What Is an Electrolyzed Water Generator?

An electrolyzed water generator is a device that generates electrolyzed water by electrolyzing salt water or other liquids.
The two largest categories of electrolyzed water are hypochlorite water, which is acidic electrolyzed water, and alkaline electrolyzed water. Acid electrolyzed water is further classified into strongly acidic electrolyzed water, weakly acidic electrolyzed water, and slightly acidic electrolyzed water according to pH.
Acid electrolyzed water (hypochlorite water) is used for sterilization and cleaning, while alkaline electrolyzed water is particularly effective in cleaning lipids and proteins. Strongly acidic electrolyzed water, weakly acidic electrolyzed water, and slightly acidic electrolyzed water that meets the requirements of various laws and regulations can be used as food additives and agricultural chemicals that can be used on organic agricultural products.
This is because electrolyzed water is very safe as long as it complies with regulations. Electrolysis generators are widely used in fields and sites where sanitation is required.
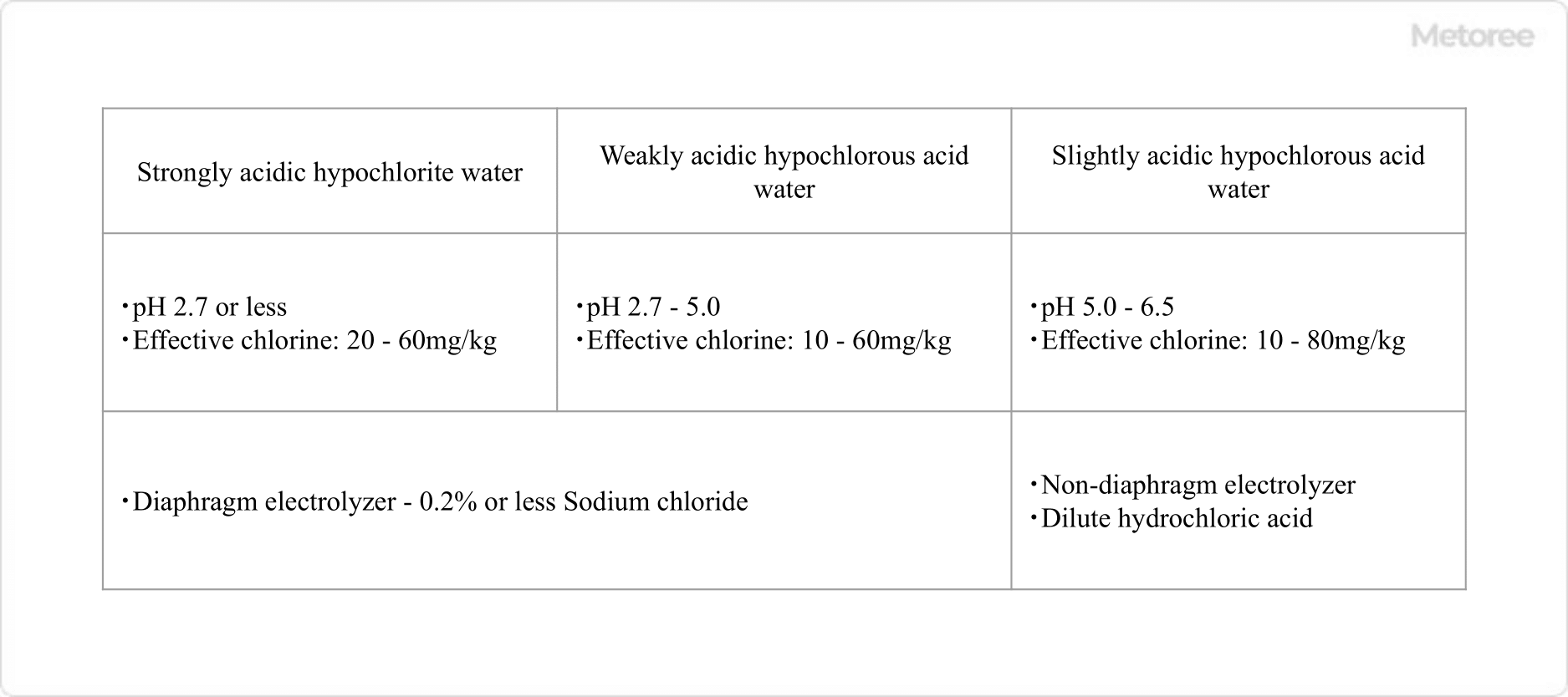
Figure 1. Types of acidic electrolytic water
Uses of Electrolyzed Water Generators
Because of the excellent sterilizing and cleaning effects of electrolyzed water, electrolyzed water generators are widely used where hygiene control is required. Specifically, they are used in the food industry, medical industry, childcare and nursing care industry, and cleaning industry.
