What Is Ethanolamines?
Ethanolamines is the generic name for three different compounds: monoethanolamine, diethanolamine, and triethanolamine.
When simply referring to ethanolamines, we are referring to monoethanolamine, which is 2-aminoethanol. Monoethanolamine is a liquid with an ammonia odor, viscosity, and hygroscopicity. It is also known as amino ethyl alcohol or colamine.
Ethanolamines are classified as a Class 4 hazardous material. Monoethanolamine is also designated as a deleterious substance and should be handled with care.
| Chemical Formula | C2H7NO |
| English Name | Ethanolamines |
| English Name Alias | Monoethanolamine |
| Molecular Weight | 61.08 |
| Melting Point | 10 ~ 10.5℃ |
Uses of Ethanolamines
1. Monoethanolamine
Monoethanolamine is widely used as an emulsifier because it is soluble in water and oil. It can also be used in synthetic detergents, metal corrosion inhibitors, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and agricultural chemicals. In addition, monoethanolamine is used to gas clean gas mixtures to remove acidic gases.
2. Diethanolamine
Diethanolamine can be used as an emulsifier in detergents, cosmetics, and waxes, and as a wetting agent in textiles.
3. Triethanolamine
Triethanolamine is used as a base catalyst in condensation reactions, in organic synthesis reactions, as an emulsifier, plasticizer, anti-corrosion additive, and humectant. It is also used in analysis as a collector of nitrogen dioxide in the atmosphere.
Properties of Ethanolamines
Ethanolamines have the properties of both alcohols and amines. Monoethanolamine has a density of 1.012 g/cm3, a melting point of 10.3°C, and a boiling point of 170°C.
Diethanolamine has a density of 1.090 g/cm3, a melting point of 28.0°C, and a boiling point of 217°C. Triethanolamine has a density of 1.126 g/cm3, a melting point of 20.5°C, and a boiling point of 208°C. Ethanolamines dissolve well in water and acetone. Due to its basic nature, it absorbs acidic gases such as carbon dioxide (CO2) and hydrogen sulfide (H2S). It can also react with fatty acids to yield esters.
Structure of Ethanolamines
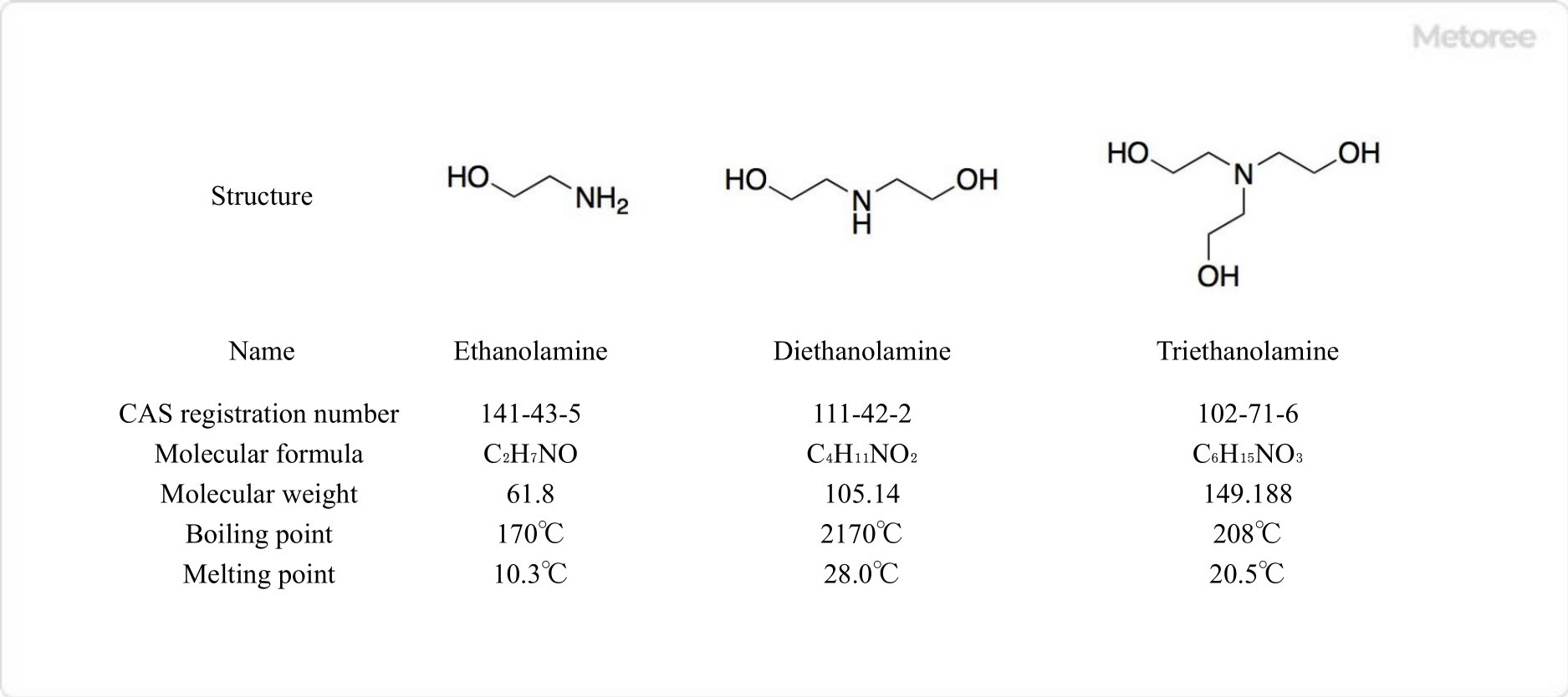
Figure 1. Structure of Ethanolamines
1. Monoethanolamine
Monoethanolamine is both a primary amine and a primary alcohol. Its chemical formula is C2H7NO and its molar mass is 61.08 g/mol.
