What Is a Countersunk Head Screw?

Countersunk head screws, also known as flat head screws, feature a tapered head that narrows towards the screw side, resembling a dish when viewed from the side. Unlike flat head nails, which have a flat top face, the top face of a countersunk head screw is rounded. These screws have a relatively small nominal head diameter and typically feature a slotted or cross-shaped drive.
Uses of Countersunk Head Screws
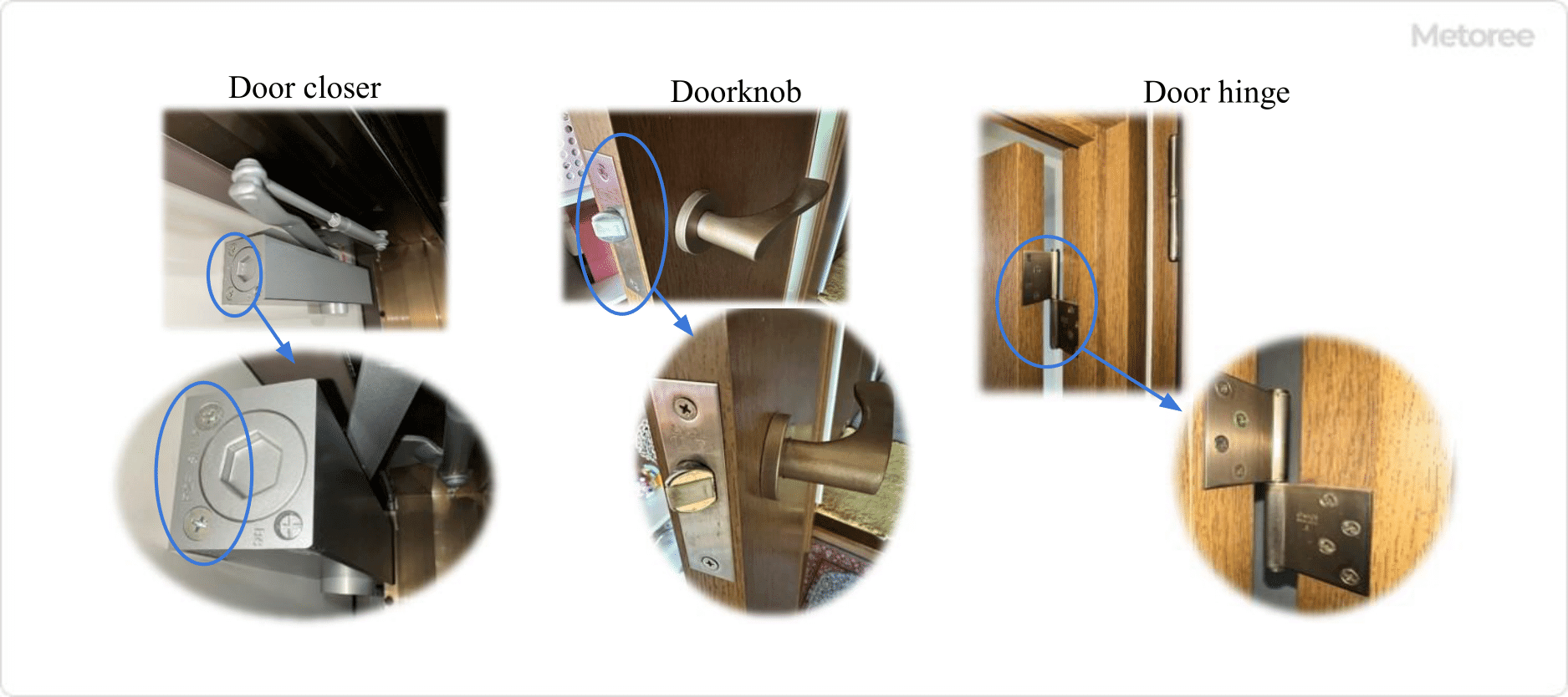
Figure 1. Example of Using Countersunk Head Screws
Countersunk head screws are primarily used as fasteners in applications with female threads, such as door closers, knobs, and hinges. They are designed to fit into a tapered counterbore in the fastened object, ensuring the screw head does not protrude beyond the object’s surface, as illustrated in Figure 1.
While similar in application to round countersunk head nails, which have a rounded top face, countersunk head screws feature a flat head that can prevent snagging on cross-holes.
