What Is a Filament?

A filament is the light-emitting part of a lighting device such as a white bulb. It is a resistive element located inside a glass bulb and shaped like a long, thin wire. A filament emits light when heated by an electric current.
When first invented, the filament was called a carbon bulb because carbonized paper was used as the material. However, the filament burned out as soon as it glowed for about one minute, and it was not at a level where it could be used in everyday life.
Therefore, today, a metal called tungsten is almost exclusively used.
Uses of Filaments
Filaments are used as light sources for lighting bulbs.
1. Incandescent Lamps
Incandescent light bulbs are well-known as the main use of filaments. The filaments are made of coiled thin tungsten wire. However, many recent general lighting bulbs use double coiled filaments to prevent heat loss.
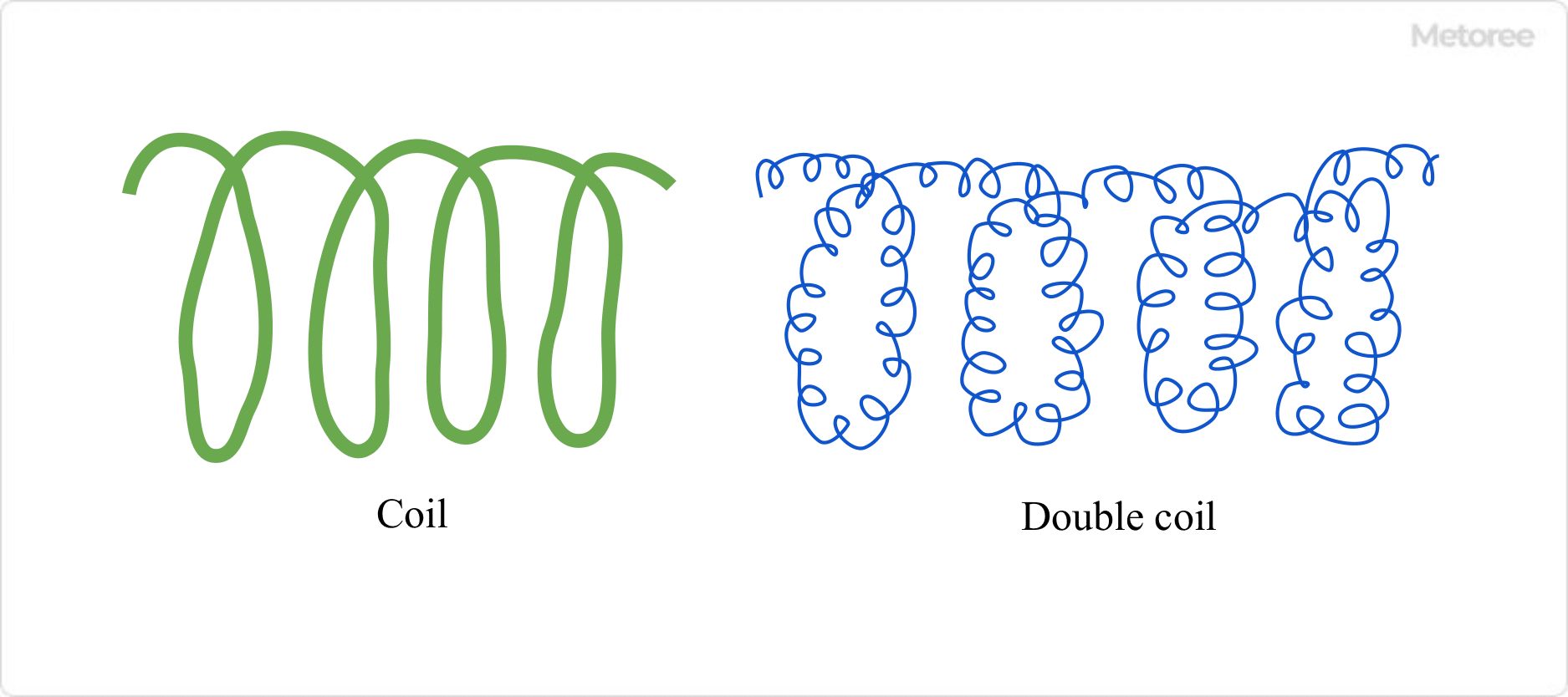
Figure 1. Coil and Double coil
There are many different types of incandescent bulbs, including halogen bulbs, mini-krypton bulbs, and fluorescent bulbs. The inside of the glass bulb is filled with an inert gas to prevent evaporation of the filaments (e.g., argon, nitrogen, krypton, xenon).