For example, applications in food factories and restaurant kitchens include the cleaning and sterilization of equipment and utensils, and the sterilization of food ingredients. Major applications in the medical industry also include sterilization and cleaning of medical equipment in hospitals.
In childcare and nursing care facilities, the use of sanitizers in various aspects of maintaining a hygienic environment includes washing baby bottles and tableware, hygienic hand washing, and sterilizing and cleaning by wiping down the facility.
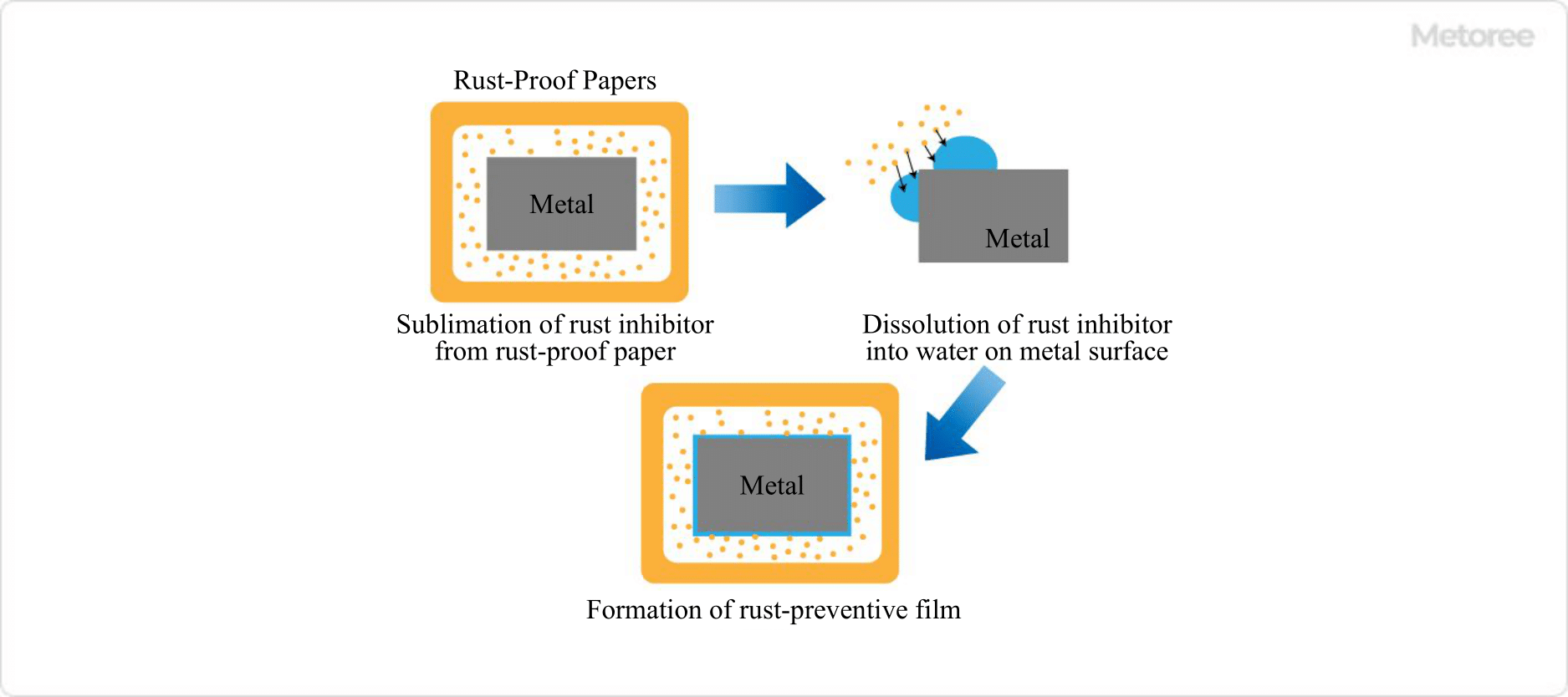
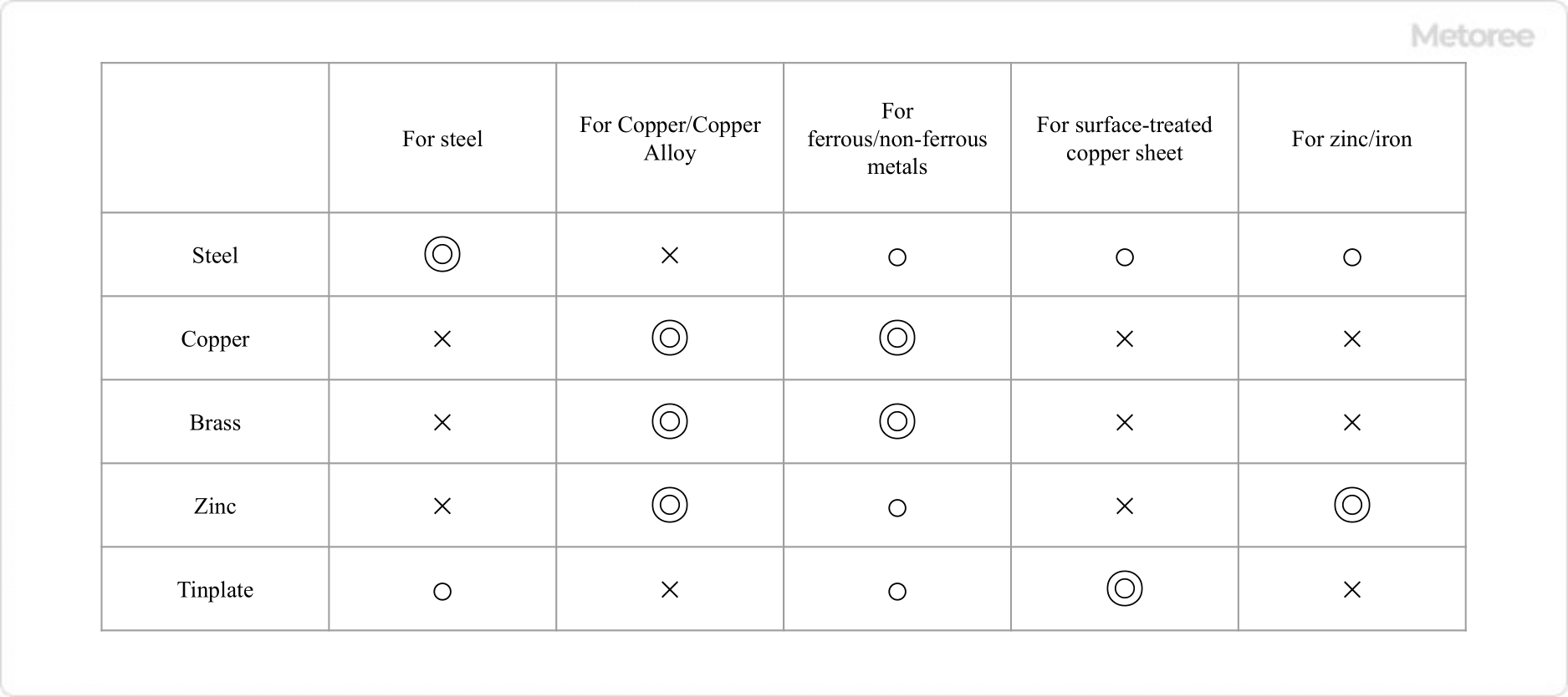
Factories that handle metal or plastic parts may use electrolyzed water generators, especially for the purpose of rust prevention with alkaline electrolyzed water. This application takes advantage of the fact that alkaline electrolyzed water is excellent for removing protein and lipid-based stains.
