What Is L-Threonine?
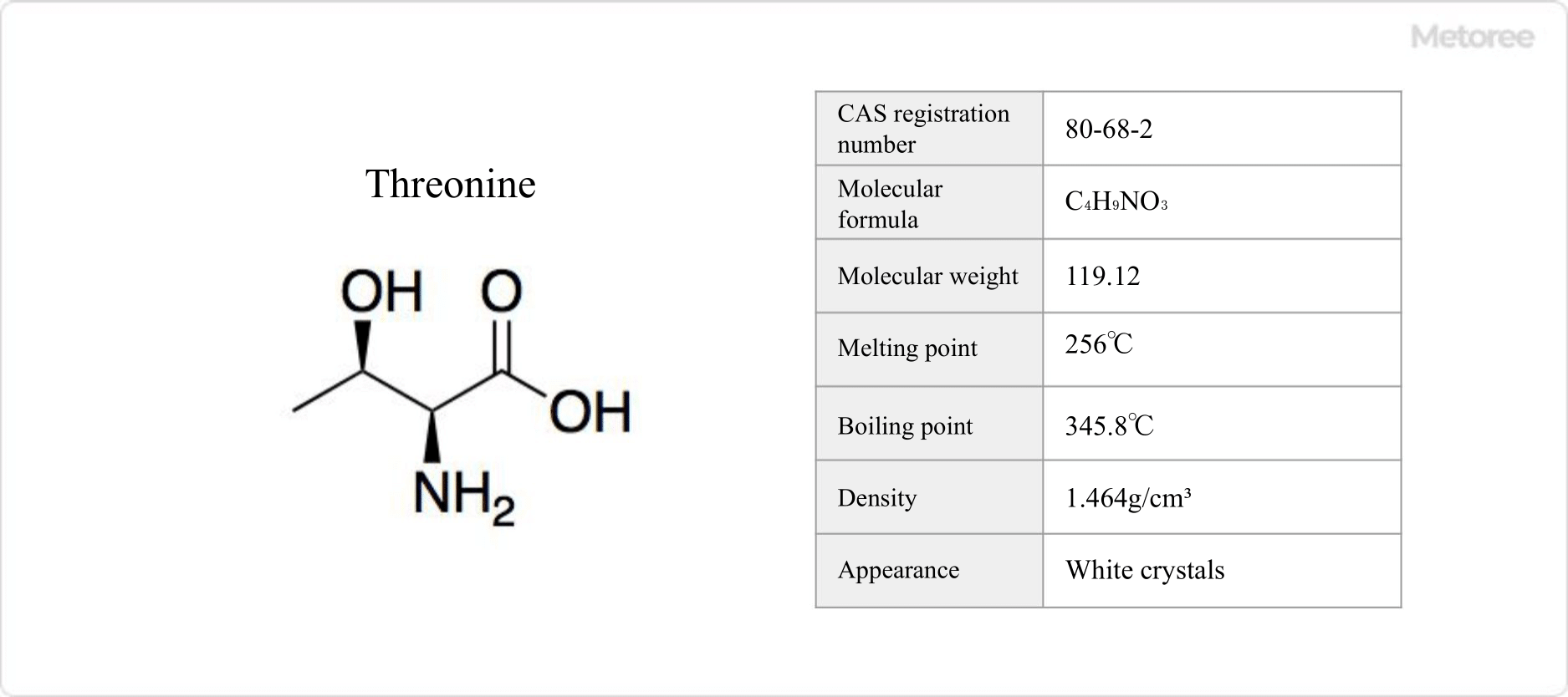
Figure 1. Basic Information on L-Threonine
L-threonine, an essential amino acid, plays a critical role in protein synthesis in humans. It is a vital nutrient, sourced from dietary intake of eggs, chicken, skim milk, and gelatin, among others.
Uses of L-Threonine
Beneficial for preventing fatty liver and regulating gastric acid, L-threonine supports skin moisture and hair health through collagen and keratin production. It is also crucial in animal feed to ensure nutritional balance.
