What Is a Capacitive Proximity Sensor?
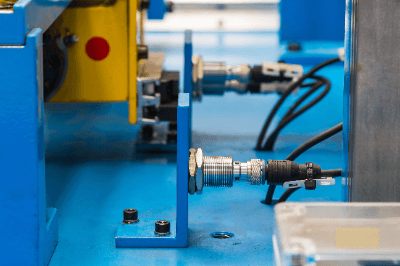 Capacitive Proximity Sensors are a type of non-contact sensor that detect the presence or absence of an object. They can detect an object by the change in capacitance when the object enters the electric field.
Capacitive Proximity Sensors are a type of non-contact sensor that detect the presence or absence of an object. They can detect an object by the change in capacitance when the object enters the electric field.
Various substances can be detected, including metal, water, oil, glass, plastic, and paper. It can also detect the contents of non-metallic containers from the outside.
However, it should be noted that detection sensitivity and distance vary depending on the object’s object size, thickness, and non-dielectric constant, as well as its susceptibility to water and moisture.
Uses of Capacitive Proximity Sensors
Capacitive Proximity Sensors are used for detecting the contents of a container from the outside and for non-contact switching.
1. Detection of Contents From Outside the Container
Capacitive Proximity Sensors are capable of detecting liquids, paper, glass, and wood behind walls, inside tanks, inside containers, and behind covers. They are mainly used for inspection and confirmation of contents.
2. Non-Contact Switches
They are used as push-button switches in elevators, switches through various panels, etc., and non-contact switches for lights, etc. They are also applied to switches for lighting and dimming room lamps in cars.
Principle of Capacitive Proximity Sensors
The principle of capacitive proximity sensors is that an object can be detected by the change in capacitance when the object enters an electric field.
When voltage is applied to an electrode and the ground, an electric field is formed between the electrode and the ground. When an object enters the electric field formed by the electrodes, the object is charged by electrostatic induction and the electrode’s capacitance changes.
1. Detection Circuit
Capacitive Proximity Sensors have a sensing electrode. When a dielectric detector enters the electric field formed by the sensing electrode, the electrode forms a capacitor with the object. The capacitance is determined by the distance to the object.
An oscillation circuit is commonly used for the detection circuit. The oscillation amplitude changes as the capacitance of the sensing electrode changes. An object is detected by comparing the amplitude changes that the oscillation circuit starts and stops. In capacitive proximity sensors, the sensing electrode is the element and oscillates.
2. Oscillation Circuit
An oscillation circuit is an electric circuit that generates electrical repetitive oscillations. An RC circuit consisting of a capacitor (C) and a resistor (R) is used to generate oscillations with frequencies ranging from 1/1,000 to several MHz.
3. CR Oscillation
CR oscillation is an oscillation circuit called a feedback type. A portion of the output of the amplifier circuit is fed back to the input to produce regular voltage fluctuations. The CR oscillation circuit rotates the phase of the amplifier output 180 degrees and returns it to the input.
Other Information on Capacitive Proximity Sensors
1. Mutual Interference
The use of a high-frequency oscillation circuits may cause mutual interference when proximity sensors are nearby. When multiple sensors are installed, they should be installed at a distance greater than the specified distance.
2. Change in Capacitance
Changes in capacitance are related to the size, thickness, and non-dielectric constant of the object. The larger each of these values is, the larger the capacitance will be.
Dielectric constant is an inherent electrical constant possessed by each material. The value of the dielectric constant is determined by how the electrons in each material respond to an external electric field. The non dielectric constant is expressed as the ratio of the dielectric constant of the material to the dielectric constant of a vacuum.
Because of its susceptibility to water and moisture, selection and installation considerations are important.
3. Metric Tolerance
When a standard sensing element is brought close to the sensing surface, the distance from the sensing surface to the sensing element when the switch of the capacitive proximity sensor operates is called the sensing distance. When the detector is moved away from the sensor switch during the detection operation, the switch returns to its original position. At this time, the distance between the sensing surface and the detector is called the return distance.
Hysteresis is the ratio of the difference between the return distance and the detection distance, and is one of the indicators of detection characteristics of capacitive proximity sensors. The hysteresis is approximately 1 to 15% of the sensing distance.