What Is a Stop Valve?
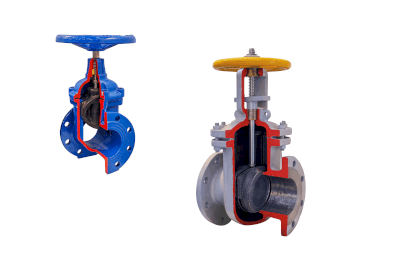
Stop valves, also known as shut-off valves, are used primarily to control the flow of fluid in a system, allowing for the complete stoppage or resumption of flow. Their application is determined by their function rather than their construction or shape.
These valves find usage across various sectors, including industrial water supply and domestic settings. They are crucial in systems where fluid flow needs to be periodically halted or allowed, such as for maintenance or in emergencies.
Uses of Stop Valves
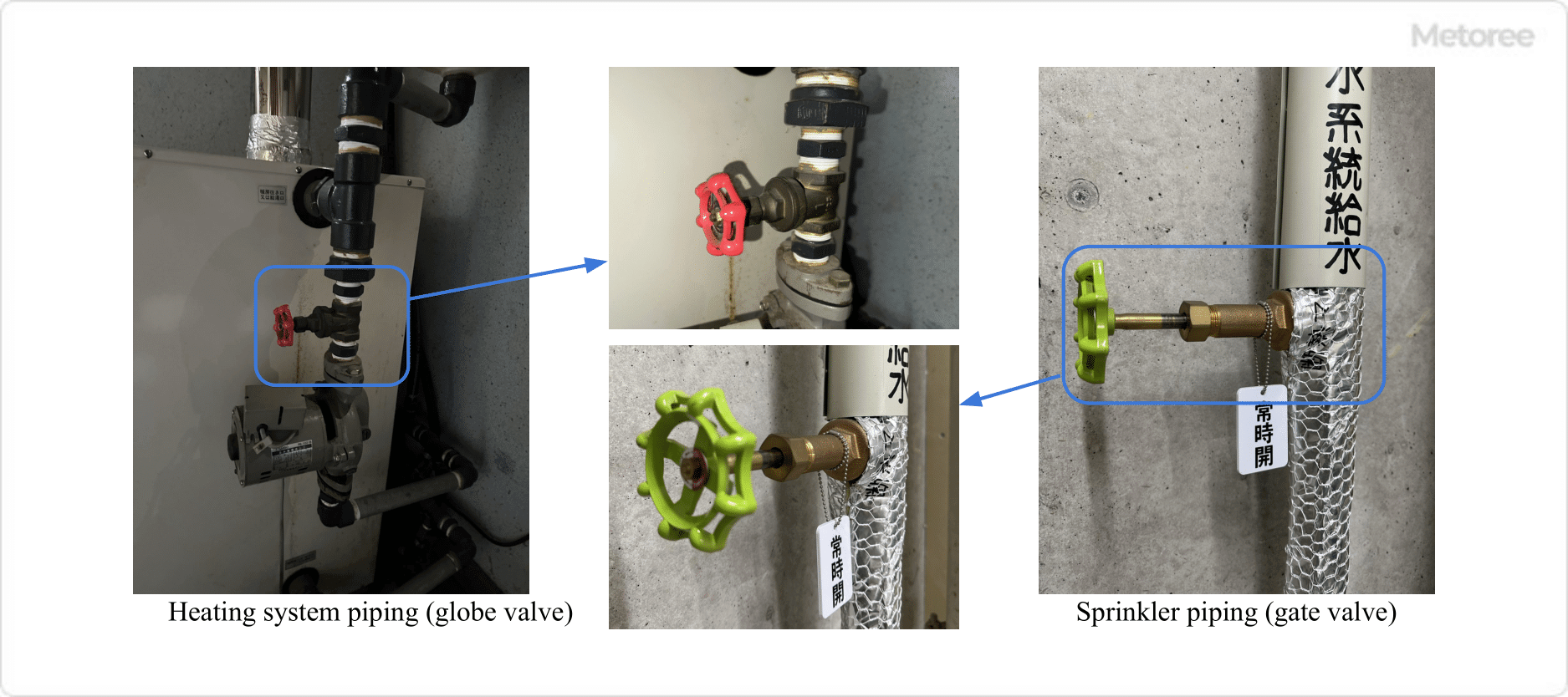
Figure 1: Example of Stop Valve Application
Stop valves are versatile, and used for temporarily shutting off fluids in processes, during maintenance, and in various piping systems in factories, the oil and gas industry, tap water, gas, heating, and sprinkler piping. They are valued for their ability to maintain open or closed states over extended periods.
