What Is a Digital Anemometer?

A digital anemometer is, as the name implies, an anemometer with a digital display.
As a feature, anyone can easily measure wind speed, and many are lightweight and compact, making them easy to carry around. Recent digital anemometers can measure not only wind speed, but also temperature and humidity at the same time, especially with hot-wire anemometers.
They also offer a wide range of functions such as data hold, unit switching, remaining battery indication, and data recording. Since it can display maximum, minimum, and average values, it is used in a variety of situations.
Uses of Digital Anemometers
Digital anemometers are used in a wide range of fields, from outdoor events and sports to construction sites, agriculture, and fishing. In recent years, digital anemometers have come in handy when flying drones.
Since drones are affected by the wind speed in the flight area, they are also used to measure the wind speed in the flight area. Digital anemometers are compact, easy to use, and can be used both indoors and outdoors.
1. For Indoor Use
- Maintenance and inspection of air conditioning equipment
- Confirmation of the effectiveness of smoke separation
- Measurement of air velocity of ventilation fans
- Measurement of exhaust air from air conditioning equipment
- Measurement of indoor convection currents
- Clean room air quality survey
- Indoor environment survey at manufacturing sites
2. Outdoors
- Safety control and wind velocity control in outdoor and high places
- Fixed to crane or outdoor site for measurement
- Weather observation
- Confirmation of drone flight conditions
Principle of Digital Anemometers
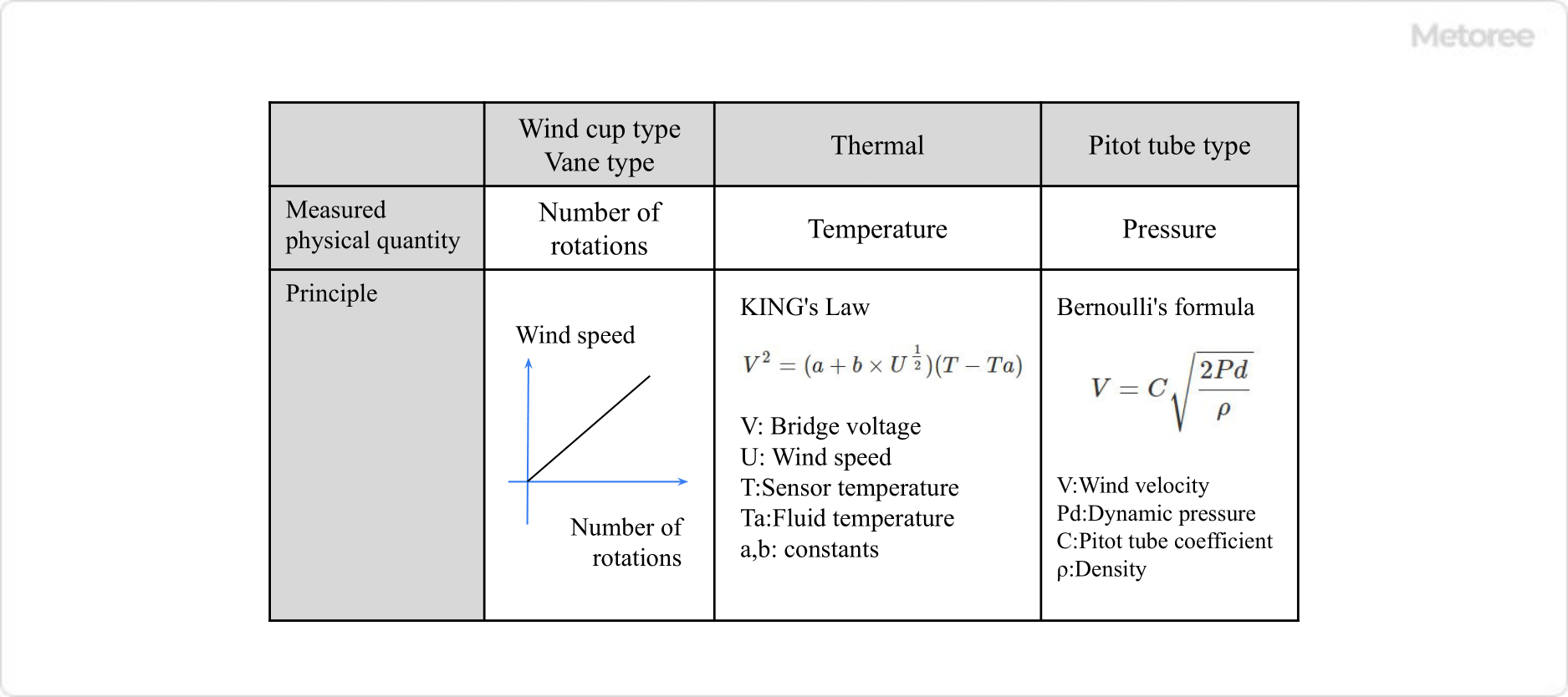
Figure 1. Principle of digital anemometer
There are several types of anemometers, but the most common types of small, portable digital anemometers are the hot-wire and vane (wing-wheel) anemometers. In addition, pitot tube and wind cup anemometers are also available.