Properties of L-Threonine
Water-soluble, with a melting point of 256°C and notable for its biochemical roles, L-threonine’s solubility and acid dissociation constants underline its biological significance.
Structure of L-Threonine
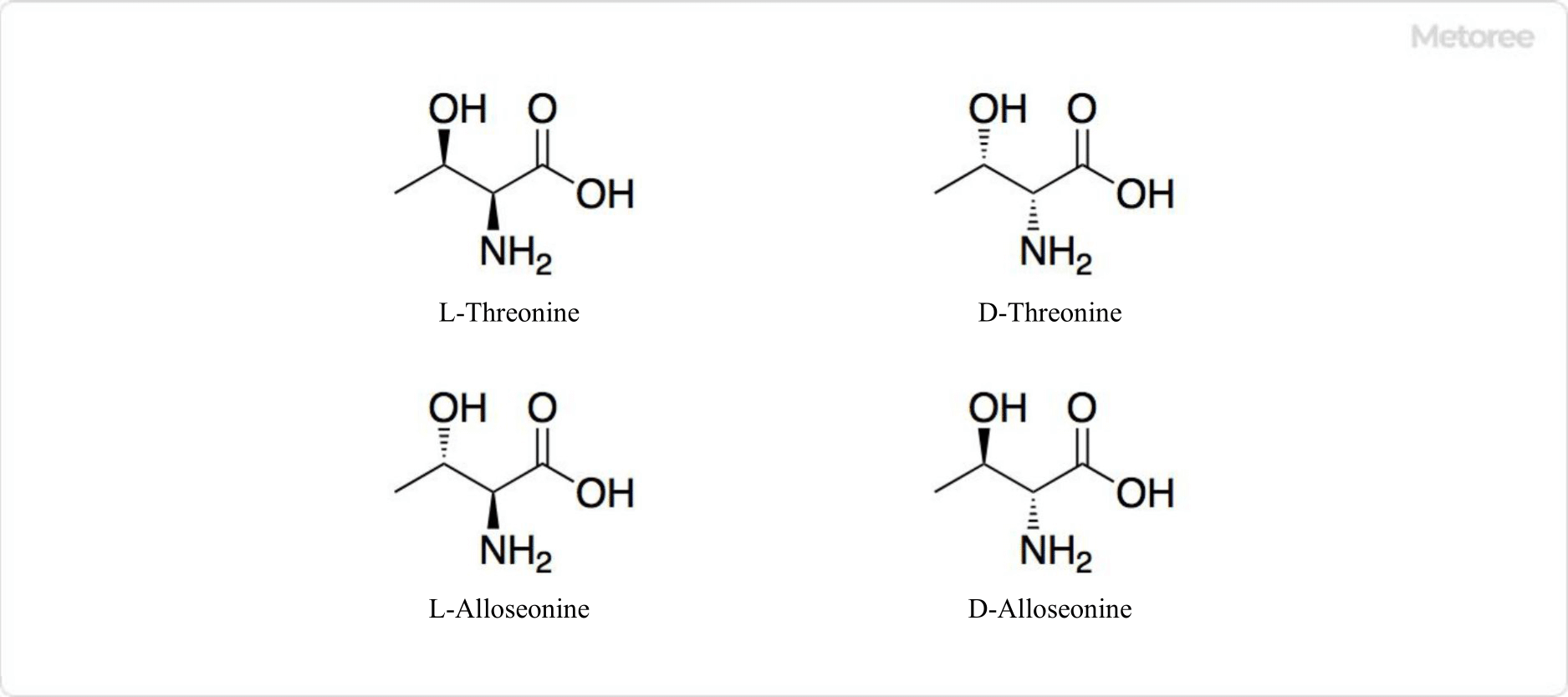
Figure 2. Isomers of L-Threonine
Characterized by its polar, uncharged side chain and presence in human proteins, L-threonine’s structural isomerism and optical activity are highlighted by its four possible isomers.