2. Dino-Ethanolamine
Diethanolamine has a secondary amine and two hydroxy groups in the molecule. Its chemical formula is C4H11NO2 and its molar mass is 105.14 g/mol.
3. Triethanolamine
Triethanolamine has a tertiary amine and three hydroxy groups in the molecule. Its chemical formula is C6H15NO3 and its molar mass is 149.188 g/mol.
Other Information on Ethanolamines
1. Synthesis of Ethanolamines
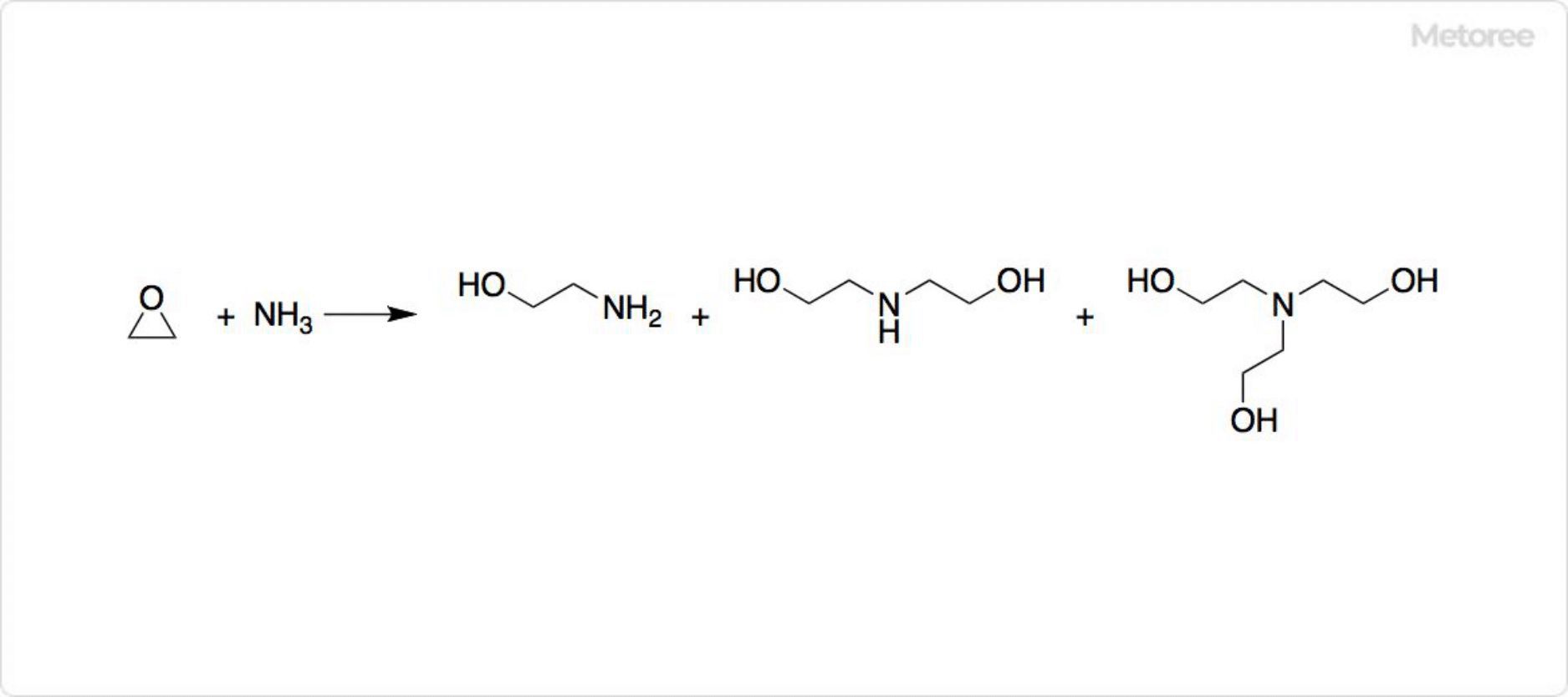
Figure 2: Synthesis of Ethanolamines
Monoethanolamine can be obtained by the reaction of ethylene oxide and ammonia. However, depending on the reaction conditions, diethanolamine and triethanolamine can also be produced. The ratio of compounds produced can be controlled by changing the stoichiometric ratio of the raw materials.