Principle of Stop Valves
Stop valves have various mechanisms and functions as follows:
1. Shut-off Mechanism
The shutoff mechanism of a stop valve is such that when the handle or actuator is operated, the valve plug is interlocked to shut off or open the flow path. There are two main types of operation:
- Rotating Action
The disc, plug, or ball of the valve plug rotates to open or close the valve.
- Linear Motion
The disc of the valve plug moves up and down to open or close the valve.
2. Flow Adjustment
Many stop valves are not suitable for precise fluid flow regulation and are not often used for this purpose. However, they may be used in situations where multiple stop valves are installed throughout a piping system, and some of the stop valves are opened and closed to adjust the flow rate of the entire system.
3. Pressure Drop and Shut-off Performance
Stop valves are used for shutting off and opening for long periods and therefore have the following requirements:
- Long opening time, suitable for constant opening, and low-pressure drop.
- Long closing time, suitable for constant closing, high shutoff performance, and no leakage.
- Smooth valve plug motion and low frictional resistance during open/close operation.
Types of Stop Valves
There are several types of stop valves by mechanism and structure, and the best selection is made according to the operating procedure/frequency and the type of fluid. The types of operating methods include manually operated manual stop valves and remotely operated automatic stop valves.
1. Globe Valve
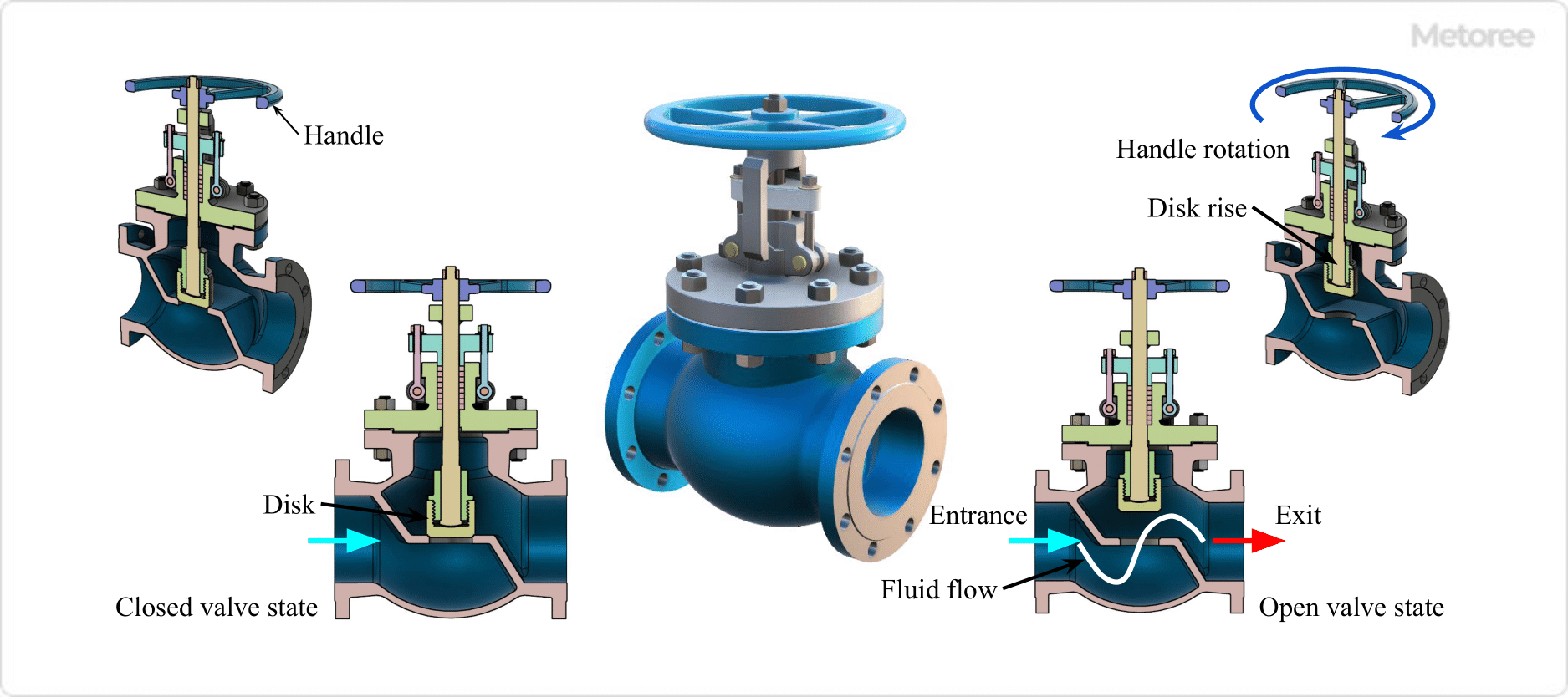
Figure 2. Globe Valve
Mechanism
Globe valves have a linear shutoff mechanism, and the valve plug moves up and down to shut off or open the flow path.
Shape
