What Is Phosphoric Acid?
Phosphoric acid, alongside nitrogen and potassium, is one of the three primary elements of fertilizer and an oxoacid of phosphorus.
Also known as orthophosphoric acid, it promotes flowering and fruiting in plants and is a crucial component of DNA and RNA, the genetic material, and cell membranes in living organisms. Phosphoric acid is essential for life.
As a natural resource, phosphorus is found as phosphate ore, and its depletion is concerning. Phosphoric acid is industrially produced through two methods: dry and wet.
Uses of Phosphoric Acid
Phosphoric acid is widely used in industry as a raw material for various phosphates, chemical polishing agents for aluminum, rust inhibitors for metals, metal cleaning agents, can cleaners, refractory auxiliaries, paint preparation agents, activated sludge processes, phosphate fertilizers, and reagents.
In food applications, it serves as an acidifier for beverages, a pH adjuster in brewing, and a raw material for phosphoric acid additives in juices, colas, and other food products.
It is also utilized as a raw material for dyeing auxiliaries, petrochemical catalysts, and pharmaceutical additives.
Properties of Phosphoric Acid
Phosphoric acid has a melting point of 42.35°C and a boiling point of 407°C. When melted, it appears as a clear, colorless liquid.
It is soluble in water, alcohol, and ether. Liquid anhydrous phosphoric acid is a strong acid and a high conductor of electricity.
Structure of Phosphoric Acid
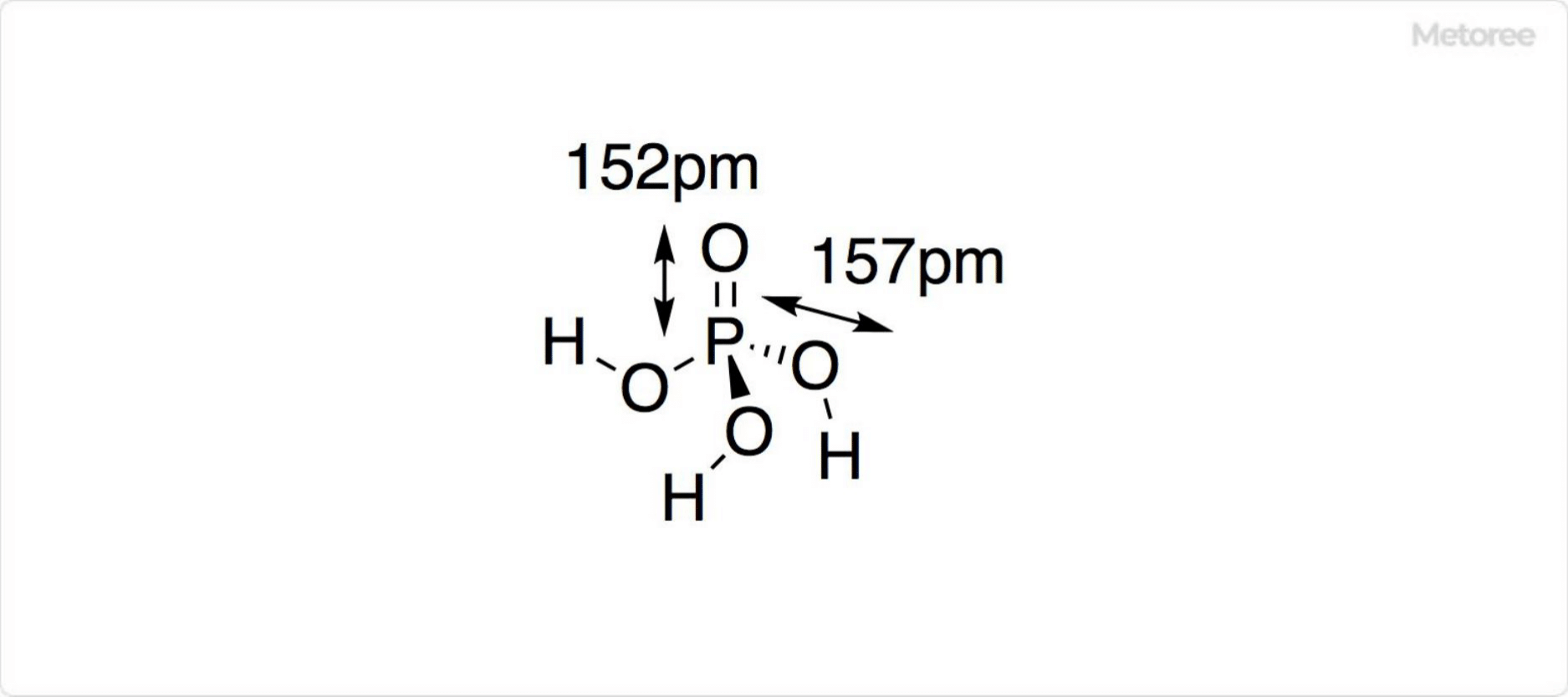
Figure 1. Structure of Phosphoric Acid
The chemical formula of phosphoric acid is H3PO4. Its molar mass is 98.00 g/mol, and its density at 25°C is 1.892. Pure phosphoric acid forms unstable crystals of the orthorhombic system.
