What Is a Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Switch?
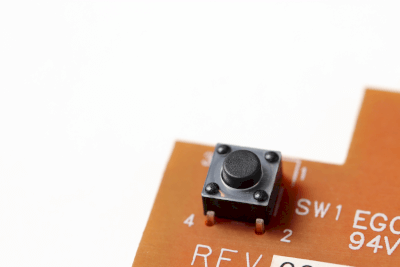
A PCB switch, which includes push-button and DIP switches, is designed for mounting on printed circuit boards. These switches are manually operated to turn contacts on and off.
PCB switches come in two primary types: auto-return and holding. Auto-return switches are active only while pressed, reverting to their original state once released. Holding-type switches maintain their state after being actuated until they are manually changed again.
Uses of PCB Switches
The choice between auto-return and holding-type switches depends on the specific application. Auto-return switches require the receiving system to quickly detect changes in state for controlling devices. These are suitable for systems where the switch status is continuously monitored by a controller. Holding-type switches, maintaining a constant state, are preferable when such instant monitoring is not necessary.
Principle of PCB Switches
PCB switches are characterized by a-contact, b-contact, and c-contact types. The a-contact (NO – Normally Open) turns ON when pressed and OFF when released, meaning no current flows through the switch when it is in its default position. The b-contact (NC – Normally Closed) operates oppositely, staying ON until pressed. The c-contact combines features of both a and b contacts, allowing for versatile switching options.