1. Hot-Wire Type
This is the most common type for indoor use. A resistive element whose resistance changes with heat is installed at the tip of the sensor, and when it receives wind, the sensor is cooled and the temperature of the hot wire decreases.
The faster the flow is, the faster the cooling is. Therefore, the resistive wind velocity is measured by utilizing the relationship between the flow velocity and the amount of cooling heat. This relationship is called the KING’s relationship. Accurate measurement is not possible outdoors because the temperature changes due to the heat of the sun and other factors.
This is a compact measuring instrument with a simple structure. It can also measure other characteristics such as wind temperature and humidity at the same time.
2. Vane Type
The measuring principle of the vane type wind sensor is to calculate the speed by measuring the number of rotations of the vane (impeller) rotating with the fluid. The principle is based on the principle that the number of rotations is proportional to the speed.
The rotational speed is largely independent of the density, pressure, and temperature of the fluid. The number of vane rotations is counted by a proximity switch or photocoupler.
Compared to the hot-wire type, it can be used outdoors because it is not affected by heat. However, it is not suitable for use when wind speed changes in small increments due to its lower accuracy in the low wind range and slower response speed.
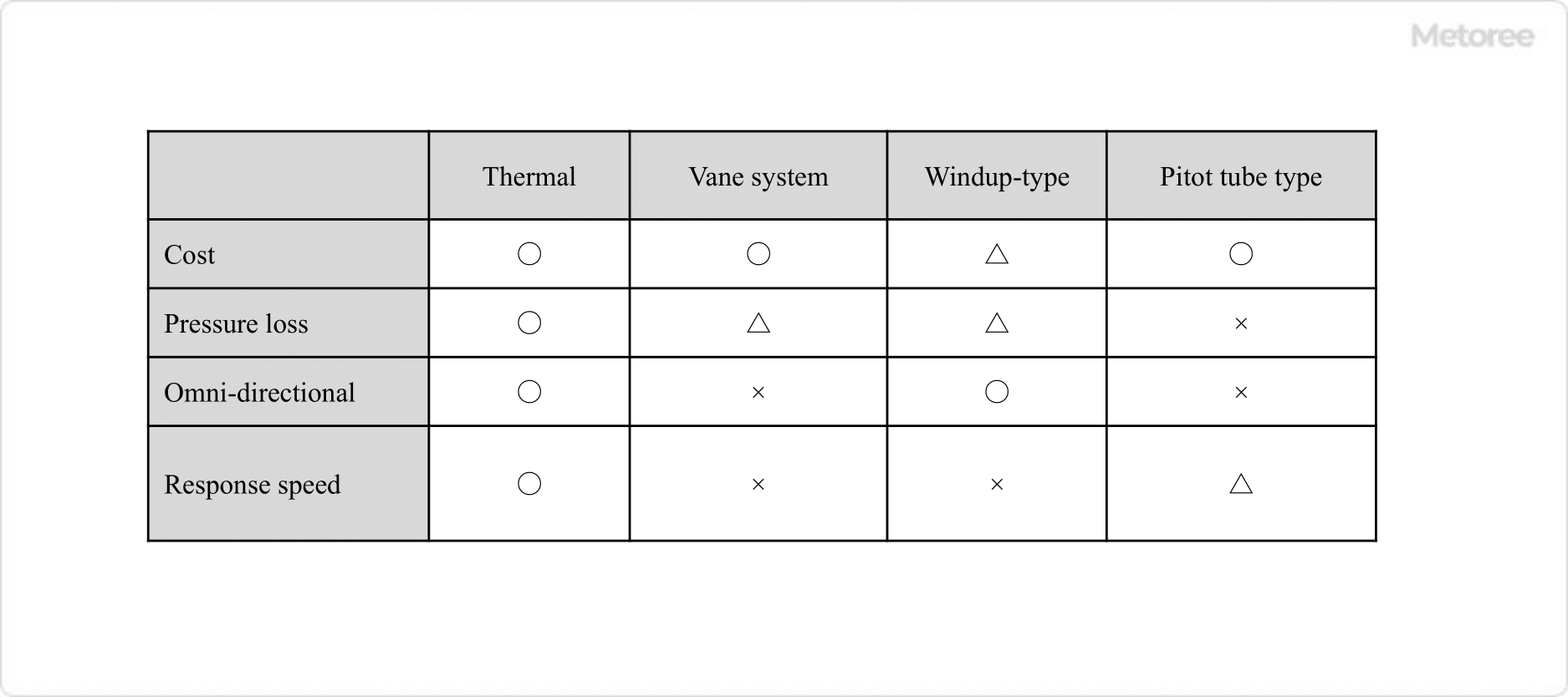
Figure 2. Types of digital anemometers
3. Pitot Tube Anemometer
Pitot tube anemometers are often used in industrial applications. Pitot tube anemometers measure wind speed from Bernoulli’s theorem by measuring the pressure difference between small holes in front of and to the side of the air flow. Accurate velocities cannot be obtained unless they are oriented perpendicular to the air flow, but they are often inexpensive because of their simple principle.
