What Is a Welding Machine?
 A welding machine (welder) is a generic term for welding machines that perform welding (melting and joining materials such as metals).
A welding machine (welder) is a generic term for welding machines that perform welding (melting and joining materials such as metals).
Welding machines include arc welders and laser welders, which perform welding only, as well as welding robots, which are equipped with welding machines and automate the welding process.
The welding methods used by Welding Machines are broadly divided into four types: “arc welding,” “gas welding,” “resistance welding,” and “laser welding.” There are several types of welding machines according to each welding method, especially arc welding machines, such as “covered arc welding machine”, “MIG/MAG welding machine”, “TIG welding machine”, and a “plasma welding machine”.
Uses of Welding Machine
Welding machines are widely used at sites where metal products are manufactured by processing, joining, and assembling metal materials, construction sites, automobile manufacturing plants, and other sites where products are manufactured by joining metal to metal materials.
They are used in automobile factories for welding bodies and frames in the production line, in ship factories for welding steel plates and frames of hulls, and in other situations where welding is performed by automatic welding robots.
In addition to large products and manufacturing plants, automatic, semi-automatic, and manual Welding Machines of various sizes are used in steel and can manufacturing plants, construction sites for steel rebar work, and other applications.
Welding machines are usually dedicated to different welding methods.
Principle of Welding Machine
Welding is defined as “the operation of bringing two or more base materials together by heat, pressure, or both so that there is continuity between the base materials to be joined.” Welding machines are used to perform this welding process and are available in a variety of configurations to accommodate different welding methods.
For example, a stand-alone welding machine, such as a manual welder, consists of a power supply unit to generate the electric current that serves as the heat source, a welding torch at the tip of the weld, a wire supply unit to supply the welding torch with the consumable filler, and a cylinder and hose, to supply the shielding gas.
Laser welding machines consist of a laser oscillator to generate laser light, a laser focusing lens, and an assist gas supply cylinder and hose. In addition to manual welding machines, there are also automatic welding machines that move the bed with the welding base metal left, right, up, and down as programmed to move the welding point automatically.
In the case of automatic welding robots, there are machines in which a robot arm with a welding torch attached moves to the position programmed by teaching, etc., and welds, and machines that can automatically move and rotate the base material to be welded and the direction of the product to be welded, and perform welding operations automatically and continuously.
There are also machines like CAM (Computer Aided Manufacturing) that automate welding machines by using 3D CAD models and programming the welding position, welding speed, etc.
By using these automated welding machines, complex and various welding operations can be automated, enabling stable and high-quality welding work.
 A crimp terminal is a component that connects an
A crimp terminal is a component that connects an 
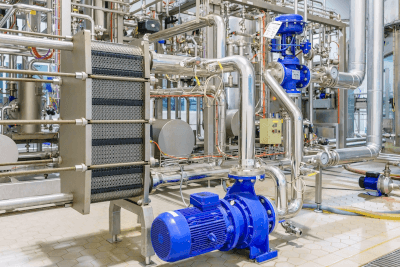 Cooling Systems are devices, equipment, or electronic equipment that are used to reduce temperature increases. Cooling Systems can be broadly classified into two types: water-cooled, which uses water to cool, and air-cooled, which uses air to cool.
Cooling Systems are devices, equipment, or electronic equipment that are used to reduce temperature increases. Cooling Systems can be broadly classified into two types: water-cooled, which uses water to cool, and air-cooled, which uses air to cool.