The valve box (valve body) of a globe valve is spherical, the flow path inside the valve box is curved, and the inlet and outlet are on the same axis. Due to this spherical shape, they are also called globe valves.
Function
Globe valves are used for flow control purposes in addition to on/off applications. The gap size between the valve plug and seat can be changed finely by the amount of rotation of the handle, allowing fine flow adjustment.
However, the disadvantage is a large pressure loss. If the pressure loss needs to be reduced, a gate valve, ball valve, or butterfly valve should be used. Since opening and closing operations cannot be performed quickly, they are mainly used as normally open and normally closed valves.
2. Gate Valve
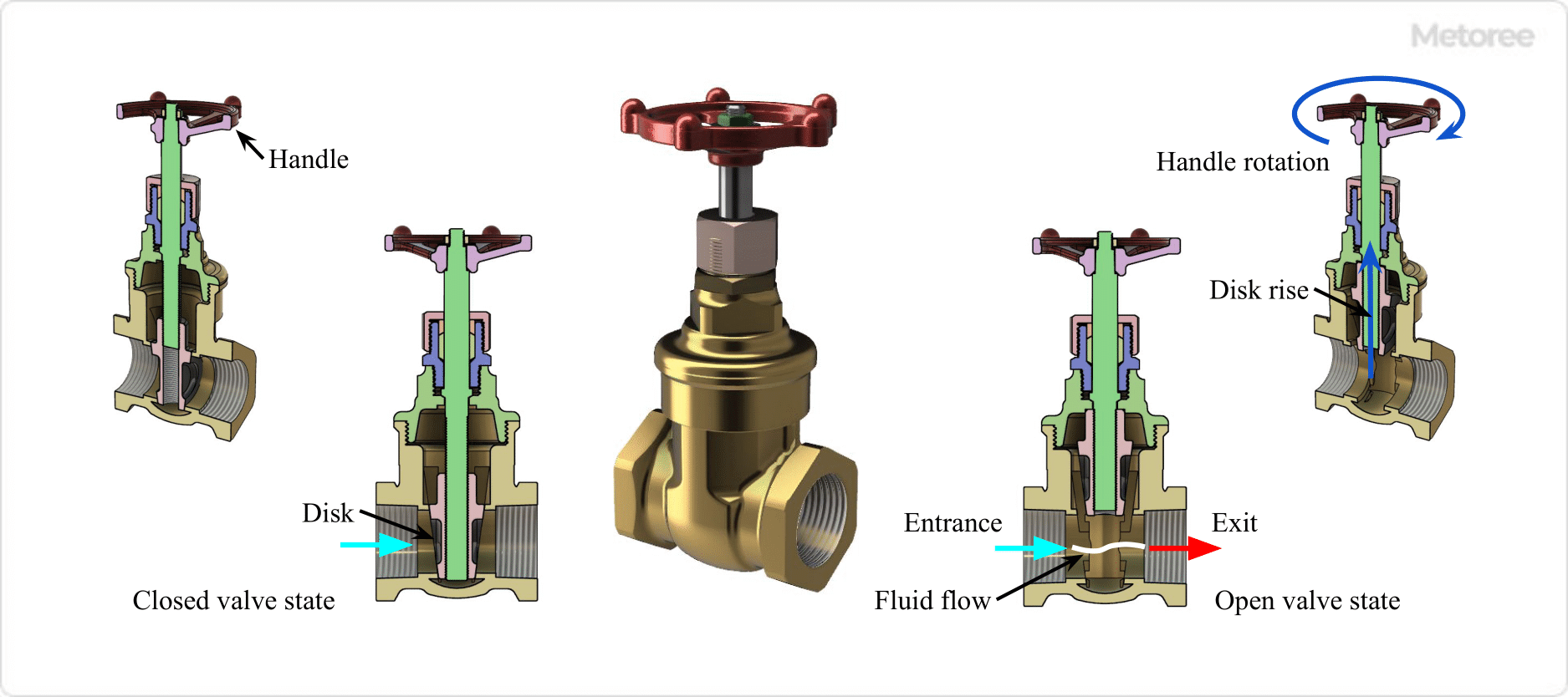
Figure 3. Gate Valve
Mechanism
A gate valve has a linear shutoff mechanism in which the valve plug (gate or wedge) moves up and down to shut off or open the flow path.
Shape
