What Is a Dual-Axis Positioning Stage?
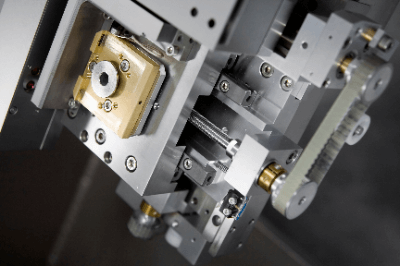
The equipment configuration generally consists of stages in each axis direction stacked on top of each other. A dual-axis positioning stage (XY-axis stage) has two axes: an X-axis for left/right movement and a Y-axis for vertical movement. The use of this stage has the advantage of facilitating positioning.
The accuracy and features vary depending on the stage guide system and feed mechanism, so selecting a stage that best suits the application is necessary.
Uses of Dual-Axis Positioning Stages
The main applications of 2-axis stages are for manufacturing semiconductor devices and microscopic observation, which require positioning. There are various types of stages with positioning accuracy ranging from low precision to high precision depending on the guide system and feed mechanism, and they have different features.
Principles of Dual-Axis Positioning Stages
Dual-axis positioning stages are composed of a “guide mechanism” and a “feed mechanism. Since the characteristics of each mechanism differ depending on its type, the following is a description of typical kinds of stages.
Guide mechanism
- Dovetail groove type: A dovetail groove type is a guiding mechanism in which the male and female trapezoidal grooves slide together.
- Crossed roller system: A system that moves by linear contact between a roller and a V-groove rail, providing high rigidity. It is also suitable for precise positioning due to its low friction and minute feed rate.
- Ball type: This is a mechanism that moves by contact between an R-groove machined along a circular arc and a ball, which provides good contact between the R-groove and the ball and stable load capacity in all directions. The movement accuracy is not significantly different from the cross-roller system and is also suitable for accurate positioning.
Feed Mechanism
- Rack and pinion: This feed mechanism combines a rail with cut teeth called a “rack gear,” and a gear called a “pinion”. It is characterized by its ability to move the stage quickly but is unsuitable for high-precision positioning.
- Feed screw: This is a screw-type feed mechanism that utilizes the relationship between the male and the female thread. It can feed the stage at the resolution of the screw pitch, enabling fine feed, but the feed speed is slow, making it unsuitable for positioning over long strokes.
- Micrometer: This mechanism can feed stages with finer precision than a feed screw. Its internal structure is almost the same as that of a feed screw, but it is also equipped with a scale to determine the amount of travel accurately. The feed speed is also slow, so it is not suitable for positioning over long strokes.
Select the combination that best suits your application and configure Dual-Axis positioning stages from the above guide and feed mechanism choices.
The operation of Dual-Axis positioning stages is not limited to manual positioning; it may also be used as Dual-Axis positioning stages capable of automatic positioning, with each axis driven by a motor. In this case, since positioning accuracy is determined by the feed mechanism type and the drive motor’s resolution, the selection of motor specifications is also essential.
Generally, servo motors or stepping motors are used when precise positioning is required.