Principle of Countersunk Head Nails
Countersunk head screws, like their nail counterparts, are secured by screwing into a tapped female thread without the need for a nut. They are tightened using a Phillips-head or flat-blade screwdriver inserted into the cross-hole or slot. The length of these screws is measured from the top of the head to the end, in contrast to ordinary bolts, which are measured excluding the bolt head.
Types of Countersunk Head Screws
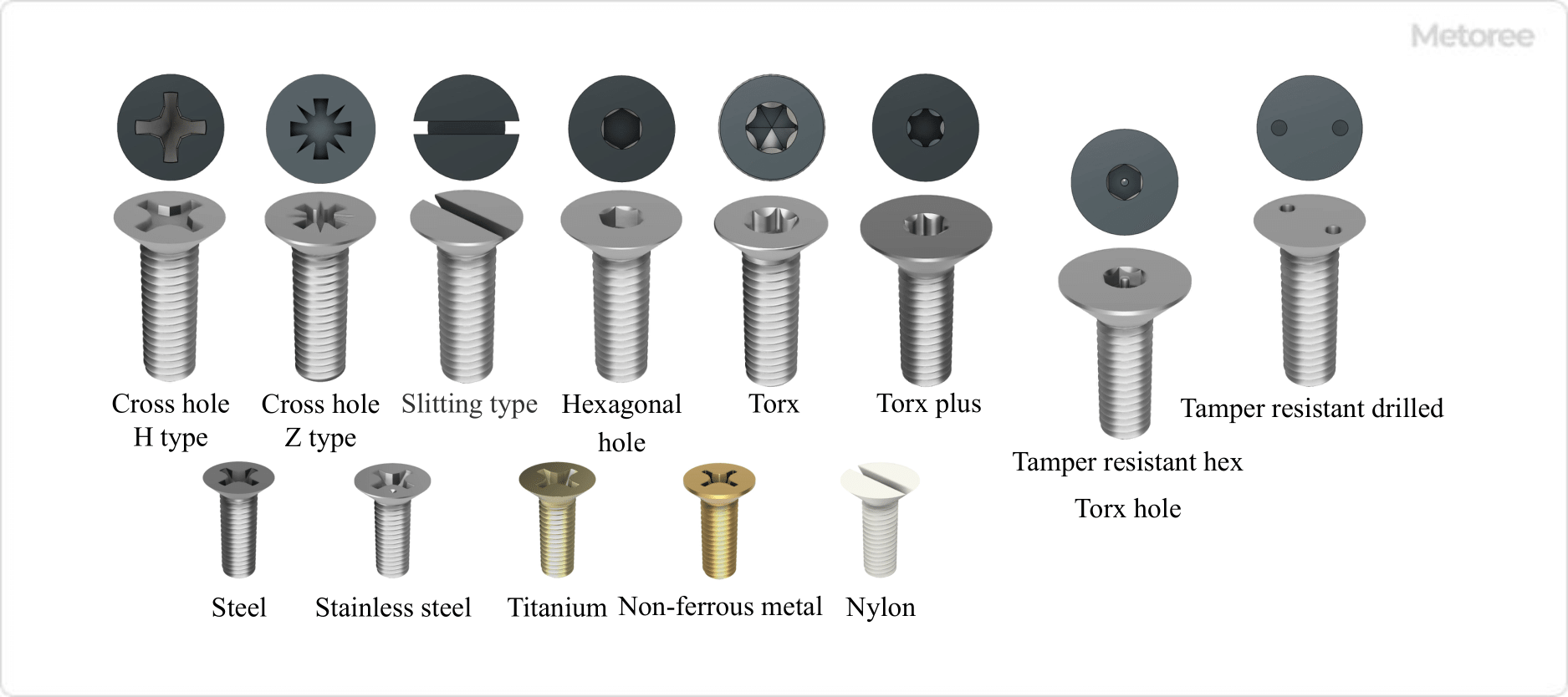
Figure 2. Types, Materials, and Shapes of Countersunk Head Screws
Countersunk head screws are categorized by head hole shape and material strength.
1. Classification by Hole Shape of Countersunk Screw Head
Different headhole shapes accommodate specific tools for tightening. The two main types are Cross (Phillips) and Suri-Wari (Flat). Phillips types are common, with a slightly concave pressure surface, while Pozidriv types feature almost vertical sides. Flat holes, or minus holes, accommodate a flathead screwdriver.
