What Is a Laser Scanner?
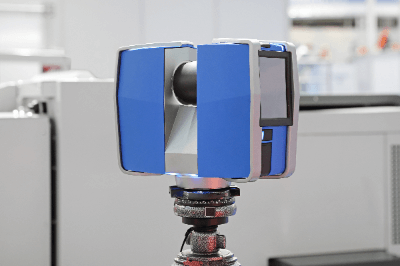 A laser scanner is a measurement device that acquires positional information of an object in three dimensions. A laser beam emitted from the scanner is directed at the object, and the reflected light is used to measure positional information, such as distance and angle.
A laser scanner is a measurement device that acquires positional information of an object in three dimensions. A laser beam emitted from the scanner is directed at the object, and the reflected light is used to measure positional information, such as distance and angle.
Non-contact, non-prismatic measurement is possible, so measurements can be taken safely. It can also acquire a large amount of 3D information as point cloud data.
There are four main types of laser scanners:
- Ground-based 3D lasers
- UAV lasers
- Aerial lasers
- MMS (Mobile Mapping System)
Uses of Laser Scanners
The main applications are surveying in facility design, plant maintenance, construction sites, etc. They are also useful for documenting existing conditions and creating CAD models.
Other uses include measuring topography, surveying displacement in tunnels and existing structures for civil engineering and maintenance and repair, and accurately recording accident and crime scenes in criminal investigations.
Furthermore, they are also used to measure surface profiles projected in 3D projection mapping and can be used in a variety of other situations.
Principle of Laser Scanners
Laser scanners measure positional information by irradiating a laser beam onto an object and detecting the reflected light. Position information can be measured without directly touching the object.
There are two main measurement methods.
1. Time-Of-Flight Method
A laser beam is irradiated onto an object, and the time it takes for the reflected laser beam to return and the laser irradiation angle are measured. The distance is calculated from the measurement time, and the coordinate position is calculated using the measurement angle and XYZ coordinates.
This enables the acquisition of 3D coordinate data, as well as a great deal of information for each point, such as RGB color coordinates, reflection intensity, reflection rate, and even angle information.
The time-of-flight method requires a longer measurement time to obtain more information, but it can provide highly accurate measurements.
2. Phase Shift Method
Multiple modulated laser beams are irradiated onto an object, and the distance to the object is determined by measuring the phase difference between the reflected light from the object and the emitted light.
Compared to the time-of-flight method, the phase-shift method is more prone to noise in the measurement and has a shorter measurement distance. However, the measurement time is much shorter.
Summary
The time-of-flight method is suitable for high-precision measurement, and the phase-shift method is suitable for measurement time.
The data acquired by the laser scanners are read by dedicated software.
Coordinate data is expressed as dots on the screen, and based on this information, the measured local conditions are reproduced on the PC. The data within the detection range is comprehensively acquired, so the situation can be reproduced.
Other Information on Laser Scanners
Cars and Laser Scanners
Modern automobiles are equipped with ADAS (advanced driver assistance systems), which supports safe driving.
In the last few years, advances in automated driving technology have led to the addition of a new sensor based on laser scanners called LIDAR (light detection and ranging).
LIDAR is a sensor that can detect objects at a close range with higher accuracy than conventional radar. LIDAR is used in automated driving because it is necessary to measure the distance to an object with higher precision.
However, laser scanners cannot replace millimeter-wave radar and other sensors. Each has its advantages and disadvantages, and they are used in a complementary manner.
Laser scanners are excellent at detecting objects at short distances with high accuracy, but their detection performance is easily affected by bad weather conditions such as rain and fog.
Millimeter wave radar is less susceptible to weather conditions and has a better detection performance for objects at long distances than laser scanners. However, the detection performance of millimeter-wave radar is inferior to that of laser scanners for objects at close range, and for objects with poor radio wave reflectivity.