What Is Coumarin?
Coumarin is an aromatic compound with a lactone (cyclic ester) structure.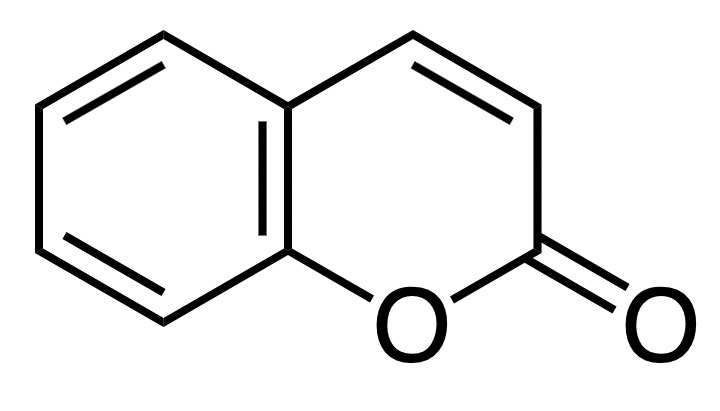 It is stable in a solid state at room temperature, but is soluble in alcohol, ether, chloroform, and volatile oils, so it is often used in a dissolved state. This compound is found in cherry leaves, cinnamon, and plants of the tangerine and legume families. Its characteristic feature is its aroma, and it is also a component of the sweet aroma of sakura mochi (cherry blossom cakes).
It is stable in a solid state at room temperature, but is soluble in alcohol, ether, chloroform, and volatile oils, so it is often used in a dissolved state. This compound is found in cherry leaves, cinnamon, and plants of the tangerine and legume families. Its characteristic feature is its aroma, and it is also a component of the sweet aroma of sakura mochi (cherry blossom cakes).
It also has antioxidant, antibacterial, and anti-blood coagulation effects, and is believed to be effective in preventing swelling and aging.
Distribution and Forms of Presence of Coumarin
Coumarin is abundantly contained in plants of the family Ceraceae, tangerine family, and leguminous family, and exists as a glycoside in plant organisms. Glycoside here refers to the presence of coumarin bound to sugars. Interestingly, coumarin as a glycoside does not have a specific aroma. The sweet aroma characteristic of sakura-mochi, as described above, is not due to the coumarin glycoside, but to the coumarin resulting from its hydrolysis.
Physicochemical Properties of Coumarin
1. Molecular Formula
C9H6O2
2. Molecular Weight
146.14
3. Structural Formula
As shown above.
4. Melting Point
72°C
5. Solvent Solubility
Easily soluble in diethyl ether, chloroform, pyridine, soluble in ethanol
6. Fluorescence
Emits yellowish green fluorescence when irradiated with ultraviolet light.
Synthesis of Coumarin
It is synthesized from salicylaldehyde, acetic anhydride, and sodium acetate by the Parkin reaction.
Characteristics and Uses of Coumarin
1. Unique Aroma
Coumarin is one of the components of the so-called “cinnamon aroma,” from which the sweet aroma of sakura-mochi is derived. This aroma is also reported to have a relaxing effect. Because of these characteristics, it is used as an ingredient in air fresheners and perfumes.
2. Health Benefits
Coumarin is reported to improve blood flow and is thought to be effective in preventing swelling. In addition, its antioxidant properties help to remove active oxygen in the body. Because of these characteristics, coumarin is also expected to have an anti-aging function. On the other hand, it can cause liver damage if consumed in large quantities. Therefore, its use in the food industry is approved only as a component of flavorings and as a food additive for flavoring.
3. Coumarin-Related Compounds as Pharmaceuticals
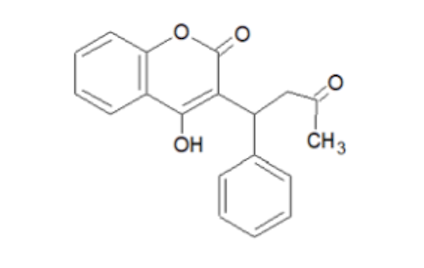
Some compounds with coumarin skeleton have blood coagulation inhibitory activity. A typical example is warfarin. This compound is a biologically active substance synthesized from dicoumarol, a metabolite of coumarin, as a lead compound, and is currently used as a blood coagulation inhibitor and rodenticide.
4. Fluorescence and Use as a Diesel Fuel Identifier
In some countries, coumarin is added to kerosene and fuel oil. The yellowish-green fluorescence of commercially available kerosene when irradiated with a black light is due to this coumarin as an additive, and is not a property of the kerosene itself. This use of coumarin is a good example of utilizing the two chemical properties of coumarin, its high fat-solubility and fluorescence.