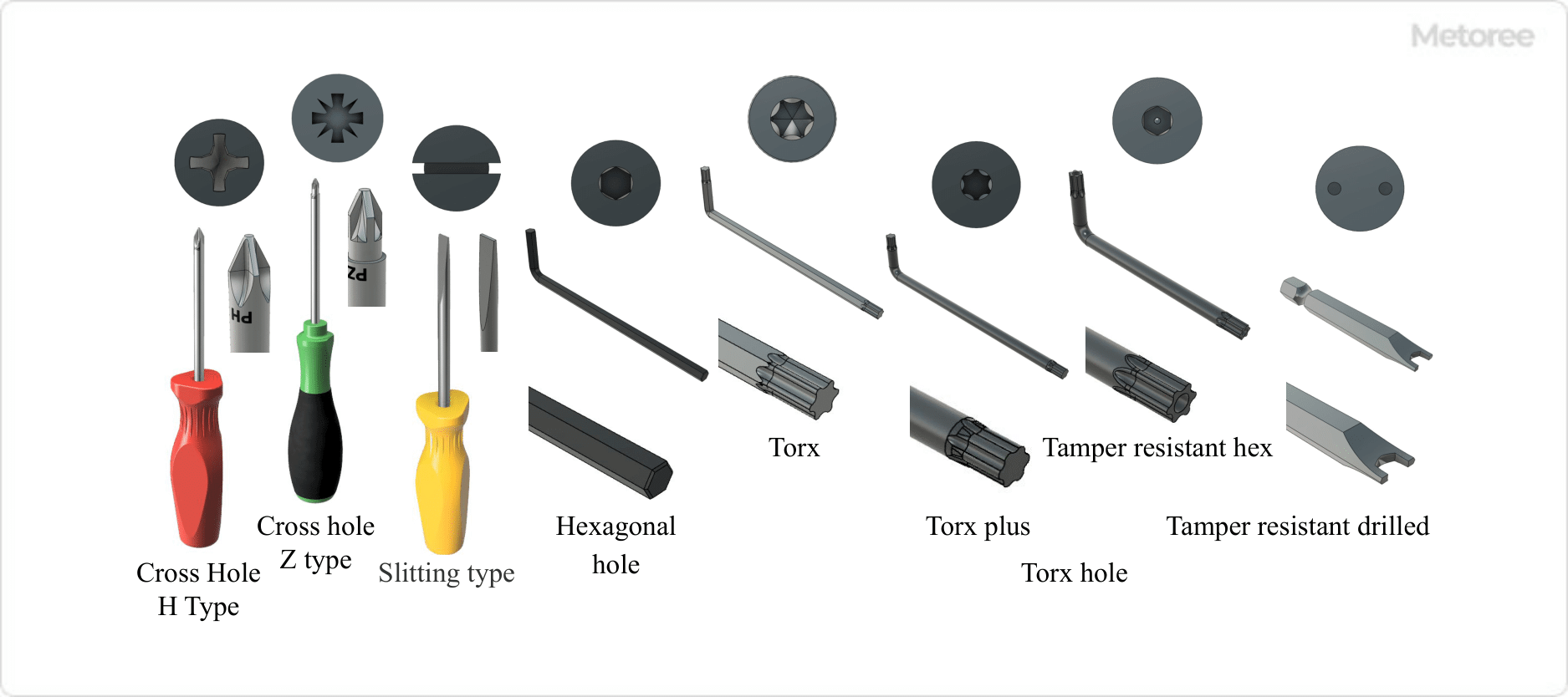
Figure 3. Hole and Tool Geometry of the Head of Countersunk Head Screws
Hexagonal and Torx holes are also available, providing higher tightening force and requiring specific tools for operation.
2. Classification by Material (Strength Classification)
Materials for countersunk head screws include steel, stainless steel, and nonferrous metals, each classified by strength and applicable standards.
Other Information on Countersunk Head Screws
Standards for countersunk head screws include ISO 7046, among others. It’s important to match the screw to the female thread’s standard to ensure compatibility. Additionally, countersunk head screws come in various sizes, typically from M2 to M8, with recommended lengths ranging from 4 to 60 mm.