Some also exist with a vacuum inside, and incandescent bulbs produce different colors and intensities of light depending on the type of gas. In recent years, some incandescent bulbs other than halogen and mini krypton bulbs have been discontinued because of their poor energy efficiency.
In addition, due to this energy efficiency, light-emitting diodes called LEDs (light emission diodes) are increasingly being used these days.
2. Filaments LED Bulbs
Filaments LED bulbs are bulbs in which the filaments are reproduced by LEDs. Filament LED bulbs are characterized by their dim brightness.
The reason is that they use long, thin, thread-like LEDs. In addition, many models do not have a heat dissipating part called a heat sink. Therefore, there is a design limitation that prevents the use of LEDs with very high power. The main applications of LED bulbs are for supplementary lighting and joint lighting.
On the other hand, general LED bulbs can use larger LED chips and are often brighter than filament LED bulbs.
Filaments LED bulbs have a longer lifespan than incandescent or fluorescent light bulbs, but a shorter length than general LED bulbs. Specifically, it is around 15,000 hours. Since a typical LED bulb lasts 30,000 to 40,000 hours, this is about half the lifespan of a typical LED bulb.
Principle of Filaments
Incandescent bulbs use the principle that an electric current flows through filaments to generate Joule heat, which radiates heat and emits light. Joule heat is the heat energy generated when an electric current is passed through a conductor.
Therefore, to make the bulb usable for a long time, the filaments must be made of a material with high resistance and high heat resistance. Otherwise, the filaments themselves will not be able to withstand the heat and will burn, making them unusable as a light source.
