What Is Crimping Machinery?
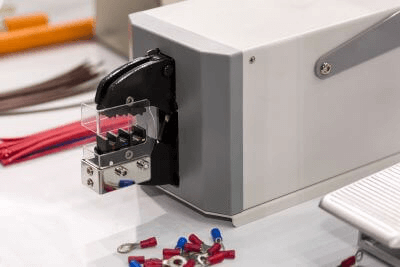
Crimping machinery is a tool used to perform a process called “crimping,” which is used to join metal terminals and wires.
Crimping refers to the process of electrically joining wires and crimp terminals by crushing them with a special caulking die. Crimping machinery is used to crush the wire and crimp terminal by placing a special crimping die on the top and bottom of the wire and crimping the terminal between the wire and terminal.
The crimping part of the crimping machinery looks like a pair of pliers, and the application of force causes plastic deformation on the crimping terminal side, causing the terminal to bite into the wire, thereby binding it.
There are both manual and electric crimping machines, and they are used in different ways depending on the application. The electric type is mainly used for thick wires in particular. The reason for this is that the size of the crimp terminal increases proportionally with the size of the wire, making it difficult for the terminal to undergo plastic deformation during crimping, and therefore greater force is required to crimp the terminal, which cannot be handled by human power in some cases.
Uses of Crimping Machinery
Crimping machinery is used to crimp wires in various places.
Examples include automobiles and home appliances. In order to enable the use of various functions, many wires are wired inside these products, and each wire and crimp terminal is inserted into the connector, which is the joint between the wires, in a pair. By using crimping machinery to crimp these wires and terminals, a highly reliable electrical connection can be achieved.
The specific procedure for the crimping operation is to strip the wire coating to expose the inner core wire, and then set the wire on the crimping terminal with the wire overlapping the terminal. The wires are then clamped from the top and bottom with a special crimping machine, and force is applied to cause plastic deformation of the terminals and bond them together.
Crimping is also used for parts that are sensitive to heat or chemicals. In addition to crimping, soldering can also be used to electrically bond wires, but soldering requires the application of heat, making soldering difficult in some cases. In contrast, crimping does not require heat or chemicals, so it is used for many wires because of its high speed and reliability of electrical connection.
Principle of Crimping Machinery
Crimping machinery is a tool to join wires and crimp terminals by applying a load and crushing them with a special caulking die.
There are both manual and electric crimping machinery, and here we introduce the principle and features of these two types of crimping machinery.
1. Manual Crimping Machinery
The crimpers are shaped like pliers and are hand held by a person. The wire and crimp terminal are set, and the crimp is made by crushing the wire between the terminals.
The advantage is that because the crimping is performed by human hands, the work can be easily performed anywhere, and the crimping can be done mechanically and electrically with a high degree of reliability.
The disadvantage is that the load applied during the operation is limited due to the fact that it is manually powered. Therefore, especially in the case of thick wires, the crimping may not work well because of the force that tries to undo the deformed crimp terminal when load is applied.
2. Electric Crimping Machinery
Crimping is performed in the same way as with manual crimping machinery, but the crushing operation is performed electrically.
The advantage of the electric crimping machine is that it can crimp even thick wires. The thicker the wire, the larger the crimp terminal becomes in proportion to the wire size, so a large amount of force is required to generate plastic deformation in the terminal. However, with electric crimping machinery, the load applied can be easily controlled, so even thick wires can be joined.
Electric crimping machinery is used especially for wires in areas where large currents are flowing, because very thick wires are used due to heat resistance.
The disadvantage is that they cannot be easily installed anywhere. Because they are electrically powered, they require batteries or a power source to operate, making outdoor use difficult. They are also heavy and difficult to miniaturize, and the price of the main unit is high.