What Is 3D CAD?
 3D CAD, standing for “Computer Aided Design,” is a type of CAD software that enables users to create three-dimensional designs and models on a computer. There are two main types of CAD: 2D CAD and 3D CAD.
3D CAD, standing for “Computer Aided Design,” is a type of CAD software that enables users to create three-dimensional designs and models on a computer. There are two main types of CAD: 2D CAD and 3D CAD.
Uses of 3D CAD
3D CAD is categorized into architectural and mechanical types and further divided into high-end, mid-range, and low-end CAD based on functionality. The choice of CAD type depends on the specific needs and complexity of the design task.
1. High-end CAD
High-end CAD is used for complex designs involving numerous parts, such as in automotive and appliance manufacturing. Examples include CATIA, Creo Parametric (formerly Pro/ENGINEER), and NX. These systems offer advanced 3D modeling and extensive simulation functions.
2. Mid-Range CAD
Mid-range CAD is more affordable and user-friendly compared to high-end CAD, though it may have limited simulation capabilities. However, its core 3D modeling functions are robust, making it suitable for university research and simple product design. Examples include SolidWorks, Inventor, TopSolid, and Solid Edge.
3. Low-end CAD
Low-end CAD offers inexpensive or free options suitable for personal or hobbyist use. While adequate for basic design tasks, they may not be sufficient for complex geometries or multi-part assemblies. Examples include Inventor LT, 123d design, DesignSpark, and Creo Elements Direct Modeling Express.
Principles of 3D CAD
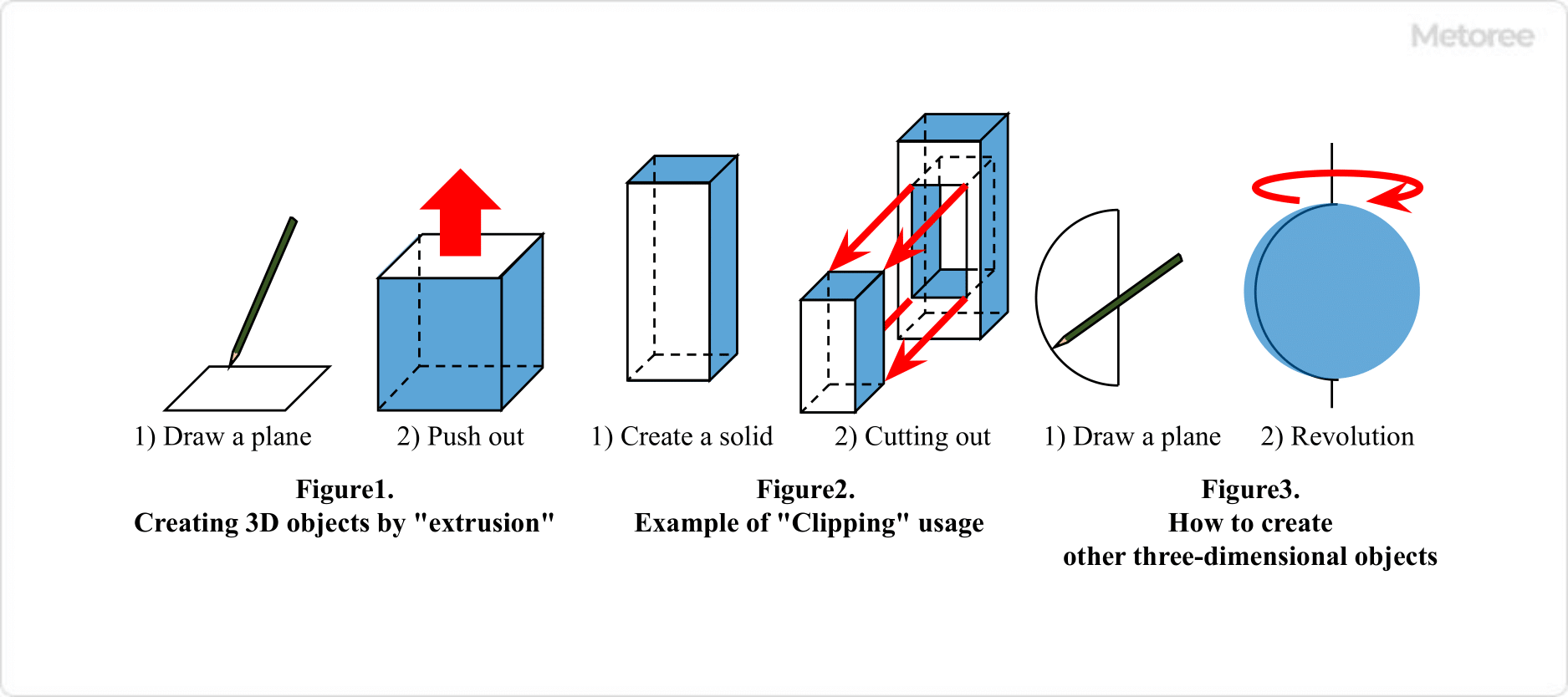
The fundamental steps to create a 3D model are consistent across different CAD software packages. The process typically involves selecting a plane, drawing a 2D sketch, and then extruding this sketch to create a three-dimensional object. Repeating the process of extrusion and cutting on different planes allows for the creation of the required 3D shape. Each CAD software may offer unique functions for model creation, so selecting the most suitable software for the specific application is important.
Other Information on 3D CAD
1. Situations in Which 3D CAD Is Used
3D CAD is particularly useful in scenarios where 2D design falls short, offering enhanced visibility, structural analysis, and clearance checks. It also enables the animation of designed parts to check their motion and range.
2. Advantages of 3D CAD
3D CAD allows for more intuitive modeling than 2D CAD, and design changes can be directly informed by analysis. It facilitates easier clearance checking in complex designs and enables rapid prototyping through CAM data or 3D printing. 3D models are also easily understandable, improving communication in large-scale, multi-departmental design projects.
3. 3D CAD User Engineer Examination
The 3D CAD User Engineer Examination certifies the knowledge and skills of engineers who use 3D CAD, ensuring proficiency in this advanced design tool.