Tungsten has an extremely high melting point of 3,653K (3,379°C), the highest among the metallic elements. Therefore, it does not melt even when heated by Joule heat. This is why tungsten is often used for filaments.
The inside of the bulb is filled with an inert gas, which ensures that the bulb has a long service life. However, the inert gas also removes heat from the filaments (heat loss) through thermal conduction and convection of the gas itself. As shown in Figure 2, the relationship between enclosed gas and heat loss tends to be smaller for elements with a larger atomic weight.
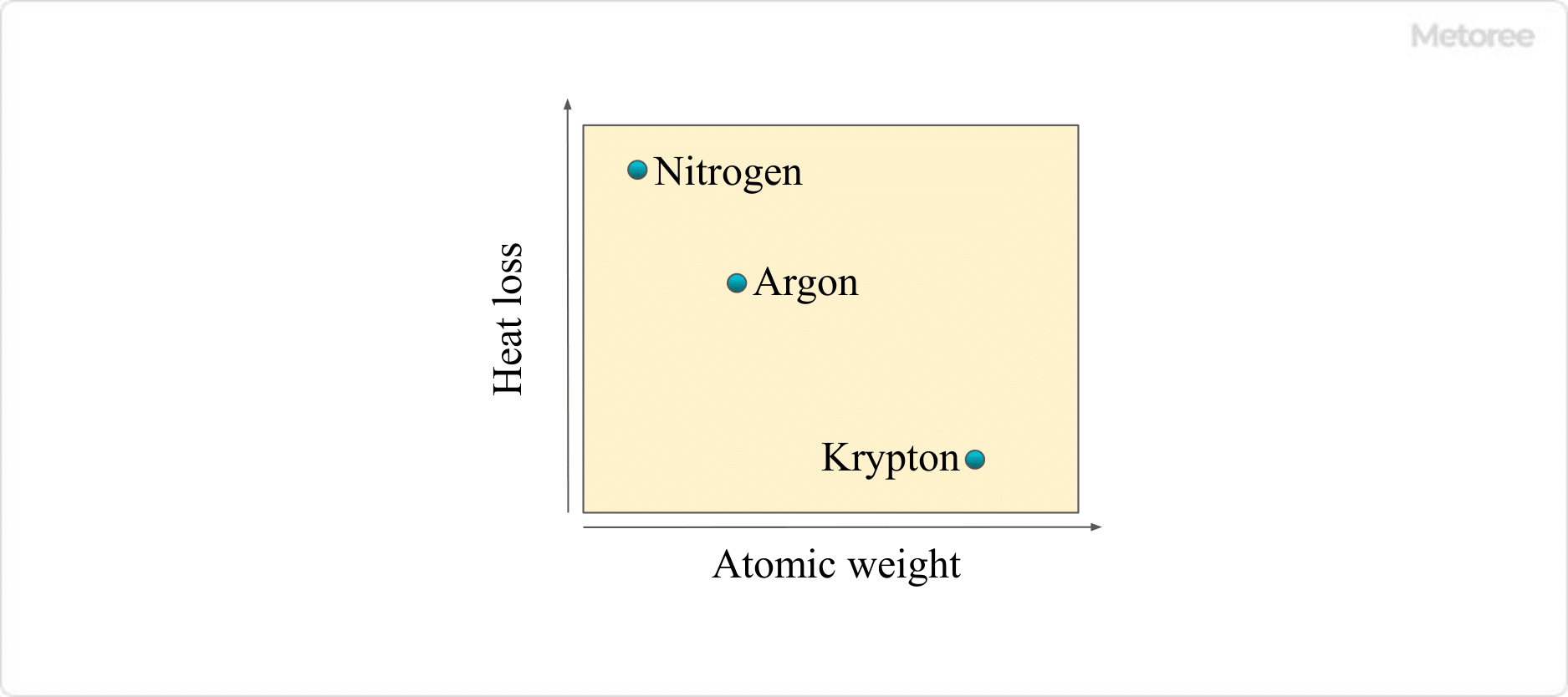
Figure 2. Enclosed gas and heat loss
Other Information on Filaments
1. Bamboo Filaments
In 1879, Edison invented the practical incandescent light bulb. At that time, the filament material used was Japanese bamboo. Bamboo was suitable as filament material because of its thick fibers, strength, and longevity.
When the light bulb was first developed, Edison used a filament made of carbonized cotton thread coated with soot and tar and succeeded in keeping the bulb lit continuously for 40 hours. However, from the standpoint of practicality, it was essential to develop a light bulb that could continue to light for even longer.
Therefore, we repeated experiments to investigate the lighting time by using various familiar materials, such as paper and thread as filaments. In the process, we found a souvenir fan from Japan and made a light bulb with filaments made of bamboo used as the framework of the fan.
When he conducted lighting experiments with that light bulb, he found that the lighting time was longer than with previous materials and reached a level of practicality. Edison then proceeded to conduct lighting experiments using various types of bamboo from around the world to find the best bamboo for the filaments.
He found that when Hachiman bamboo from Kyoto, Japan, was used, the light stayed lit for an average of more than 1,000 hours, leading to its practical application.