Phosphoric acid ions adopt a tetrahedral structure. The bond distance between phosphorus and oxygen (P-O) in aluminum phosphoric acid crystals is 152 pm.
Other Information on Phosphoric Acid
1. Synthesis of Phosphoric Acid
Burning phosphorus produces diphosphorus pentoxide, which, when dissolved in a dilute aqueous solution of phosphoric acid, yields pure phosphoric acid. This thermal synthesis method is environmentally friendly, although impurities in the mined phosphorus must be removed.
Phosphoric acid can also be obtained by reacting approximately 35% sulfuric acid with phosphate ore. This wet synthesis method can be purified through filtration, but may contain impurities such as hydrofluoric acid, resulting in lower purity than the thermal synthesis method.
2. Structure of Phosphoric Acid Ion
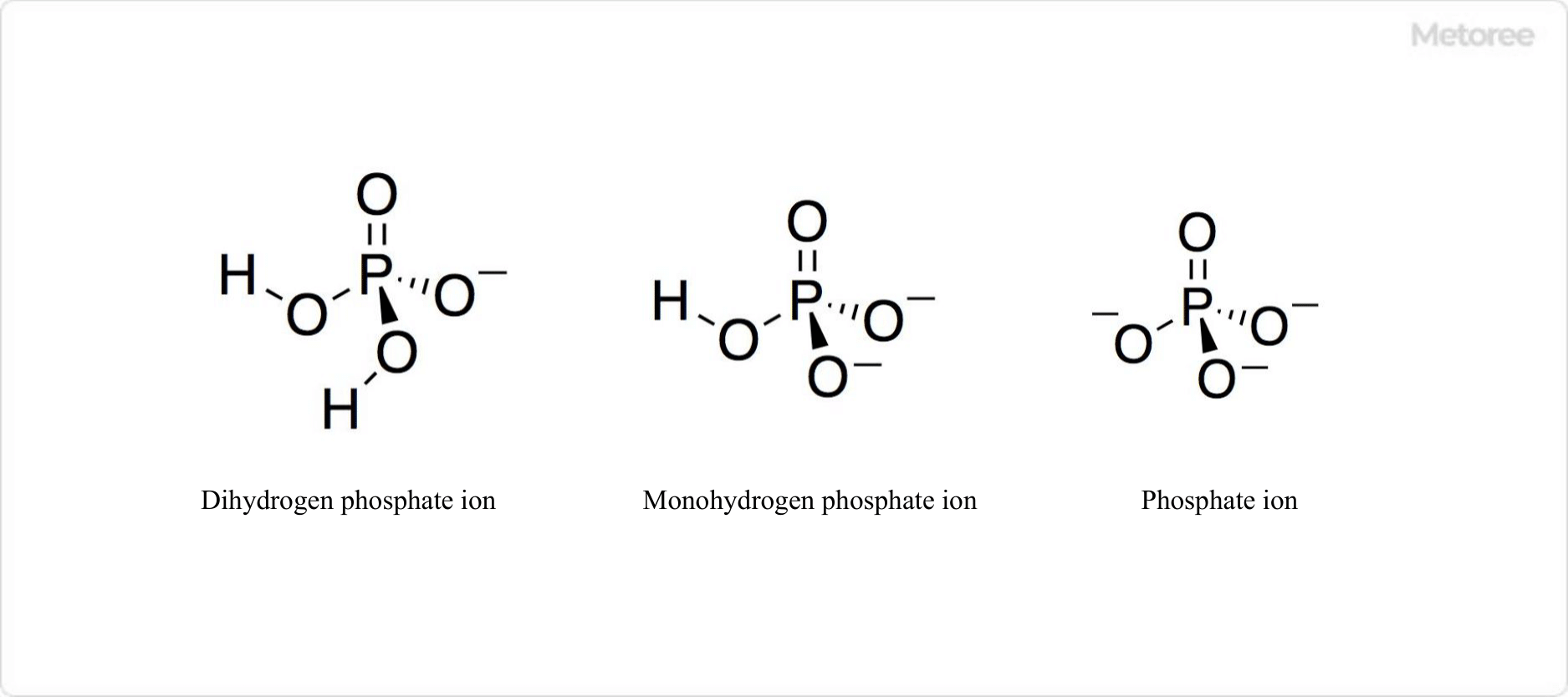
Figure 2. Structure of Phosphoric Acid Ion
Phosphoric acid, a trivalent acid, ionizes in aqueous solution, releasing three hydrogen ions. The ionization stages produce dihydrogen phosphate (H2PO4–), hydrogen phosphate (HPO42-), and phosphate (PO43-) ions.
