What Is Insulated Wire?
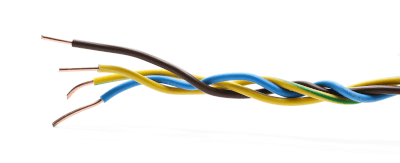
Insulated wire is an electric wire that has been treated with insulation.
Electric power, supplied by electric power companies, is transmitted to various locations at ultra-high voltages called extra-high voltage. The special high-voltage power lines are on steel towers several tens of meters high and are bare because there is no danger of people coming into contact with them. Therefore, there is a risk of electric shock if a person comes in contact with the tower touching it.
In contrast, power is transmitted to ordinary homes and commercial facilities at high-voltage or low-voltage. These are protected by insulating materials because of the danger of accidental contact by people. These are called insulated wires.
Uses of Insulated Wire
A familiar example is wiring on utility poles. You can see black wires laid overhead on utility poles erected on the street. They appear black because they are insulated with cross-linked polyethylene or rubber. Insulated wire is also commonly used for wiring laid within the walls of ordinary homes.
Also, when you disassemble a household appliance, you may see vinyl-coated wires inside. This is a type of insulated wire called vinyl wire. The outlet cords used in dryers and other appliances are also insulated wire.
Insulated wire is rarely seen in ordinary households.
Principle of Insulated Wire
Insulated wires are divided into shielded and unshielded wires.
First, unshielded wires have a long, thin copper at the center that serves as an electrical circuit; insulated wires called VVF cables, etc., consist of a single copper wire, while cables called VCTF, etc., consist of many thin copper wires twisted together. Regardless of whether it is a single wire or a stranded wire, the standard of the cable is called by the thickness of the internal copper wire. The thicker the wire, the more current it can carry. The thickness of the copper wire is determined by the power requirements of the terminal equipment used. As a reference, a 100V household outlet, for example, requires about 15A, and a VVF cable with a cross-sectional area of 1.6mm2 is used.
The surface of the cable is covered with an insulating coating to prevent human contact with the internal power lines. Rubber, cross-linked polyethylene, or vinyl chloride are used as the insulation coating. For household and other applications, only vinyl chloride is used. For industrial use, both cross-linked polyethylene and vinyl chloride are used to provide double insulation.
Shielded wires are made by shielding the vinyl chloride and other materials with aluminum or copper to prevent induced voltages. Generally, shielded wires are used for high-voltage applications where there is a risk of electric shock to the human body due to induced voltage. In some cases, they are also used for weak electric cables to eliminate errors caused by induction.