What Is a Blind Flange?
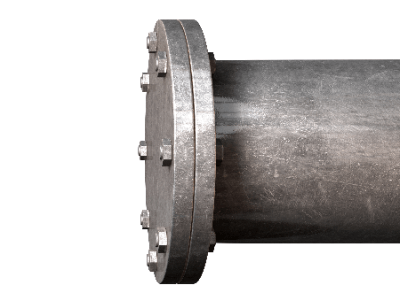
A blind flange or blank flange is a type of joint used in piping and is a flange that stops the flow of the fluid at the end of a pipe. Generally, “closed flange” and “blind flange” are used as synonymous terms.
Uses of Blind Flanges
Blind flanges are used to temporarily or permanently stop the flow of fluid at the end of a pipe by attaching it to the mating side of the pipe end flange.
To select blind flanges, the material, pressure resistance, size (inside and outside diameter), etc., are selected based on the type of fluid, pressure, temperature, flow rate, etc. Basically, the same specification, material, and size as the flange installed on the mating side should be selected.
Although valves and other devices may be used to stop the flow of fluid, blind flanges are used to close the opening at the end of pipe and blind flanges completely. This prevents foreign matter from entering through the opening and enables the pipe to be closed without being exposed to the atmosphere.
Principle of Blind Flanges
The principle of blind flanges is exactly the same as that of ordinary piping flanges: the flange surfaces to be connected are tightly sealed by adhering to each other. The difference from a normal piping flange is that the flange has no holes for pipes, but only holes for bolts.
As with ordinary piping flanges, a gasket is generally inserted between the flanges to increase the adhesiveness of the flanges. The flanges are tightened together with bolts and nuts to increase and maintain the adhesion. In this case, the bolts and nuts must be tightened evenly.
For this reason, bolts and nuts are generally tightened diagonally rather than in sequence. It is also important to tighten the bolts and nuts at the specified torque value for the gasket material and bolt/nut. The tightening torque is gradually increased in diagonal order until the required tightening torque value is reached.
When used with high-temperature fluid, the tightening of the threads may loosen due to thermal expansion after the actual flow of high-temperature fluid. In such cases, the bolts and nuts must be re-tightened.
Although the material of the membrane flange varies depending on the fluid used, generally austenitic stainless steels such as carbon steel, SUS304 and SUS316, or carbon steel castings, are used. As mentioned above, the same material as that of the mating flange should be used.
Selection of the type, model, and material of the gasket to be inserted between the flanges is also important to improve and maintain sealing performance. Selection criteria are usually defined by various standards, and selection is based on the type of fluid, temperature, and pressure.