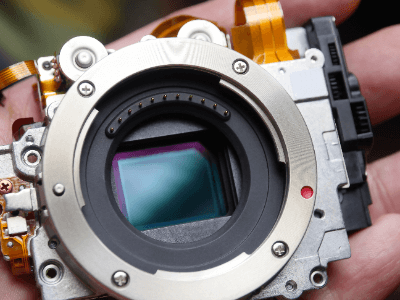 A CMOS camera module is a camera equipped with a CMOS
A CMOS camera module is a camera equipped with a CMOS 