2. Filament and Spun Yarn
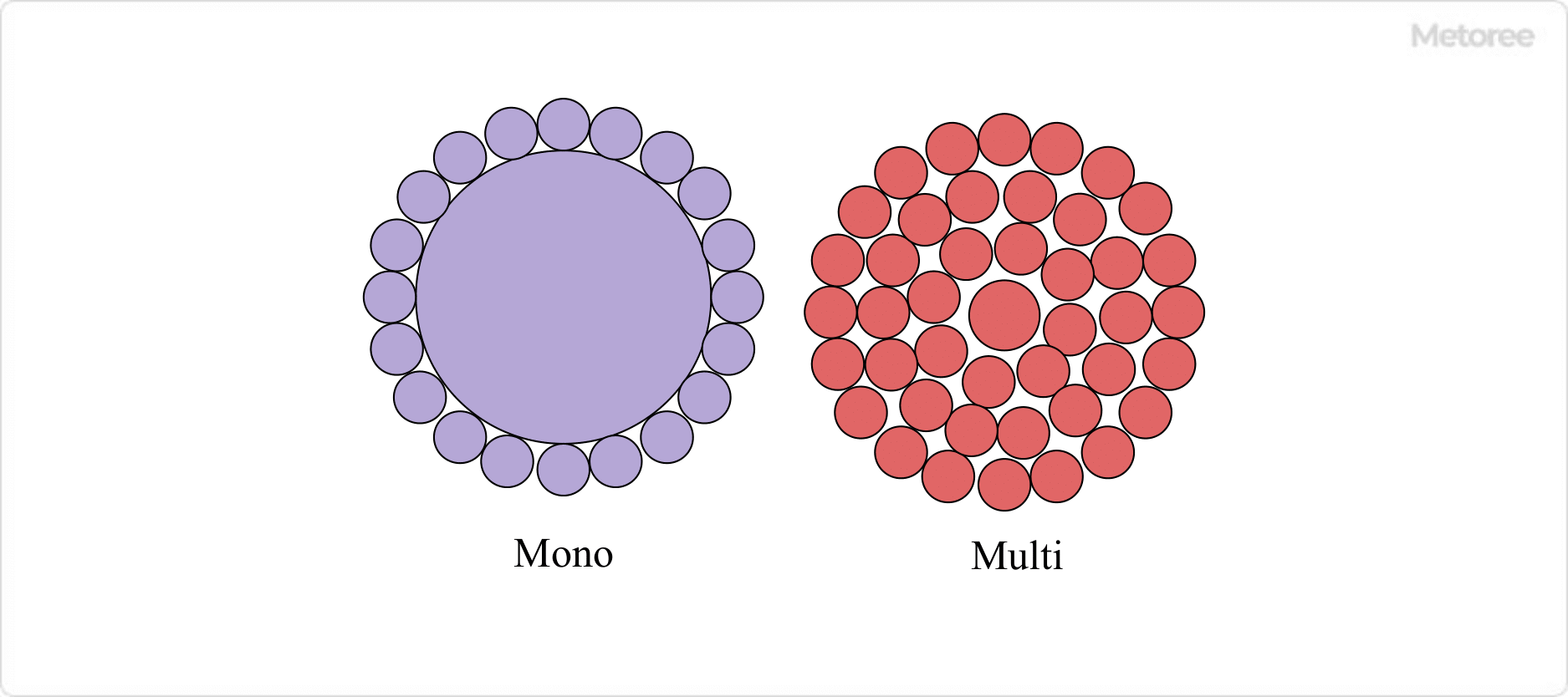
Figure 3. Monofilament and multifilament
The word filament is used to refer to the light source part of a light bulb, and a long continuous fiber, like silk, is called filament yarn.
Filament is a word that originally meant something fibrous. On the other hand, spun yarn is made by aligning short fibers parallel to each other, like cotton yarn, and twisting them to make a single strand.
Filament yarn comes in two types: monofilament and multifilament. The former is a single long strand of yarn, like a fishing line. The latter refers to a single thread made by twisting dozens of threads together. In natural fibers, silk thread falls into this category. Raw silk is made from unraveled cocoons exhaled by silkworms, and silk thread is made from cleaned cocoons.
There is no particular type of spun yarn, and almost all natural fibers, such as cotton and hemp, fall under this category.