The pKa values at 25°C are pKa1 = 2.12, pKa2 = 7.21, and pKa3 = 12.67, respectively.
3. Dehydration Reaction of Phosphoric Acid
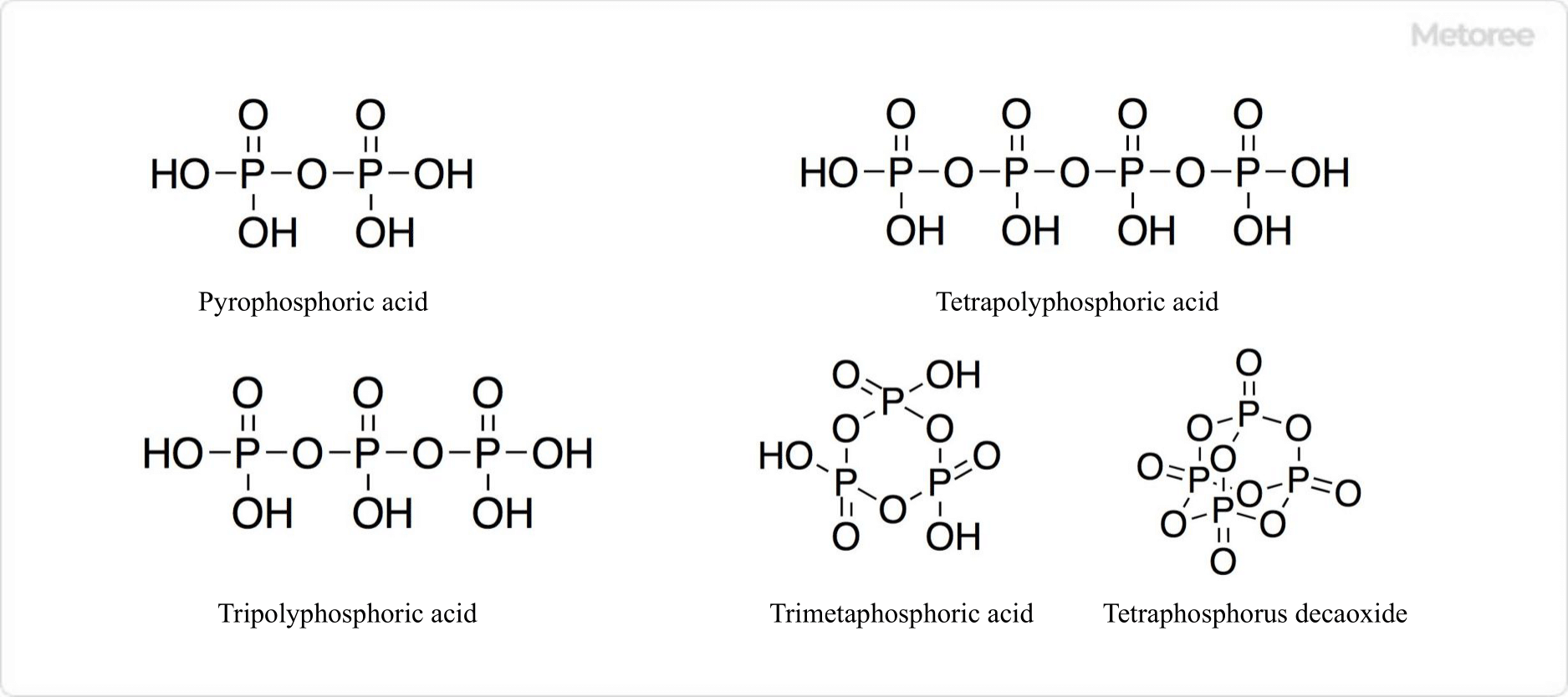
Figure 3. Structure of Condensed Phosphoric Acid
Upon heating, phosphoric acid undergoes a dehydration reaction. At 150°C, it becomes anhydrous, and at 200°C, two molecules react to form pyrophosphoric acid. Higher temperatures lead to the formation of meta-phosphoric acid, a condensed compound, when one water molecule per phosphoric acid unit is desorbed. Diphosphorus pentoxide, produced by further dehydration, reacts violently with water and is used as a drying agent.
4. Phosphoric Acid and Health
Phosphorus, found in foods of biological origin such as vegetables and meat, is used as an acidity additive in foods and beverages. It is a necessary mineral for the human body, with recommended daily amounts set by health authorities.