4. Wind Cup Wind Velocity Sensor
The wind cup, which is shaped like a cup, rotates using the fact that the wind pressure on its front side and back side differs depending on the strength of the wind. Wind speed is measured by measuring the number of rotations. Because of the rotating motion, the response to changes in wind speed is slow, and it is not suitable for measurements in the low wind speed range.
Because of these differences in principle and characteristics, it is necessary to select the appropriate type of anemometer according to the purpose and application.
Other Information on Digital Anemometers
Advantages of Digital Anemometer
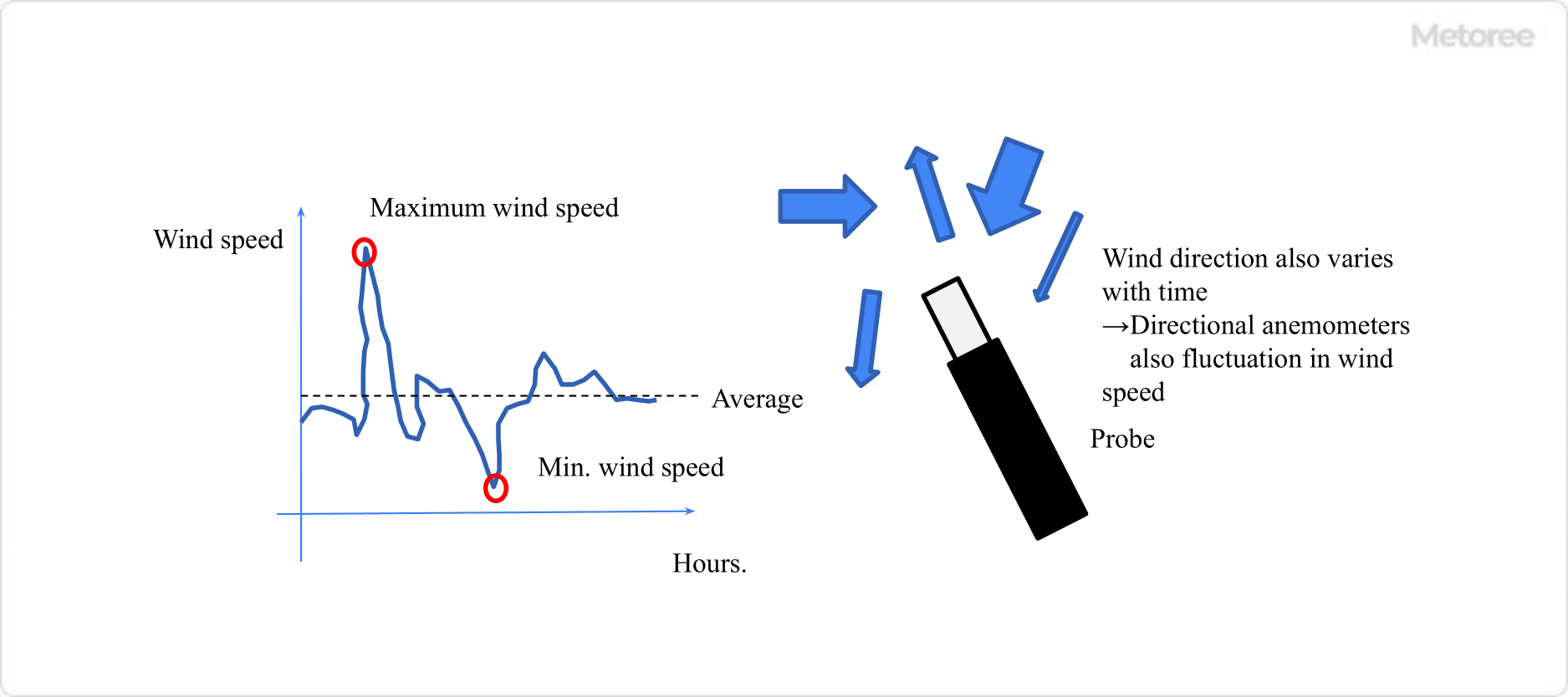
Figure 3. Temporal variation of wind speed and direction
The advantage of using a digital anemometer is that it automates the measurement of average, maximum, and minimum wind speeds. Normally, wind speed fluctuates greatly with time. Furthermore, since wind speed often varies with direction, even the direction of the anemometer probe can affect the accuracy, and hand vibration can change the value.
Even when average wind speed is desired, if the value fluctuates, it is difficult to obtain accurate data that does not involve subjectivity. The display unit of a digital anemometer is equipped with functions to calculate the average wind speed during these 00 seconds and to display the maximum and minimum wind speeds during these 00 seconds, etc., so that fair data can be obtained no matter who handles it.