Other Information on L-Threonine
1. Biosynthesis of L-Threonine
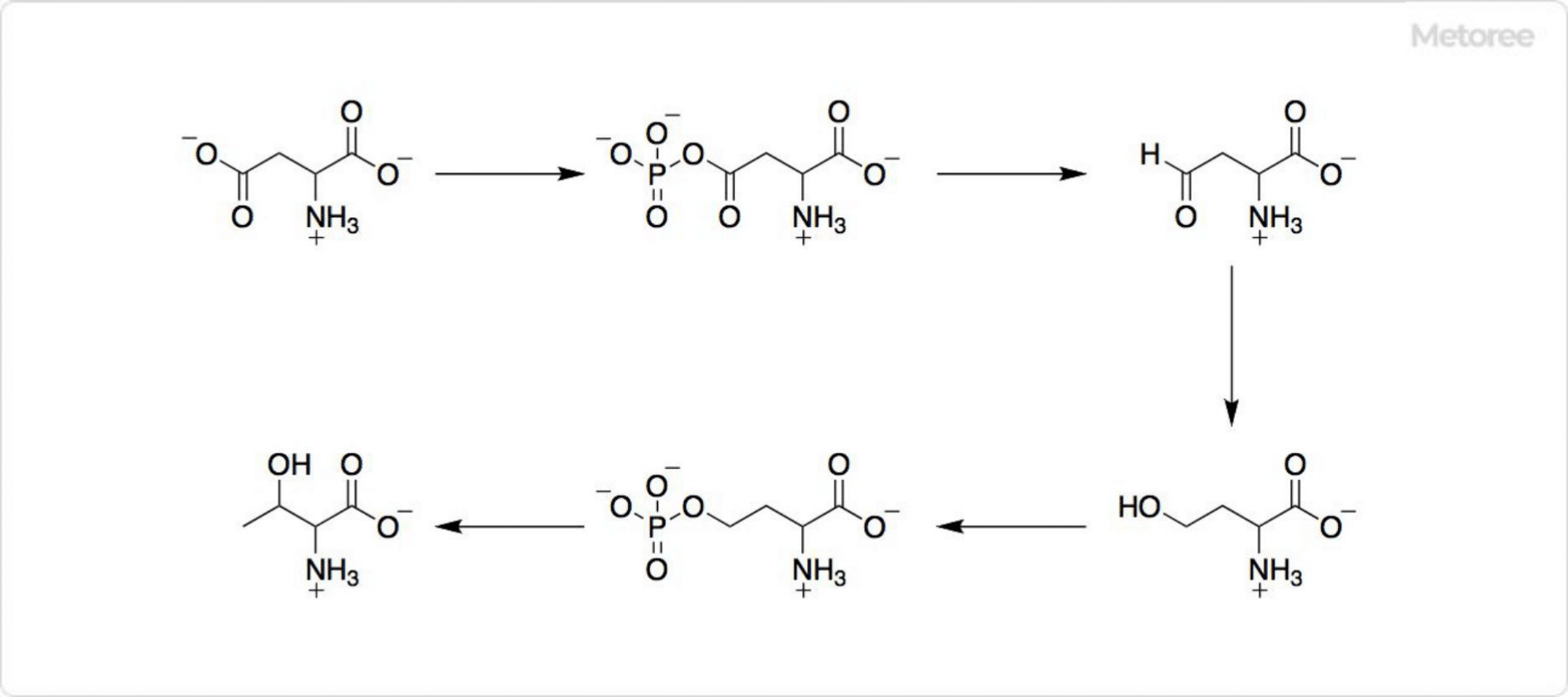
Figure 3. Biosynthesis of L-Threonine
While humans must obtain L-threonine through diet, plants, and microorganisms synthesize it from aspartic acid, following a multi-step biochemical pathway involving several enzymes.
2. Metabolism of L-Threonine
L-threonine’s metabolic pathways vary across species, contributing to vital processes such as glycine and acetyl CoA production in animals and playing a role in the biosynthesis of essential biomolecules like vitamin B12 in bacteria.