Principle of Electrolyzed Water Generators
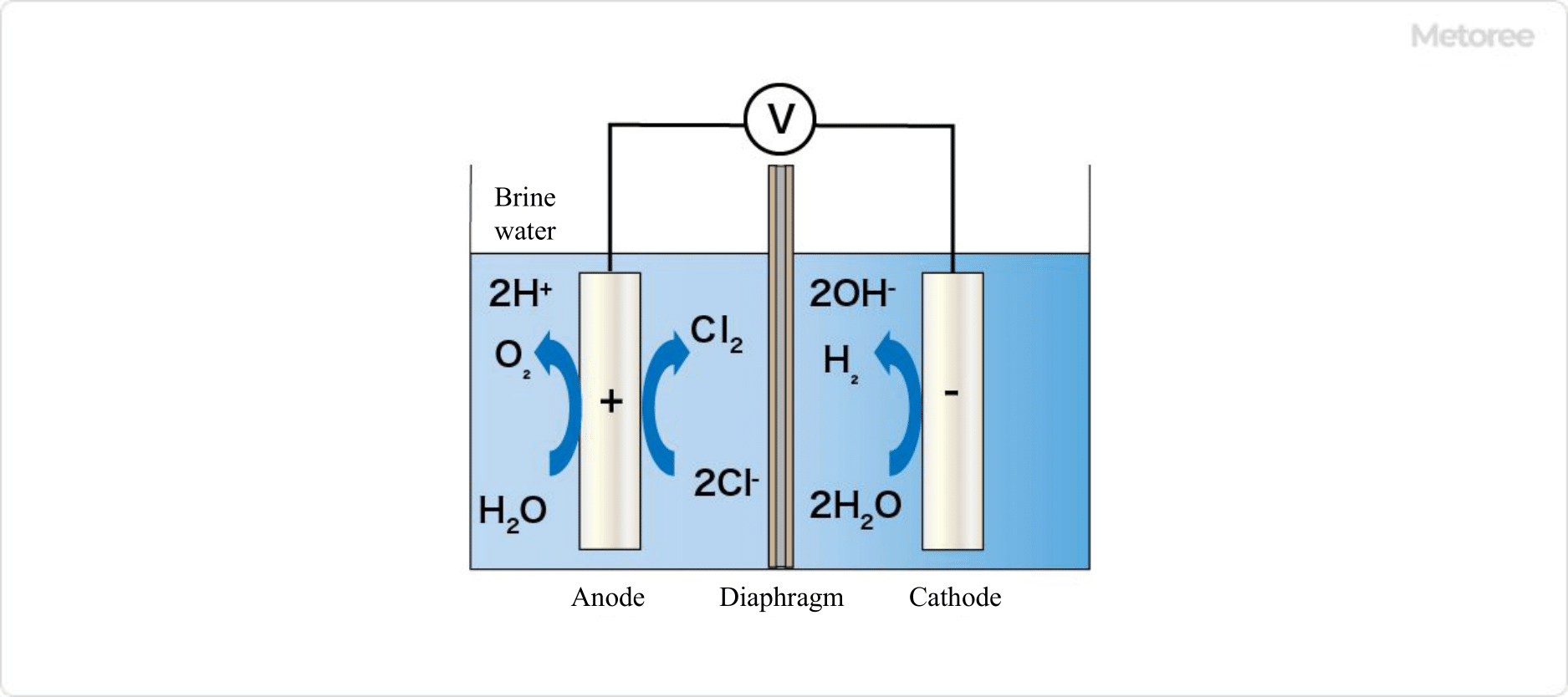
Figure 2. Overview of strongly acidic electrolytic water generator (two-diaphragm type)
There are two types of electrolyzed water: acidic electrolyzed water, such as hypochlorite water, and alkaline electrolyzed water. Most electrolyzed water generators have a dual-chamber electrolyzer structure with the anode and cathode separated by a diaphragm (two-diaphragm type).
When raw water, such as tap water, to which a small amount of salt such as hydrochloric acid or potassium chloride is added, is electrolyzed in the electrolyzer, the generated ions are separated by the diaphragm. The acidic electrolyzed water generated in a two-chamber electrolysis tank is mainly strongly acidic electrolyzed water.
When salt water is electrolyzed, the following reactions occur at the anode in the electrolyzer.
- H2O → O2 + 2 H+
- 2Cl- + 2e- → Cl2
When the generated chlorine molecules react with water, hypochlorite water, or acidic electrolyzed water, is generated. The electrolyzed water produced at this time is strongly acidic electrolyzed water.
On the other hand, the reaction that occurs on the cathode side is as follows:
- H2O → H2 + OH-
Because the cathode side is separated from the anode side by a membrane, the concentration of hydroxide ions (-OH) increases. As a result, alkaline electrolytic water is produced.