2. Related Compounds of Ethanolamines
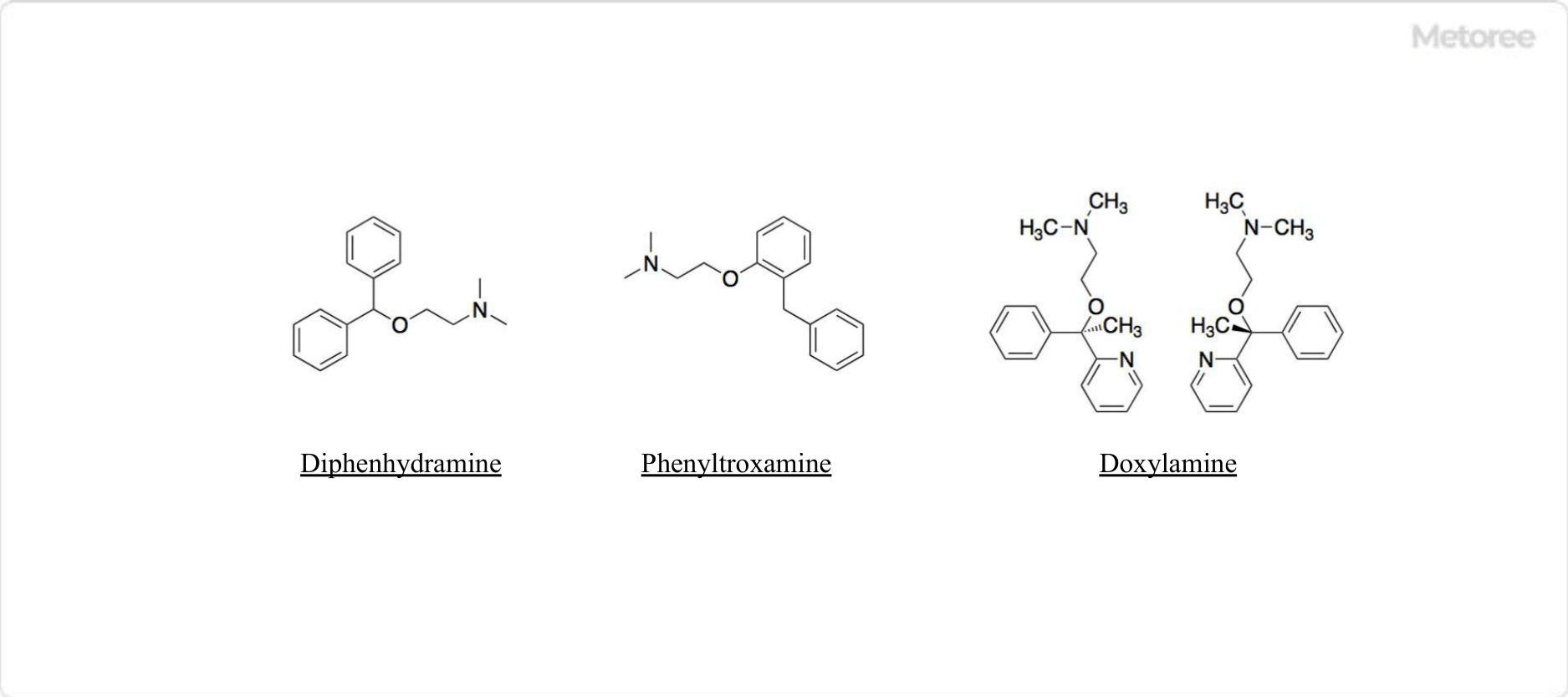
Figure 3. Compounds With the Substructure of Ethanolamines
Ethanolamines are found in the common structure of antihistamines. Specifically, in the first-generation antihistamines diphenhydramine, phenyltoloxamine (Percogesic), and doxylamine (Unisom), ethylamine is linked to diphenylmethane. It is also the ethylamine substructure linked to diphenylmethane in percogesic and doxylamine (Unisom).
It is still considered an effective substance for allergic diseases. Ethanolamines are abundant in phospholipids and are also found in biological membranes.