A gate valve has a nearly straight flow path in the valve box, with the inlet and outlet on the same axis.
Function
The shutoff valve is used for on/off applications where it completely shuts off or opens up. Since the flow path is straight, the pressure loss when fully open is extremely small.
3. Ball Valve
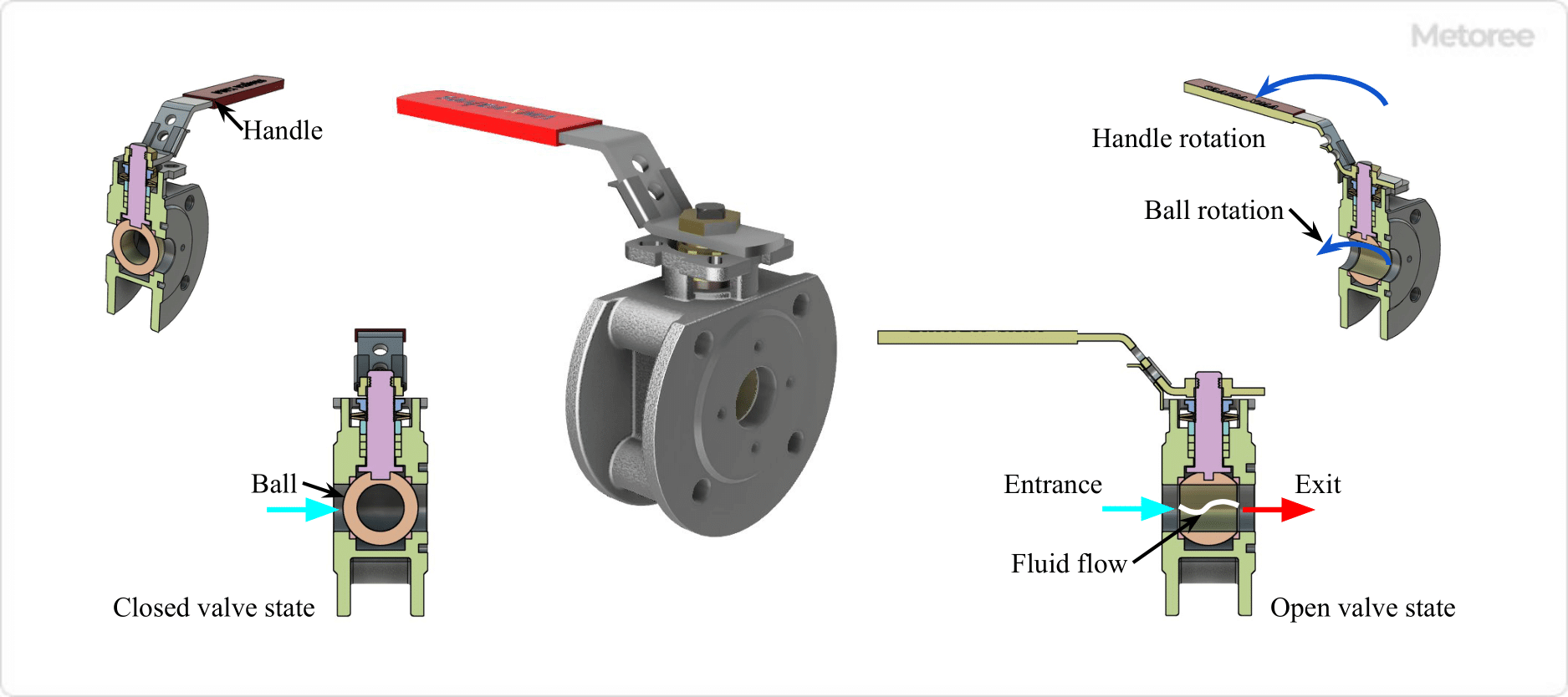
Figure 4. Ball Valve
Mechanism
A ball valve has a rotary shutoff mechanism in which a spherical plug (ball) with a hole in it rotates to shut off or open the flow path.
Shape
In a ball valve, the flow path in the valve housing is nearly straight, with the inlet and outlet on the same axis. Flow occurs when the hole in the center of the plug is aligned with the flow path in the valve box.
Function
Ball valves are quick to open and close. They are primarily used for on/off applications, but some can be used for flow control applications. When fully open, the valve plug does not remain in the flow path, resulting in a small pressure drop.