Types of Electrolyzed Water Generator
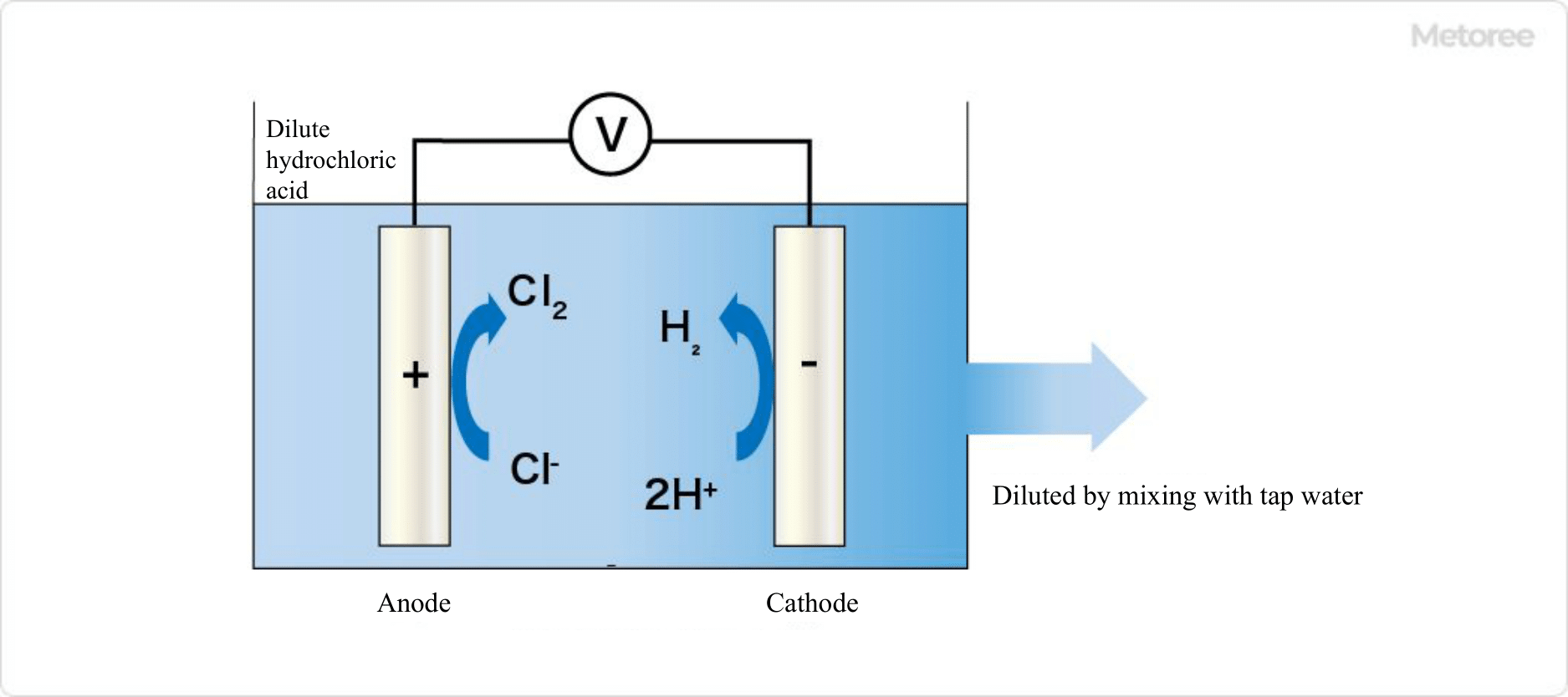
Figure 3. Overview of microacidic electrolyzed water generator
Electrolyzed water generators can be classified according to their structure and the intended electrolyzed water.
1. Classification by Structure
In addition to the two-chamber electrolyzed water generator mentioned above, there is a one-chamber electrolyzed water generator that produces slightly acidic electrolyzed water. Like strongly acidic electrolyzed water, slightly acidic electrolyzed water is approved as a food additive and is defined as “produced water with a pH of 5.0 to 6.5 and an effective chlorine concentration of 10 to 30 ppm obtained by electrolyzing 2 to 6% hydrochloric acid in a non-diaphragm electrolysis tank.
It is characterized by a lower effective chlorine concentration than strongly acidic electrolyzed water and a high sterilizing power at a near-neutral pH. It is widely used for cleaning and sterilizing various types of food and kitchen utensils. Because of its low effective chlorine concentration, it is particularly suitable for cleaning cut vegetables and fruits. The one-chamber electrolyzer is a system in which hydrochloric acid, previously prepared at 2-6%, is directly electrolyzed and then mixed with raw water to generate it.
Chlorine gas (Cl2) is generated by electrolysis of hydrochloric acid at the anode in the electrolyzer, and hydrogen gas (H2) is generated at the cathode. The generated chlorine molecules react with water to produce hypochlorite water, or acidic electrolyzed water, which is diluted to the desired concentration by mixing with raw water.
2. Classification by Electrolytic Water
When classified by electrolytic water, there are three:
- Strongly acidic electrolyzed water generator
- Slightly acidic electrolyzed water generator
- Alkaline electrolyzed water generator
As indicated in the principle of section, the mechanism of the device itself is the same, since strongly acidic electrolyzed water and alkaline electrolyzed water are generated simultaneously by a single electrolysis. Note, however, that some products drain alkaline electrolytic water and use acidic electrolytic water exclusively.
In addition, there are various sizes and shapes, including large stationary type products that can be used in factories, under-counter type stationary type products, and small water supply unit type products that can be hung on the wall.