What Is an Electrical Circuit Component?
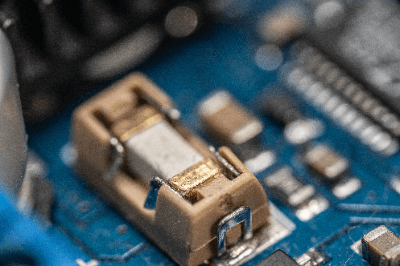
An electrical circuit component is a type of fuse designed for direct mounting on electronic circuit boards using surface mount technology.
These components serve as protection devices in electronic circuits. They protect against overcurrents and short circuits by interrupting the current flow when it exceeds a predetermined threshold, thus preventing damage to the circuit or device.
Being mechanical devices, these fuses are highly reliable and offer a long service life. Their compact size allows for high-level integration directly on the circuit board.
However, selecting the appropriate current rating and response time is crucial. An incorrect rating can result in accidental interruptions or inadequate protection if the circuit’s current exceeds the fuse’s capacity.
Applications of Electrical Circuit Component Fuses
Electrical circuit component fuses are used in various applications, playing a crucial role in circuit and device reliability by guarding against overcurrents and short circuits. Some common applications include:
1. Telecommunications Equipment
In telecommunications, where network and data transmission reliability is vital, these fuses safeguard communication circuits. For instance, they are used in network interfaces and data communication circuits to prevent surges and short circuits, ensuring data accuracy and network stability.
2. Automotive Components
In modern automobiles, these fuses protect sophisticated electronic control systems like engine control units and airbag control modules, contributing to vehicle safety and preventing electrical system damage in accidents.
3. Consumer Electronic Products
Commonly found in home appliances and consumer electronics, these fuses contribute to the stable, long-term operation of devices like televisions, refrigerators, computers, and smartphones by protecting them from overcurrents and malfunctions.
Principles of Electrical Circuit Component Fuses
These fuses operate on a simple principle: they blow when the current exceeds a certain threshold. Comprising a conductor made of metal foil or wire, they allow current to pass with minimal resistance under normal conditions. However, upon overheating due to overcurrent, the conductor melts, breaking the current path and interrupting the circuit power.
How to Select Electrical Circuit Component Fuses
When choosing these fuses, consider the following factors:
1. Mounting Method
Choose the appropriate package shape for the board’s design and size, considering options like chip fuses and leaded fuses.
2. Rated Current
Ensure the fuse’s rated current matches the circuit’s current flow. Exceeding this rating triggers the fuse to interrupt, protecting the circuit.
3. Rated Voltage
Select a fuse with a rated voltage that can safely interrupt the operating voltage of the circuit. Exceeding this voltage can lead to fuse failure and potential hazards.
4. Response Time
Match the fuse’s response time with the circuit’s requirements. Shorter response times provide quicker interruption in overcurrent situations but also increase the risk of false disconnections.