4. Butterfly Valve 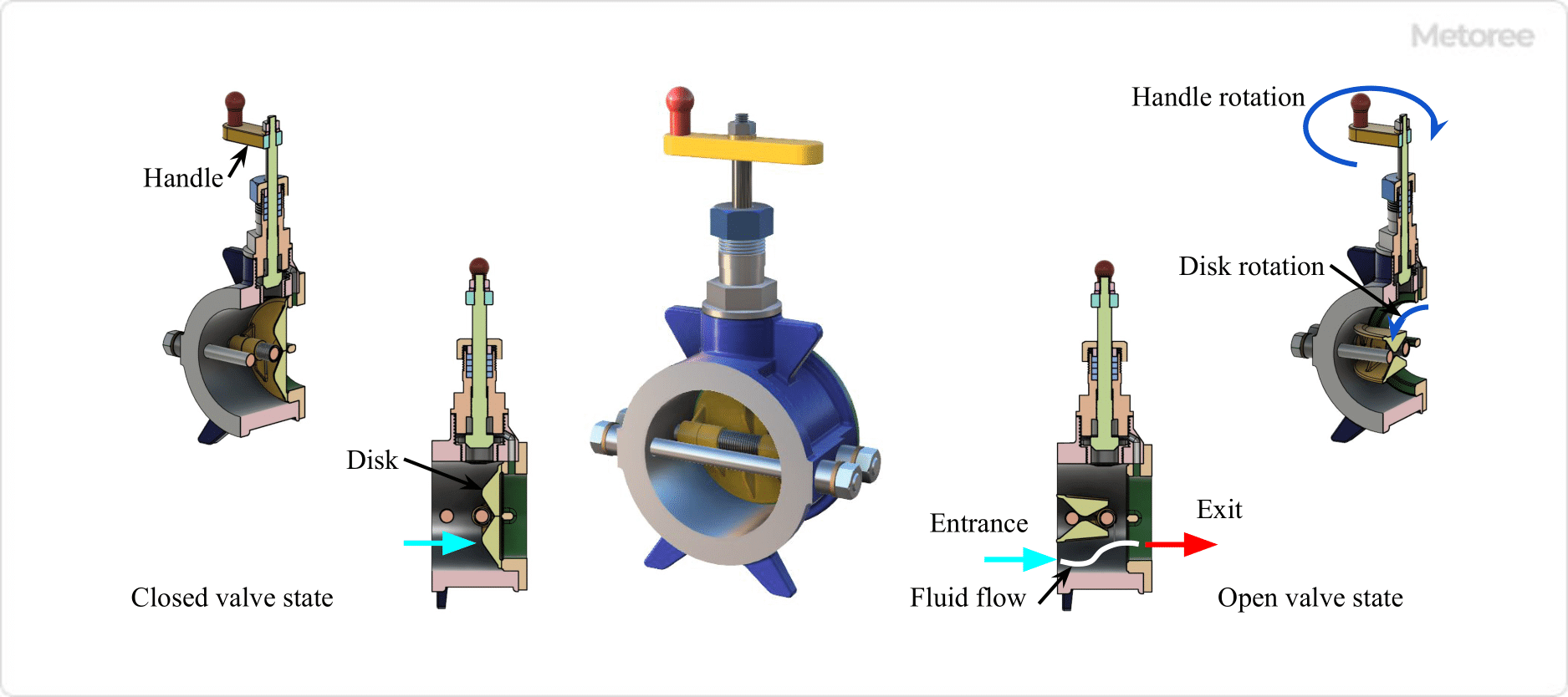
Figure 5. Butterfly Valve
Mechanism
Butterfly valves have a rotary shutoff mechanism that rotates a two-part valve plug to shut off or open the flow path. The valve is called a butterfly valve because the shape and action of the valve disc resemble the wings of a butterfly.
Shape
The valve housing of a butterfly valve is disk-shaped or rectangular. The flow path in the valve box is almost straight, and the inlet and outlet are on the same axis.
Function
Butterfly valves can be opened and closed quickly and are suitable for small to large valve diameters. Although primarily used for on/off applications, the flow rate can be adjusted by the angle of rotation of the valve plug.
Although the valve plug remains in the flow path when fully open, the pressure loss is relatively small.
5. Plug Valve
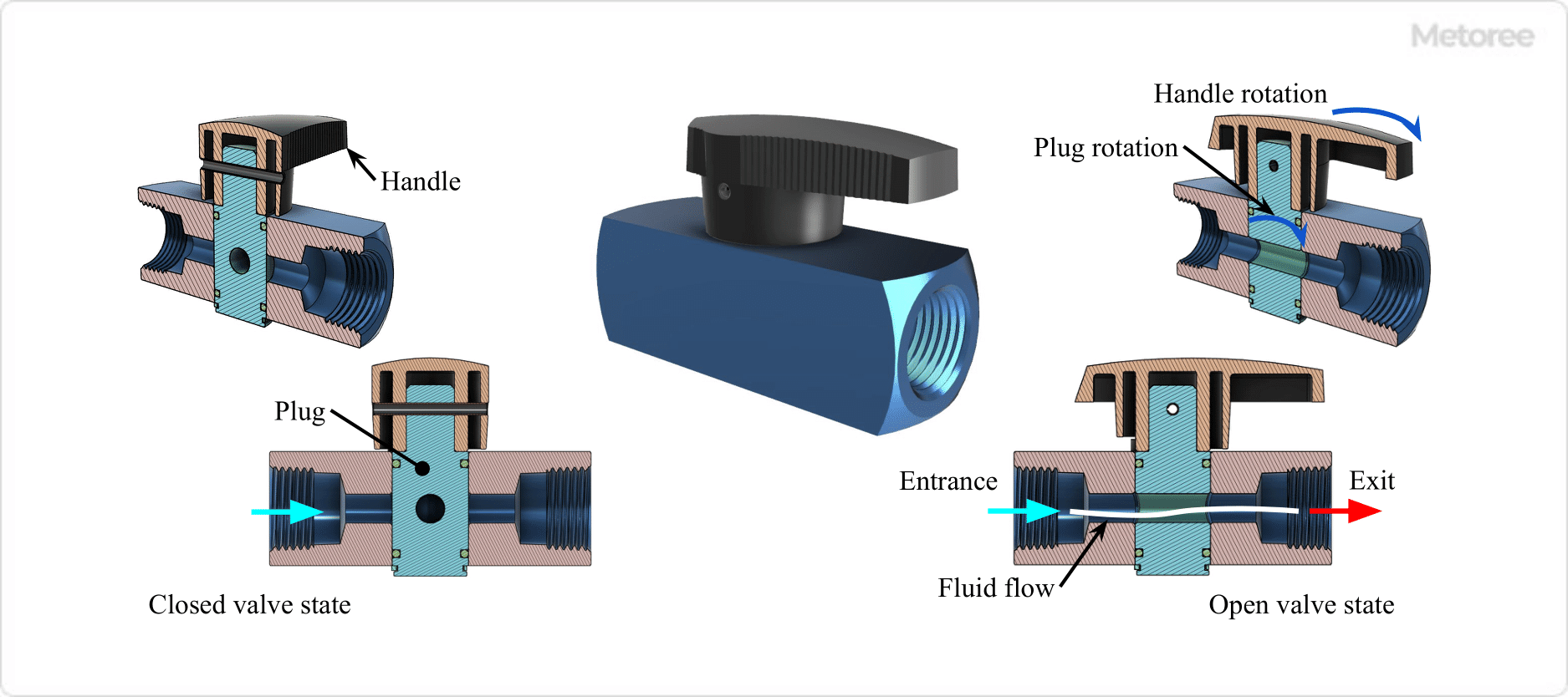
Figure 6. Plug Valve
Mechanism
A plug valve is a rotary shutoff mechanism in which a cylindrical plug with a hole in it rotates to shut off or open the flow path.
Shape
In a plug valve, the flow path inside the valve housing is nearly straight, with the inlet and outlet on the same axis. Flow occurs when the hole in the center of the plug is aligned with the flow path in the valve box.
Function
Plug valves can be opened and closed quickly and are primarily used for on/off applications. When fully open, the valve plug does not remain in the flow path, and the pressure loss is small.
6. Diaphragm Valve
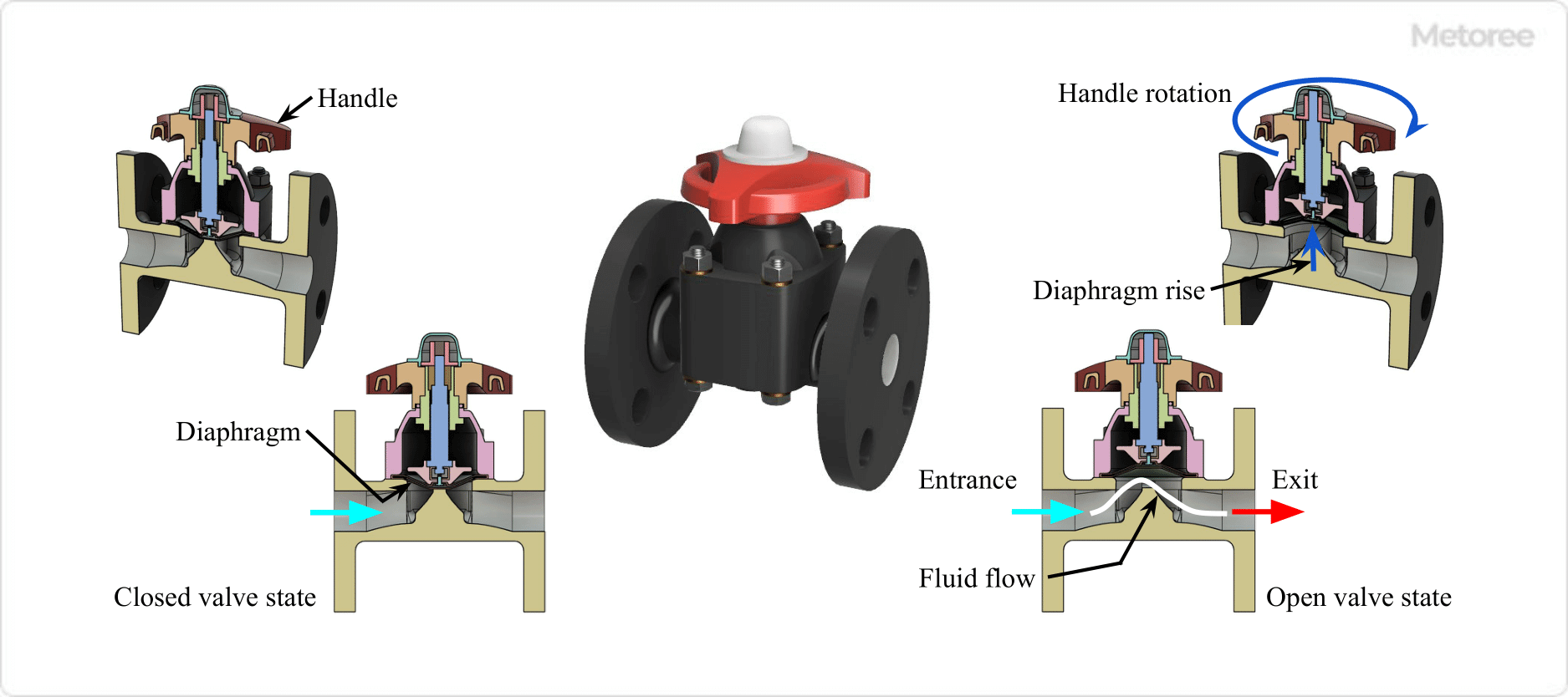
Figure 7. Diaphragm Valve
Mechanism
Diaphragm valves have a linear shutoff mechanism, in which the valve plug (diaphragm) deforms up and down to shut off or open the flow path.
Shape
In a diaphragm valve, the flow path in the valve housing is a gentle curve, and the inlet and outlet are on the same axis. The flow is shut off when the valve plug adheres to the seat and flows when the seat is opened.
Function
Diaphragm valves are used for on/off applications as well as for flow control applications at intermediate openings. They are compatible with corrosive and abrasive fluids and are used in the pharmaceutical, food, and chemical industries.










 An exhaust valve is a device designed to release air, commonly used in pneumatic systems to efficiently discharge compressed air from the piping. Due to its ability to expel large volumes of air rapidly, it is often referred to as a
An exhaust valve is a device designed to release air, commonly used in pneumatic systems to efficiently discharge compressed air from the piping. Due to its ability to expel large volumes of air rapidly, it is often referred to as a